
EBK INTRODUCTION TO CHEMICAL ENGINEERIN
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259878091
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCGRAW HILL BOOK COMPANY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 12.13P
Problems 12.9 through 12.14 refer to the Txy diagram for ethanol(1)/ethyl acetate(2) shown in Fig.12.20.
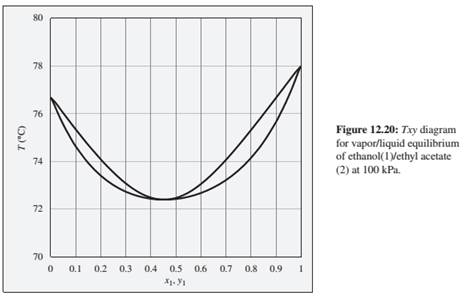
12.13. Consider an ethanol( 1 i/ethyl acetate(2) mixture with x1= 0.20. initially at 80°C and 100 kPa. Describe the evolution of phases and phase compositions as the temperature is gradually reduced to 70°C.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Water at 60° F is being pumped from a stream to a reservoir whose surface is 210 ft above the pump. The pipe from the pump to the reservoir is an 8-in Schedule 40 steel pipe 2500 ft long. The pressure at the pump inlet is - 2,36 psig. If 4.00 ft³/s is being pumped,
a). Compute the pressure at the outlet of the pump. Answer: 0,997 MPa
b). Compute the power delivered by the pump to the water. Answer: 151 hp
Consider the friction loss in the discharged line, but neglect other losses
1. Consider a mixture of 2.5.0% ethane, 2.0% butane, and 1.7% n-pentane by volume.a. Estimate the LFL and UFL of the mixture. Is it flammable?b. Estimate the LOC for this mixture.
Estimate the LFL and UFL for propylene using Equations 6-10 and 6-11 in the textbook,and compare these to the experimental values given in the table in Appendix B.
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK INTRODUCTION TO CHEMICAL ENGINEERIN
Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.1PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.2PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.3PCh. 12 - Problems 12.3 through 12.8 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.3 through 12.8 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.3 through 12.8 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.3 through 12.8 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.3 through 12.8 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.9 through 12.14 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.9 through 12.14 refer to the Txy...
Ch. 12 - Problems 12.9 through 12.14 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.9 through 12.14 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.9 through 12.14 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.9 through 12.14 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.15PCh. 12 - Problems 12.16 through 12.21 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.16 through 12.21 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.16 through 12.21 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.16 through 12.21 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.16 through 12.21 refer to the Pxy...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.21PCh. 12 - Problems 12.22 through 12.28 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.22 through 12.28 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.22 through 12.28 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.22 through 12.28 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.22 through 12.28 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.22 through 12.28 refer to the Txy...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.28PCh. 12 - Problems 12.29 through 12.33 refer to the xy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.29 through 12.33 refer to the xy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.29 through 12.33 refer to the xy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.29 through 12.33 refer to the xy...Ch. 12 - Problems 12.29 through 12.33 refer to the xy...Ch. 12 - Consider a binary liquid mixture for which the...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.35PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.36P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Determine the minimum compression ratio required to raise the temperature of air overhexane to its AIT. Assume an initial temperature of 20°C.2. Ethanol is kept in a storage vessel that is vented with air (at 25°C and 1 atm). Is theequilibrium mixture of vapor above the liquid and air flammable? What if the liquid isacetone instead?arrow_forwardHydrogenation of Ethylbenzene to Styrene Reaction: C₈H₁₀ → C₈H₈ + H₂ΔHᵣ°(300°C) = -124 kJ/mol (exact value unknown) Process Description: The basis is 1000 kg/h of separated styrene. The reaction conversion rate is 35%. The temperature increase in heat exchanger 2 is adiabatic. A fresh stream of pure ethylbenzene (25°C) enters a mixing vessel, where it is combined with a recycle stream (from the distillation column, as explained later), which also consists of pure ethylbenzene at 25°C. After mixing, the stream is sent to a heat exchanger (HX1), where the mixture is heated to 200°C. Next, the mixture enters an adiabatic heat exchanger (HX2), where it is further heated to 300°C by adding steam (at 350°C). This steam is used to prevent side reactions and carbon deposition in the reactor. The heated mixture is then fed into the reactor, where the reaction takes place with a conversion rate of 35%. As a result, the mixture cools down to 260°C. The resulting mixture is then sent to HX4, where…arrow_forwardChemical Engineering Questionarrow_forward
- 4.16 aarrow_forward8. The thermal decomposition of nitric oxide at elevated temperatures 2NO → N₂+02 has been studied in a batch reactor where at temperatures below 2000K the rate expression that applies to low conversions is: r = kCm05 Co At high conversions, or when the initial mixture contains a high concentration of O2 the rate expression is given by: r = k' Cм0.5 C15C0,5 To explain these kinetics the following chain reaction mechanism has been proposed: Initiation: Propagation: 2NON₂O +0 k₂ E1=272.0 kJ/mol 0+ NO O₂+ N E₂-161.0 kJ/mol N+NO N₂+0 E3-1.4 kJ/mol K4 20+ MO₂+M E4=14.0 kJ/mol ks Termination: where M is any molecule capable of the energy transfer necessary to stabilize the oxygen molecule. Once appreciable amounts of O2 are present in the reaction mixture, the initiation reaction that is the primary source of atomic oxygen is no longer the first reaction. Instead, the following reaction begins to dominate the chain initiation process: Initiation (high O2): ks NO +0₂ NO₂+0 E5=198.0 kJ/mol a.…arrow_forward2:41 2) If the number-average degree of polymerization for styrene obtained by the bulk polymerization at 25°C is 5,000, what would be the number-average degree of polymerization if conducted in a 10% solution in toluene (900g of toluene per 100 g of styrene) under otherwise identical conditions? State any assumptions that are needed. (see Table 2-4). Table 2-4 Representative Values of Chain-Transfer Constants Monomer Styrene Chain-Transfer Agent T (°C) C x 104 Styrene 25 bas 0.279 * 50 0.35-0.78 Polystyrene 50 1.9-16.6 Benzoyl peroxide 50 0.13 Toluene 60 0.125 Methyl methacrylate Methyl methacrylate 30 0.117 70 0.2 Poly(methyl methacrylate) 50 0.22-1000 Benzoyl peroxide 50 0.01 Toluene 40 0.170 3) 2 3) Methyl methacrylate is copolymerized with 2-methylbenzyl methacrylate (M₁) in 1,4- dioxane at 60°C using AIBN as the free-radical initiator. (a) Draw the repeating unit of poly(2-methylbenzyl methacrylate). (b) From the data given in the table below, estimate the reactivity ratios of…arrow_forward
- A piston–cylinder device initially contains 0.6 m3 of saturated water vapor at 250 kPa. At this state, the piston is resting on a set of stops, and the mass of the piston is such that a pressure of 300 kPa is required to move it. Heat is now slowly transferred to the steam until the volume becomes 1 m3. Use the data from the steam tables. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the final temperature. The final temperature is ºC. Determine the work done during this process Determine the total heat transferarrow_forwardConsider a mixture of carbon monoxide and water at 25°C:a. Does an azeotrope exist for this mixture at 25°C? If so, at what composition andpressure? If not, how do you know?b. If the total composition of the mixture is 10. mol% carbon monoxide, what will bethe pressure limits of VLE for this mixture at 25°C? show all the calculation stepsarrow_forwardA passive solar house was determined to lose heat to the outdoors at an average rate of 50,000 kJ/h during a typical 10-hour winter night. The house is to be maintained at 22°C at all times. Passive heating is accomplished by 50 glass containers each containing 20 L of water that is heated to 80°C during the day by absorbing solar energy. A 15-kW back-up electric resistance heater turns on whenever necessary to keep the house at 22°C. (a) How many hours does the electric heating system run during a typical winter night? (b) How many hours would the electric heater run during a typical winter night if the house did not have passive solar heating? For the density and specific heat of water at room temperature, use p = 1 kg/L and cp = 4.18 kJ/kg.°Carrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Equilibrium - Chemical Equilibrium - Chemistry Class 11; Author: Ekeeda;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8V9ozZSKl9E;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY