
Mechanics of Materials, Student Value Edition Plus Mastering Engineering with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134326054
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 1.2, Problem 1.18P
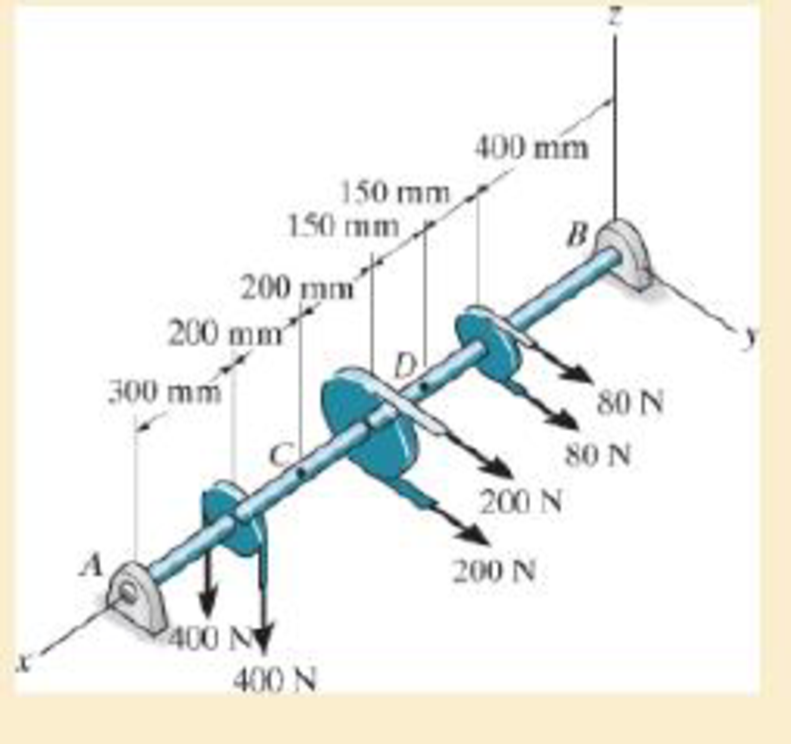
The shaft is supported at its ends by two bearings A and B and is subjected to the forces applied to the pulleys fixed to the shaft. Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at point C. The 400-N forces act in the -z direction and the 200-N and 80-N forces act in the +y direction. The journal bearings at A and B exert only y and z components of force on the shaft.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
ә
レ
Figure below shows a link mechanism in which the link OA rotates uniformly in an
anticlockwise direction at 10 rad/s. the lengths of the various links are OA=75 mm, OB-150 mm,
BC=150 mm, CD-300 mm. Determine for the position shown, the sliding velocity of D.
A
A
B
#
Space Diagram
o NTS (Not-to-Scale)
C
10
=--20125
735)
750 x2.01
اه
2
レ
Tanism in which the link OA mm. O
anticlockwise direction at 10 rad/s, the lengths of the various links are OA=75mm, OB=150mm,
BC=150mm,CD=300mm. Determine for the position shown, the sliding velocity of D.
A
A
Space Diagram
o NT$ (Not-to-Scale)
B
#
C
か
750 x2.01
165
79622
Ashaft fitted with a flywheel rotates at 300 rpm. and drives a machine. The torque
required to drive the machine varies in a cyclic manner over a period of 2 revolutions. The torque drops
from 20,000 Nm to 10,000 Nm uniformly during 90 degrees and remains constant for the following 180
degrees. It then rises uniformly to 35,000 Nm during the next 225 degrees and after that it drops to
20,000 in a uniform manner for 225 degrees, the cycle being repeated thereafter.
Determine the power required to drive the machine and percentage fluctuation in speed, if the driving
torque applied to the shaft is constant and the mass of the flywheel is 12 tonnes with radius of gyration of
500 mm. What is the maximum angular acceleration of the flywheel.
35,000
TNM
20,000
10,000
0
90
270
495
Crank angle 8 degrees
720
Chapter 1 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, Student Value Edition Plus Mastering Engineering with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (10th Edition)
Ch. 1.2 - In each case, explain how to find the resultant...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal force,...Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal normal and shear...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...
Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings on the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings at cross...Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the distributed load shown....Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the distributed load shown....Ch. 1.2 - The boom DF of the jib crane and the column DE...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - The blade of the hacksaw is subjected to a...Ch. 1.2 - The blade of the hacksaw is subjected to a...Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the triangular distributed load...Ch. 1.2 - The beam supports the distributed load shown....Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported at its ends by two bearings...Ch. 1.2 - The shaft is supported at its ends by two bearings...Ch. 1.2 - The hand crank that is used in a press has the...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - The metal stud punch is subjected to a force of...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - Determine the resultant internal loadings acting...Ch. 1.2 - The pipe has a mass of 12 kg/m. If it is fixed to...Ch. 1.2 - If the drill bit jams when the brace is subjected...Ch. 1.2 - The curved rod AD of radius r has a weight per...Ch. 1.2 - A differential element taken from a curved bar is...Ch. 1.5 - In each case, determine the largest internal shear...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest internal normal force in the...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the internal normal force at section A...Ch. 1.5 - The lever is held to the fixed shaft using the pin...Ch. 1.5 - The single-V butt joint transmits the force of 5...Ch. 1.5 - The uniform beam is supported by two rods AB and...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress on the cross...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress on the cross...Ch. 1.5 - If the 600-kN force acts through the centroid of...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress at points A,...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress in rod AB if...Ch. 1.5 - The supporting wheel on a scaffold is held in...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest intensity w of the uniform...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area A and is...Ch. 1.5 - The small block has a thickness of 0.5 in. If the...Ch. 1.5 - If the material fails when the average normal...Ch. 1.5 - If the block is subjected to a centrally applied...Ch. 1.5 - The plate has a width of 0.5 m. If the stress...Ch. 1.5 - The board is subjected to a tensile force of 200...Ch. 1.5 - The boom has a uniform weight of 600 lb and is...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the average normal stress in each of the...Ch. 1.5 - If the average normal stress in each of the...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the maximum average shear stress in pin...Ch. 1.5 - If P=5 kN, determine the average shear stress in...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the maximum magnitude P of the loads the...Ch. 1.5 - The column is made of concrete having a density of...Ch. 1.5 - The beam is supported by two rods AB and CD that...Ch. 1.5 - The beam is supported by two rods AB and CD that...Ch. 1.5 - If P = 15 kN, determine the average shear stress...Ch. 1.5 - The railcar docklight is supported by the...Ch. 1.5 - The plastic block is subjected to an axial...Ch. 1.5 - The two steel members are joined together using a...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The two members used in the construction of an...Ch. 1.5 - The 2-Mg concrete pipe has a center of mass at...Ch. 1.5 - The 2-Mg concrete pipe has a center of mass at...Ch. 1.5 - The pier is made of material having a specific...Ch. 1.5 - Rods AB and BC have diameters of 4 mm and 6 mm,...Ch. 1.5 - The uniform bar, having a cross-sectional area of...Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The bar has a cross-sectional area of 400(106) m2....Ch. 1.5 - The prismatic bar has a cross-sectional area A. If...Ch. 1.5 - The prismatic bar has a cross-sectional area A. If...Ch. 1.5 - The bars of the truss each have a cross-sectional...Ch. 1.5 - The bars of the truss each have a cross-sectional...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the largest load P that can be applied...Ch. 1.5 - Determine the greatest constant angular velocity ...Ch. 1.5 - The radius of the pedestal is defined by r =...Ch. 1.7 - Rods AC and BC are used to suspend the 200-kg...Ch. 1.7 - If it is subjected to double shear, determine the...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum average shear stress...Ch. 1.7 - If each of the three nails has a diameter of 4 mm...Ch. 1.7 - The strut is glued to the horizontal member at...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum average shear stress...Ch. 1.7 - If the eyebolt is made of a material having a...Ch. 1.7 - If the bar assembly is made of a material having a...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 1.7 - The pin is made of a material having a failure...Ch. 1.7 - If the bolt head and the supporting bracket are...Ch. 1.7 - Six nails are used to hold the hanger at A against...Ch. 1.7 - If A and B are both made of wood and are 38 in....Ch. 1.7 - Prob. 1.70PCh. 1.7 - The connection is made using a bolt and nut and...Ch. 1.7 - The tension member is fastened together using two...Ch. 1.7 - The steel swivel bushing in the elevator control...Ch. 1.7 - The spring mechanism is used as a shock absorber...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the size of square bearing plates A and...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum load P that can be applied...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required diameter of the pins at A...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for wires AB and...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for wires AB and...Ch. 1.7 - The cotter is used to hold the two rods together....Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required diameter of the pins at A...Ch. 1.7 - The steel pipe is supported on the circular base...Ch. 1.7 - The boom is supported by the winch cable that has...Ch. 1.7 - The boom is supported by the winch cable that has...Ch. 1.7 - The assembly consists of three disks A, B, and C...Ch. 1.7 - The two aluminum rods support the vertical force...Ch. 1.7 - The two aluminum rods AB and AC have diameters of...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the required minimum thickness t of...Ch. 1.7 - Determine the maximum allowable load P that can be...Ch. 1.7 - The compound wooden beam is connected together by...Ch. 1.7 - The hanger is supported using the rectangular pin....Ch. 1.7 - The hanger is supported using the rectangular pin....Ch. 1.7 - The rods AB and CD are made of steel. Determine...Ch. 1.7 - The aluminum bracket A is used to support the...Ch. 1.7 - If the allowable tensile stress for the bar is...Ch. 1.7 - The bar is connected to the support using a pin...Ch. 1 - The beam AB is pin supported at A and supported by...Ch. 1 - The long bolt passes through the 30-mm-thick...Ch. 1 - Determine the required thickness of member BC to...Ch. 1 - The circular punch B exerts a force of 2 kN on the...Ch. 1 - Determine the average punching shear stress the...Ch. 1 - The 150 mm by 150 mm block of aluminum supports a...Ch. 1 - The yoke-and-rod connection is subjected to a...Ch. 1 - The cable has a specific weight (weight/volume)...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Consider the adage Never ask a question for which you do not want the answer. a. Is following that adage ethica...
Experiencing MIS
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Write a summary list of the problem-solving steps identified in the chapter, using your own words.
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
CONCEPT QUESTIONS
15.CQ3 The ball rolls without slipping on the fixed surface as shown. What is the direction ...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Figure below shows a link mechanism in which the link OA rotates uniformly in an anticlockwise direction at 10 rad/s. the lengths of the various links are OA=75 mm, OB-150 mm, BC=150 mm, CD-300 mm. Determine for the position shown, the sliding velocity of D. A 45 B Space Diagram o NTS (Not-to-Scale) C Darrow_forwardmotion is as follows; 1- Dwell 45°. Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with flat follower of width 14 mm. The required 2- Rising 60 mm in 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 3- Dwell 90°. 4- Falling 60 mm for 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 5- Dwell 45°. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the cam is 50 mm.arrow_forwardAn ideal gas, occupying a volume of 0.02 m3 , has a temperature of 25 0C and is at 1.2 bar. The gas is compressed reversibly and adiabatically to a final pressure of 8 bar. Assuming the gas has an adiabatic index of γ = 1.4, calculate (a) the final temperature, (b) the final volume, (c) the work performed during the compression and (d) the heat transferred.arrow_forward
- attached is a past paper question in which we werent given the solution. a solution with clear steps and justification would be massively appreciated thankyou.arrow_forwardin this scenario, when it comes to matrix iterations it states this system is assumed out of phase. why is this?arrow_forwardQ1. A curved beam of a circular cross section of diameter "d" is fixed at one end and subjected to a concentrated load P at the free end (Fig. 1). Calculate stresses at points A and C. Given: P = 800 N, d = 30 mm, a 25 mm, and b = 15 mm. Fig.1 P b B (10 Marks)arrow_forward
