
Concept explainers
Determine material requirements plans for pans N and V and subassembly I as described in Solved Problem 3 for each of the following:
a. Assume that there are currently 100 Ns on hand and scheduled receipts of 40 Is and 10 Vs at the beginning of week 3. No Es are on hand: 120 Es are needed at the start of week 5.
b. Assume on-hand and scheduled receipts as in part a. Now suppose that 100 Es are needed at the stmt of week 5 and 55 at the start of week 7. Also, use multiples of these order sizes: N, 800; V, 200. Use lot-for-lot ordering for I.
C. Using your answer to part b, update the MRP for V, using the following additional information for each of these cases: (1) one week has elapsed (making it the start of week 2), and (2) three weeks have elapsed (making it the start of week 4).
The updated master
a)
To prepare A Material requirement plan for the given information.
Introduction: Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) is the planning or scheduling system, which is used in the manufacturing process. It is used to plan the number of items required to produce one unit of finished goods (end item).
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
On-hand balances are 100 units of Component N and 0 units of Component E. Scheduled receipts is 40 units of Component I and 10 units of Component C would arrive at the beginning of Week 3. 120 units of Component E are needed at the beginning of Week 5.
Product structure tree:
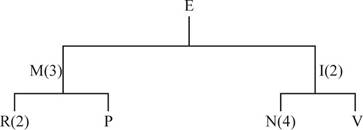
Prepare master schedule:
| Week | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Quantity | 120 |
Develop a material requirement planning for End item E:
- It is given that Person X has received an order to deliver 120 units of End item E, which must be shipped at the start of week 5.
- Beginning inventory is given as 0 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 120 units (120-0).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 120 units in the beginning of week 5. Hence, they need to order for 120 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 4.
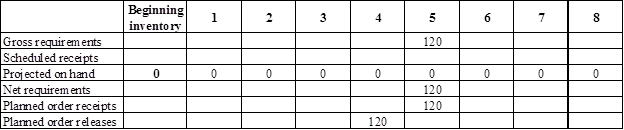
Develop a material requirement planning for Component I (2):
- End item E is the parent item of Component I (2). Hence, the planned order release of E is the gross requirement for Component I (2). As number of units required is 2 for Component I, the planned order release row should be multiplied with 2 to attain the gross requirement column of Component I.
- Beginning inventory is given as 0 units.
- Scheduled receipt is 40 units at the beginning of week 3.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 200 units on week 4 (240-40).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 200 units in the beginning of week 4. Hence, they need to order for 200 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 3.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 5 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for Component N (4):
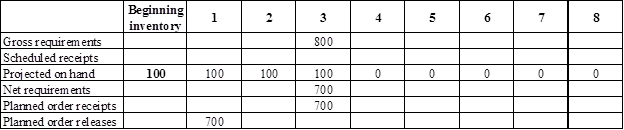
- Component I (2) is the parent item of Component N (4). Hence, the planned order release of Component I (2) is the gross requirement for Component N (4). As number of units required is 4 for Component N, the planned order release row should be multiplied with 2 to attain the gross requirement column of Component N.
- Beginning inventory is given as 100 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 700 units on week 3 (800-100).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 2 weeks. The company requires 700 units in the beginning of week 3. Hence, they need to order for 700 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) two weeks before (as the lead-time is 2 weeks). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 1.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 4 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
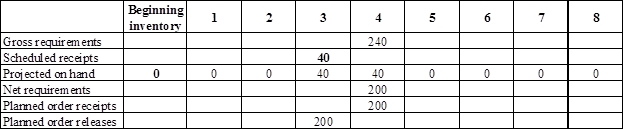
Develop a material requirement planning for Component V:
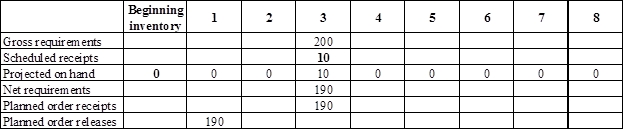
- Component I (2) is the parent item of Component V. Hence, the planned order release of Component I (2) is the gross requirement for Component V. As number of units required is 1 for Component V, the planned order release row should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of Component V.
- Beginning inventory is given as 0 units.
- Scheduled receipt is 10 units at the beginning of week 3.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 190 units on week 3 (200-10).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 2 weeks. The company requires 700 units in the beginning of week 3. Hence, they need to order for 700 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) two weeks before (as the lead-time is 2 weeks). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 1.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 4 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
b)
To prepare A Material requirement plan for the given information.
Introduction: Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) is the planning or scheduling system, which can be used in the manufacturing process. It is used to plan the number of items required to produce one unit of finished goods (end item).
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
On-hand balances are 100 units of Component N and 0 units of Component E. Scheduled receipts is 40 units of Component I and 10 units of Component C would arrive at the beginning of week 3. 100 units of Component E are needed at the beginning of week 5 and 55 units needed at the beginning of week 7. Lot size is multiple of 800 for Component N, multiples of 200 for Component V, and lot-for-lot for Component E and Component I.
Product structure tree:
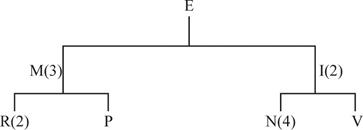
Develop a material requirement planning for End item E:
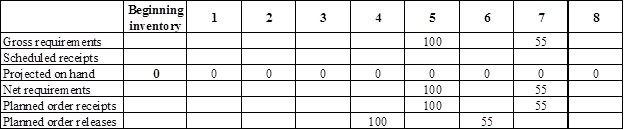
- It is given that Person X has received an order to deliver 100 units of End item E in the start of week 5 and 55 units of End item E in the start of week 7.
- Beginning inventory is given as 0 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 100 units in week 5 (100-0).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 100 units in the beginning of Week 5. Hence, they need to order for 100 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 4.
Develop a material requirement planning for Component I (2):
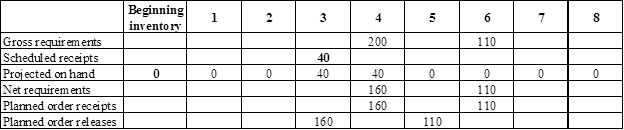
- End item E is the parent item of Component I (2). Hence, the planned order release of E is the gross requirement for Component I (2). As number of units required is 2 for Component I, the planned order release row should be multiplied with 2 to attain the gross requirement column of Component I.
- Beginning inventory is given as 0 units.
- Scheduled receipt is 40 units at the beginning of week 3.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 160 units on week 4 (200-40).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 160 units in the beginning of week 4. Hence, they need to order for 160 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 3.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 5 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for Component N (4):
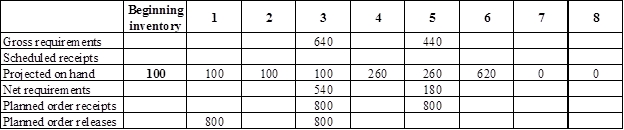
- Component I (2) is the parent item of Component N (4). Hence, the planned order release of Component I (2) is the gross requirement for Component N (4). As number of units required is 4 for Component N, the planned order release row should be multiplied with 2 to attain the gross requirement column of Component N.
- Beginning inventory is given as 100 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 540 units on week 3 (640-100).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 2 weeks. The company requires 540 units in the beginning of week 3. Hence, they need to order for 800 units (as the lot size is multiples of 800) two weeks before (as the lead-time is 2 weeks). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 1.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 4 is 260 units. Calculation is as follows:
- Projected on hand inventory for week 6 is 620 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for Component V:
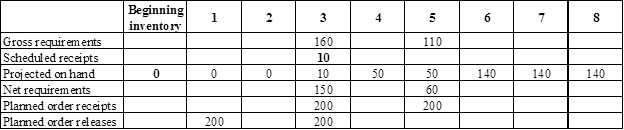
- Component I (2) is the parent item of Component V. Hence, the planned order release of Component I (2) is the gross requirement for Component V. As number of units required is 1 for Component V, the planned order release row should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of Component V.
- Beginning inventory is given as 0 units.
- Scheduled receipt is 10 units at the beginning of week 3.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 150 units on week 3 (160-10).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 2 weeks. The company requires 150 units in the beginning of week 3. Hence, they need to order for 200 units (as the lot size is multiples of 200) two weeks before (as the lead-time is 2 weeks). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 1.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 4 is 50 units. Calculation is as follows:
- Projected on hand inventory for week 6 is 140 units. Calculation is as follows:
c)
1)
To prepare: Material requirement plan for the given information.
Introduction: Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) is the planning or scheduling system, which can be used in the manufacturing process. It is used to plan the number of items required to produce one unit of finished goods (end item).
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
On-hand balances are 100 units of Component N and 0 units of Component E. Scheduled receipts is 800 units of Component N and 200 units of Component V would arrive at the beginning of week 3. Lot size is multiple of 800 for Component N, multiples of 200 for Component V, and lot-for-lot for Component E and Component I.
Week 1 has elapsed. Hence, plan has to be prepared from week 2 through week 9. 100 units of Component E are needed at the beginning of week 5 and 55 units needed at the beginning of week 7. In addition to that, 100 units of End item E are needed in week 9.
Product structure tree:
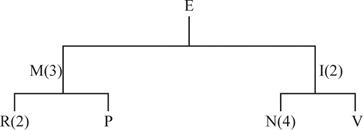
Develop a material requirement planning for End item E:
- It is given that Person X has received an order to deliver 100 units of End item E in week 5, 55 units in week 7, and 100 units in week 9.
- Beginning inventory is given as 0 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 100 units (100-0).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 100 units in the beginning of week 5. Hence, they need to order for 100 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 4.
Develop a material requirement planning for Component I (2):
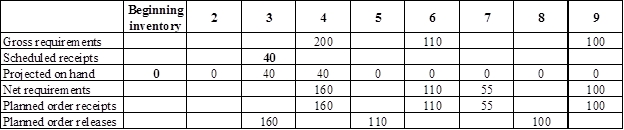
- End item E is the parent item of Component I (2). Hence, the planned order release of E is the gross requirement for Component I (2). As number of units required is 2 for Component I, the planned order release row should be multiplied with 2 to attain the gross requirement column of Component I.
- Beginning inventory is given as 0 units.
- Scheduled receipt is 40 units at the beginning of week 3.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 160 units on week 4 (200-40).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 160 units in the beginning of week 4. Hence, they need to order for 160 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 3.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 5 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for Component N (4):
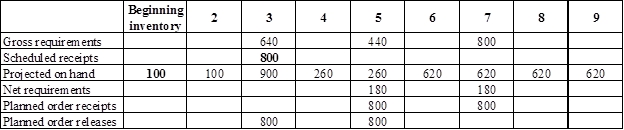
- Component I (2) is the parent item of Component N (4). Hence, the planned order release of Component I (2) is the gross requirement for Component N (4). As number of units required is 4 for Component N, the planned order release row should be multiplied with 2 to attain the gross requirement column of Component N.
- Beginning inventory is given as 100 units.
- Scheduled receipt is 800 units at the beginning of week 3
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 180 units on week 5 (440-260).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 2 weeks. The company requires 180 units in the beginning of week 5. Hence, they need to order for 800 units (as the lot size is multiples of 800) two weeks before (as the lead-time is 2 weeks). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 3.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 4 is 260 units. Calculation is as follows:
- Projected on hand inventory for week 6 is 620 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for Component V:
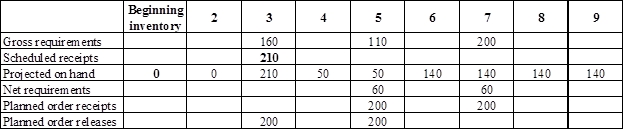
- Component I (2) is the parent item of Component V. Hence, the planned order release of Component I (2) is the gross requirement for Component V. As number of units required is 1 for Component V, the planned order release row should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of Component V.
- Beginning inventory is given as 0 units.
- Scheduled receipt is 210 units at the beginning of week 3.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 60 units on week 5 (110-50).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 2 weeks. The company requires 700 units in the beginning of week 3. Hence, they need to order for 700 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) two weeks before (as the lead-time is 2 weeks). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 1.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 4 is 50 units. Calculation is as follows:
- Projected on hand inventory for week 6 is 140 units. Calculation is as follows:
1)
To prepare: Material requirement plan for the given information.
Introduction: Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) is the planning or scheduling system, which can be used in the manufacturing process. It is used to plan the number of items required to produce one unit of finished goods (end item).
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
On-hand balances are 100 units of Component N and 0 units of Component E. Scheduled receipts is 800 units of Component N and 200 units of Component V would arrive at the beginning of week 3. Lot size is multiple of 800 for Component N, multiples of 200 for Component V, and lot-for-lot for Component E and Component I.
Week 1 has elapsed. Hence, plan has to be prepared from week 2 through week 9. 100 units of Component E are needed at the beginning of week 5 and 55 units needed at the beginning of week 7. In addition to that, 100 units of End item E are needed in week 9.
Product structure tree:

Develop a material requirement planning for End item E:

- It is given that Person X has received an order to deliver 100 units of End item E in week 5, 55 units in week 7, and 100 units in week 9.
- Beginning inventory is given as 0 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 100 units (100-0).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 100 units in the beginning of week 5. Hence, they need to order for 100 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 4.
Develop a material requirement planning for Component I (2):

- End item E is the parent item of Component I (2). Hence, the planned order release of E is the gross requirement for Component I (2). As number of units required is 2 for Component I, the planned order release row should be multiplied with 2 to attain the gross requirement column of Component I.
- Beginning inventory is given as 0 units.
- Scheduled receipt is 40 units at the beginning of week 3.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 160 units on week 4 (200-40).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 160 units in the beginning of week 4. Hence, they need to order for 160 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 3.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 5 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for Component N (4):

- Component I (2) is the parent item of Component N (4). Hence, the planned order release of Component I (2) is the gross requirement for Component N (4). As number of units required is 4 for Component N, the planned order release row should be multiplied with 2 to attain the gross requirement column of Component N.
- Beginning inventory is given as 100 units.
- Scheduled receipt is 800 units at the beginning of week 3
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 180 units on week 5 (440-260).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 2 weeks. The company requires 180 units in the beginning of week 5. Hence, they need to order for 800 units (as the lot size is multiples of 800) two weeks before (as the lead-time is 2 weeks). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 3.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 4 is 260 units. Calculation is as follows:
- Projected on hand inventory for week 6 is 620 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for Component V:

- Component I (2) is the parent item of Component V. Hence, the planned order release of Component I (2) is the gross requirement for Component V. As number of units required is 1 for Component V, the planned order release row should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of Component V.
- Beginning inventory is given as 0 units.
- Scheduled receipt is 210 units at the beginning of week 3.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 60 units on week 5 (110-50).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 2 weeks. The company requires 700 units in the beginning of week 3. Hence, they need to order for 700 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) two weeks before (as the lead-time is 2 weeks). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 1.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 4 is 50 units. Calculation is as follows:
- Projected on hand inventory for week 6 is 140 units. Calculation is as follows:
2)
To prepare: Material requirement plan for the given information.
Introduction: Materials Requirement Planning (MRP) is the planning or scheduling system, which can be used in the manufacturing process. It is used to plan the number of items required to produce one unit of finished goods (end item).
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
On-hand balances are 100 units of Component N and 0 units of Component E. Lot size is multiple of 800 for Component N, multiples of 200 for Component V, and lot-for-lot for Component E and Component I.
Two weeks (week 2 and week 3) has elapsed. Hence, plan has to be prepared from week 4 through week 11. 100 units of Component E are needed at the beginning of week 5 and 55 units needed at the beginning of week 7. In addition to that, 100 units of End item E are needed in week 9.
Planned order releases from 2nd and 3rd week should be used as scheduled receipt units. Scheduled receipt are 160 units of Component I at the start of 4th week, 800 units of Component N at the start of 5th week, and 200 units of Component V at the start of 5th week.
Product structure tree:
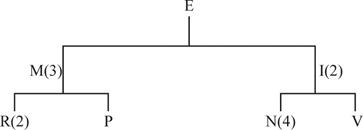
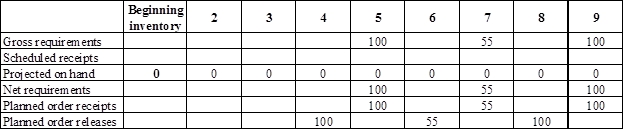
Develop a material requirement planning for End item E:
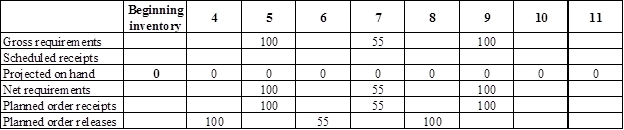
- It is given that Person X has received an order to deliver 100 units of End item E in week 5, 55 units in week 7, and 100 units in week 9.
