
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the reaction that will take place when the given compound is treated with
Concept introduction:
Diazomethane,
The stereochemistry of the double bond is preserved in the addition. If the double bond has a cis relationship, then the two substituents end up on the same side of the cyclopropane ring. If the two substituents on the double bond are trans to each other, they end up on the opposite sides of the cyclopropane ring. This also determines the product distribution if the cyclic product is chiral. If the starting
Answer to Problem 12.26P
The mechanism for the reaction when
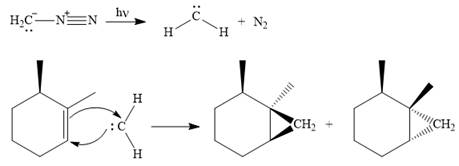
Explanation of Solution
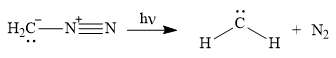
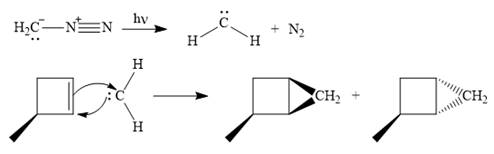
Diazomethane dissociates heterolytically when irradiated with ultraviolet light to produce a carbene and a nitrogen molecule.
The carbene then simultaneously adds to the initially double-bonded carbons. The lone pair on the carbene forms a bond with one carbon while the
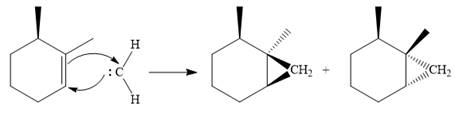
Since the starting alkene is chiral, the product will be a mixture of two enantiomers. The pair of enantiomers is produced because the carbene can add either above or below the plane of the ring in the reactant.
Thus the complete mechanism for this reaction can be drawn as
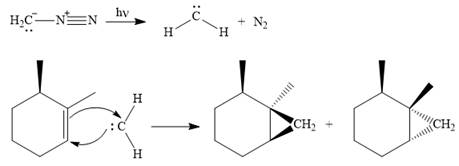
A carbene adds to an alkene or
(b)
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the reaction that will take place when the given compound is treated with
Concept introduction:
Diazomethane,
The stereochemistry of the double bond is preserved in the addition. If the double bond has a cis relationship, then the two substituents end up on the same side of the cyclopropane ring. If the two substituents on the double bond are trans to each other, they end up on the opposite sides of the cyclopropane ring. This also determines the product distribution if the cyclic product is chiral. If the starting alkene is achiral and the product chiral, the product is a racemic mixture of enantiomers. If the starting alkene is also chiral, then an unequal mixture of enantiomers is produced.
Answer to Problem 12.26P
The mechanism for the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
Diazomethane dissociates heterolytically when irradiated with ultraviolet light to produce a carbene and a nitrogen molecule.

The carbene then simultaneously adds to the initially double-bonded carbons. The lone pair on the carbene forms a bond with one carbon while the
The carbene then simultaneously adds to the initially double-bonded carbons. The lone pair on the carbene forms a bond with one carbon while the
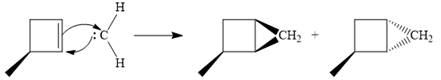
Since the starting alkene is chiral, the product will be a mixture of two enantiomers. The pair of enantiomers is produced because the carbene can add either above or below the plane of the ring in the reactant.
Thus the complete mechanism for this reaction can be drawn as:
A carbene adds to an alkene or alkyne to produce a cyclopropane ring.
(c)
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the reaction that will take place when the given compound is treated with
Concept introduction:
Diazomethane,
The stereochemistry of the double bond is preserved in the addition. If the double bond has a cis relationship, then the two substituents end up on the same side of the cyclopropane ring. If the two substituents on the double bond are trans to each other, they end up on the opposite sides of the cyclopropane ring. This also determines the product distribution if the cyclic product is chiral. If the starting alkene is achiral and the product chiral, the product is a racemic mixture of enantiomers. If the starting alkene is also chiral, then an unequal mixture of enantiomers is produced.
Answer to Problem 12.26P
The mechanism for the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
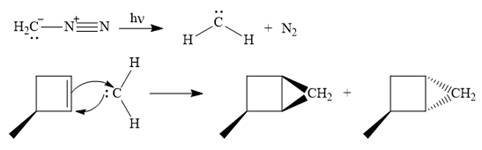
Diazomethane dissociates heterolytically when irradiated with ultraviolet light to produce a carbene and a nitrogen molecule.
![]()
The carbene then simultaneously adds to the initially double-bonded carbons. The lone pair on the carbene forms a bond with one carbon while the
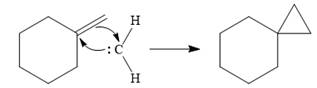
Only one product is formed in this case because of the symmetry of the reactant alkene about the axis of the double bond.
Thus, the complete mechanism for the given reaction can be drawn as
A carbene adds to an alkene or alkyne to produce a cyclopropane ring.
(d)
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the reaction that will take place when the given compound is treated with
Concept introduction:
Diazomethane,
The stereochemistry of the double bond is preserved in the addition. If the double bond has a cis relationship, then the two substituents end up on the same side of the cyclopropane ring. If the two substituents on the double bond are trans to each other, they end up on the opposite sides of the cyclopropane ring. This also determines the product distribution if the cyclic product is chiral. If the starting alkene is achiral and the product chiral, the product is a racemic mixture of enantiomers. If the starting alkene is also chiral, then an unequal mixture of enantiomers is produced.
Answer to Problem 12.26P
The mechanism for the given reaction is
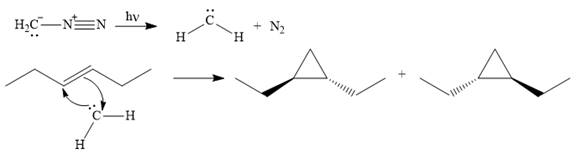
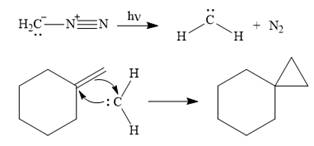
Explanation of Solution
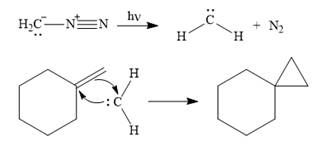
Diazomethane dissociates heterolytically when irradiated with ultraviolet light to produce a carbene and a nitrogen molecule.
![]()
The carbene then simultaneously adds to the initially double-bonded carbons. The lone pair on the carbene forms a bond with one carbon while the
The starting alkene has a trans geometry, therefore, the two substituents on the cyclopropane ring in the product are on opposite sides of the ring.
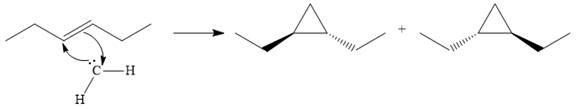
This means the product is chiral, and a racemic mixture of two enantiomers will be produced.
Thus, the complete mechanism for the reaction can be drawn as

A carbene adds to an alkene or alkyne to produce a cyclopropane ring.
(e)
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the reaction that will take place when the given compound is treated with
Concept introduction:
Diazomethane,
The stereochemistry of the double bond is preserved in the addition. If the double bond has a cis relationship, then the two substituents end up on the same side of the cyclopropane ring. If the two substituents on the double bond are trans to each other, they end up on the opposite sides of the cyclopropane ring. This also determines the product distribution if the cyclic product is chiral. If the starting alkene is achiral and the product chiral, the product is a racemic mixture of enantiomers. If the starting alkene is also chiral, then an unequal mixture of enantiomers is produced.
Answer to Problem 12.26P
The mechanism for the given reaction is
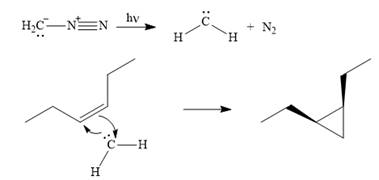
Explanation of Solution
Diazomethane dissociates heterolytically when irradiated with ultraviolet light to produce a carbene and a nitrogen molecule.
![]()
The carbene then simultaneously adds to the initially double-bonded carbons. The lone pair on the carbene forms a bond with one carbon while the
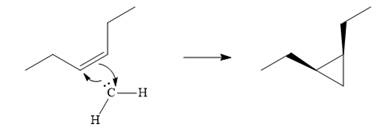
The starting alkene has a cis geometry and is symmetric. Therefore, only one product, a meso compound is produced.
Thus the complete mechanism for this reaction can be drawn as

A carbene adds to an alkene or alkyne to produce a cyclopropane ring.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms: Study Guide/solutions Manual (second)
- :0: :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: (CH3)2NH :0: ■ Select to Add Arrows :0: :0: (CH3)2NH ■ Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following H action sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings H Charges ㅁarrow_forwardPlease help me with this the problem is so confusingarrow_forward
- 14 Question (1 point) Disiamylborane adds to a triple bond to give an alkenylborane. Upon oxidation with OH, H2O2, the alkenylborane will form an enol that tautomerizes to an aldehyde. In the first box below, draw the mechanism arrows for the reaction of disiamylborane with the alkyne, and in the last box draw the structure of the aldehyde. 4th attempt Feedback i > 3rd attempt OH, H2O2 i See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardanswer with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forwardHello I need some help with Smartwork. For drawing structure B, I know the correct answer is CH₃B₂, but when I try to type it in, it keeps giving me CH₄BH₃ instead. Do you know how I should write it properly? Should I use a bond or something else?arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