- You are working as an engineer in a bearing systems design company. The flow of lubricant inside a hydrodynamic bearing (p = 0.001 kg m-1 s-1) can be approximated as a parallel, steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow between two parallel plates. The top plate, representing the moving part of the bearing, travels at a constant speed, U, while the bottom plate remains stationary (Figure Q1). The plates are separated by a distance of 2h = 1 cm and are W = 20 cm wide. Their length is L = 10 cm. By applying the above approximations to the Navier-Stokes equations and assuming that end effects can be neglected, the horizontal velocity profile can be shown to be y = +h I 2h = 1 cm x1 y = -h u(y) 1 dP 2μ dx -y² + Ay + B moving plate stationary plate U 2 I2 L = 10 cm Figure Q1: Flow in a hydrodynamic bearing. The plates extend a width, W = 20 cm, into the page.arrow_forwardQuestion 1 You are working as an engineer in a bearing systems design company. The flow of lubricant inside a hydrodynamic bearing (µ = 0.001 kg m¯¹ s¯¹) can be approximated as a parallel, steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow between two parallel plates. The top plate, representing the moving part of the bearing, travels at a constant speed, U, while the bottom plate remains stationary (Figure Q1). The plates are separated by a distance of 2h = 1 cm and are W = 20 cm wide. Their length is L = 10 cm. By applying the above approximations to the Navier-Stokes equations and assuming that end effects can be neglected, the horizontal velocity profile can be shown to be 1 dP u(y) = 2μ dx -y² + Ay + B y= +h Ꮖ 2h=1 cm 1 x1 y = −h moving plate stationary plate 2 X2 L = 10 cm Figure Q1: Flow in a hydrodynamic bearing. The plates extend a width, W = 20 cm, into the page. (a) By considering the appropriate boundary conditions, show that the constants take the following forms: U U 1 dP A =…arrow_forwardQuestion 2 You are an engineer working in the propulsion team for a supersonic civil transport aircraft driven by a turbojet engine, where you have oversight of the design for the engine intake and the exhaust nozzle, indicated in Figure Q2a. The turbojet engine can operate when provided with air flow in the Mach number range, 0.60 to 0.80. You are asked to analyse a condition where the aircraft is flying at 472 m/s at an altitude of 14,000 m. For all parts of the question, you can assume that the flow path of air through the engine has a circular cross section. (a) ← intake normal shock 472 m/s A B (b) 50 m/s H 472 m/s B engine altitude: 14,000 m exhaust nozzle E F exit to atmosphere diameter: DE = 0.30 m E F diameter: DF = 0.66 m Figure Q2: Propulsion system for a supersonic aircraft. a) When the aircraft is at an altitude of 14,000 m, use the International Standard Atmosphere in the Module Data Book to state the local air pressure and tempera- ture. Thus show that the aircraft speed…arrow_forward
- يكا - put 96** I need a detailed drawing with explanation or in wake, and the top edge of im below the free surface of the water. Determine the hydrothed if hydrostatic on the Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with roller follower of diameter 10 mm. The required motion is as follows; 1- Rising 60 mm in 135° with uniform acceleration and retardation motion. 2- Dwell 90° 3- Falling 60 mm for 135° with Uniform acceleration-retardation motion. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the cam is 50 mm. =--20125 7357 750 X 2.01arrow_forwardYou are working as an engineer in a bearing systems design company. The flow of lubricant inside a hydrodynamic bearing (µ = 0.001 kg m¯¹ s¯¹) can be approximated as a parallel, steady, two-dimensional, incompressible flow between two parallel plates. The top plate, representing the moving part of the bearing, travels at a constant speed, U, while the bottom plate remains stationary (Figure Q1). The plates are separated by a distance of 2h = 1 cm and are W = 20 cm wide. Their length is L = 10 cm. By applying the above approximations to the Navier-Stokes equations and assuming that end effects can be neglected, the horizontal velocity profile can be shown to be U y = +h У 2h = 1 cm 1 x1 y=-h u(y) = 1 dP 2μ dx -y² + Ay + B moving plate - U stationary plate 2 I2 L = 10 cm Figure Q1: Flow in a hydrodynamic bearing. The plates extend a width, W = 20 cm, into the page. (a) By considering the appropriate boundary conditions, show that the constants take the following forms: A = U 2h U 1 dP…arrow_forwardQuestion 2 You are an engineer working in the propulsion team for a supersonic civil transport aircraft driven by a turbojet engine, where you have oversight of the design for the engine intake and the exhaust nozzle, indicated in Figure Q2a. The turbojet engine can operate when provided with air flow in the Mach number range, 0.60 to 0.80. You are asked to analyse a condition where the aircraft is flying at 472 m/s at an altitude of 14,000 m. For all parts of the question, you can assume that the flow path of air through the engine has a circular cross section. (a) normal shock 472 m/s A B (b) intake engine altitude: 14,000 m D exhaust nozzle→ exit to atmosphere 472 m/s 50 m/s B diameter: DE = 0.30 m EX diameter: DF = 0.66 m Figure Q2: Propulsion system for a supersonic aircraft. F a) When the aircraft is at an altitude of 14,000 m, use the International Standard Atmosphere in the Module Data Book to state the local air pressure and tempera- ture. Thus show that the aircraft speed of…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
BEARINGS BASICS and Bearing Life for Mechanical Design in 10 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aU4CVZo3wgk;License: Standard Youtube License