- Beginning inventory is given as 0 units.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 100 units at week 5 (100-0).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 100 units in the beginning of week 5. Hence, they need to order for 100 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 4.
Develop a material requirement planning for Component I (2):
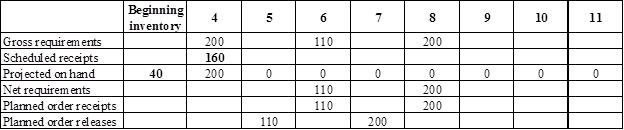
- End item E is the parent item of Component I (2). Hence, the planned order release of E is the gross requirement for Component I (2). As number of units required is 2 for Component I, the planned order release row should be multiplied with 2 to attain the gross requirement column of Component I.
- Beginning inventory is given as 40 units.
- Scheduled receipt is 160 units at the beginning of week 4.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 100 units on week 6 (110-0).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 1 week. Company requires 110 units in the beginning of week 6. Hence, they need to order for 110 units (as the lot size is lot-for-lot) on previous week (as the lead-time is 1 week). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 5.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 5 is 0 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for Component N (4):
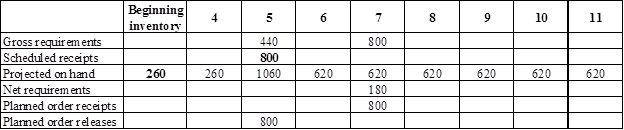
- Component I (2) is the parent item of Component N (4). Hence, the planned order release of Component I (2) is the gross requirement for Component N (4). As number of units required is 4 for Component N, the planned order release row should be multiplied with 2 to attain the gross requirement column of Component N.
- Beginning inventory is given as 260 units.
- Scheduled receipt is 800 units at the beginning of week 3
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 180 units on week 7 (800-620).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 2 weeks. The company requires 180 units in the beginning of week 7. Hence, they need to order for 800 units (as the lot size is multiples of 800) two weeks before (as the lead-time is 2 weeks). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 5.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 5 is 1,060 units. Calculation is as follows:
- Projected on hand inventory for week 6 is 620 units. Calculation is as follows:
Develop a material requirement planning for Component V:
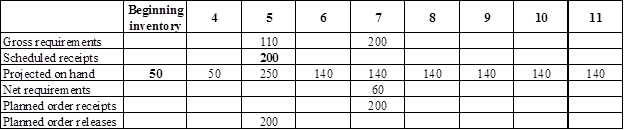
- Component I (2) is the parent item of Component V. Hence, the planned order release of Component I (2) is the gross requirement for Component V. As number of units required is 1 for Component V, the planned order release row should be multiplied with 1 to attain the gross requirement column of Component V.
- Beginning inventory is given as 50 units.
- Scheduled receipt is 200 units at the beginning of week 5.
- Net requirement can be calculated by subtracting the projected on-hand from the gross requirement. Hence, the net requirement is 60 units on week 7 (200-140).
- Planned order release is the order given by the company and planned order receipts is the order received by the firm.
- Lead-time is given as 2 weeks. The company requires 60 units in the beginning of week 7. Hence, they need to order for 200 units (as the lot size is multiples of 200) two weeks before (as the lead-time is 2 weeks). Thus, company need to order the required units in week 5.
- Projected on hand inventory for week 6 is 140 units. Calculation is as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
EBK OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
Managerial Accounting (5th Edition)
Marketing: An Introduction (13th Edition)
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Essentials of MIS (13th Edition)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
- a. The average aggregate inventory value of the product if Ruby-Star used vendor 1 exclusively is $enter your response here. (Enter your response as a whole number.) b. The aggregate inventory value of the product if Ruby-Star used vendor 2 exclusively is shown below. c. How would your analysis change if average weekly demand increased to 160 units per week? The aggregate inventory values are shown below.arrow_forwarda. What order quantity should be used? lures. (Enter your response rounded to the nearest whole number.) b. What reorder point should be used? (Enter your response rounded to the nearest whole number.) c. What is the total annual cost for this inventory system? (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places)arrow_forwardOakwood Hospital is considering using ABC analysis to classify laboratory SKUS into three categories: those that will be delivered daily from their supplier (Class A items), those that will be controlled using a continuous review system (B items), and those that will be held in a two bin system (C items). The following table shows the annual dollar usage for a sample of eight SKUS. Fill in the blanks for annual dollar usage below. (Enter your responses rounded to the nearest whole number.) SKU Unit Value Demand (units) Annual Dollar Usage 1 $1.10 30,000 $ 2 $0.02 125,000 $ 3 $0.20 65,000 S 4 $0.02 1,100 SA 5 $1.40 150 SA 678 $4.10 900 $ $0.80 350 $ $0.55 80 EA $arrow_forward
- Dyson, a high-tech home appliance maker, has cut ties with Malaysian supplier ATA IMS Bhd following an audit of the company's labour practices and allegations by a whistleblower. ATA is already under US investigation over forced labour allegations. Dyson has terminated its contracts and is in talks with its customer over the audit findings. ATA, which produces parts for Dyson's vacuum cleaners and air purifiers, tumbled 30% to its lowest since April 2020. The termination is a significant blow for Malaysia, a major electronics manufacturing hub, which has faced scrutiny this year over claims of abusive working and living conditions. Dyson terminated the relationship with six months' contractual notice, hoping it would give ATA the impetus to improve and enable an orderly withdrawal in the interests of the workers they employ. Former ATA worker Dhan Kumar Limbu was beaten by police in Malaysia after sharing information about conditions at the factory with activists. ATA denied all…arrow_forwardQuestion 4 (25 Marks) Discuss how developing internal performance measures to track the performance of supplier development, can create efficiency for Pick n Pay.arrow_forwardLeadership and people Earlier this year, Pick n Pay actioned the first priority of the plan: the introduction of a new, simplified and seasoned leadership team with proven track records. The team has already implemented strengthened structures, including establishing regional trading areas with local decision-making, with clear sight of strong long-term succession Each operating region now has a regional buying team and store management team in place to meet specific customer needs particular to that region, while also increasing staff training and productivity for an overall improved store experience. Reset the store estate To create a more sustainable supermarket business, the Group is resetting its store estate to minimise losses by creating a smaller but more profitable Pick n Pay store estate. The plan is to leverage the strength of its multi-format model with strategic conversions to lift store profitability: selected Pick n Pay stores will be converted to Boxer, where customer…arrow_forward
- Question 3 (25 Marks) Elaborate on how Pick n Pay could use information technology and ERP systems across the company and their suppliers to improve their operating model? Question 4 (25 Marks)arrow_forwardQuestion 2 (25 Marks) Discuss how you would "reset the store estate" to remain competitive and relevant in the market? Question 3 (25 Marks)arrow_forwardWhat should leaders do after conducting an employee survey? take immediate action on results take at least 6 months to review the results to make sure the leader understands them review them immediately, but do not take action right away keep results confidential from employeesarrow_forward
- One of the best ways to encourage teamwork is to: continually promote from outside of the department recognize employees who focus on their personal performance goals only reward employees who complete their own tasks and also assist with problems outside of their department discuss individual performance issues at staff meetingsarrow_forwardWhat can happen if a leader doesn't encourage teamwork? team members will support each other more the environment can become overly competitive and hostile turnover will descrease team members become more motivatedarrow_forwardunderstand 4 Classwork LSC Drag the name of the figure of speech to its example. 12 February 2025 personification Onomatopoeia Simile Metaphor Hyperbole Onomatopoeia metaphor 1. He tried to help but his legs were wax. Metaphor 2. The man flights like a lion on the soccer field. Simile 3. The books fell on the table with a loud thump. Onomatopoeia 4. Rita heard the last piece of pie calling her name. Personification 5. The rustling leaves kept me away. Personification 6. Kisses are the flowers of affection. 7. He's running faster than the windarrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning




