
Concept explainers
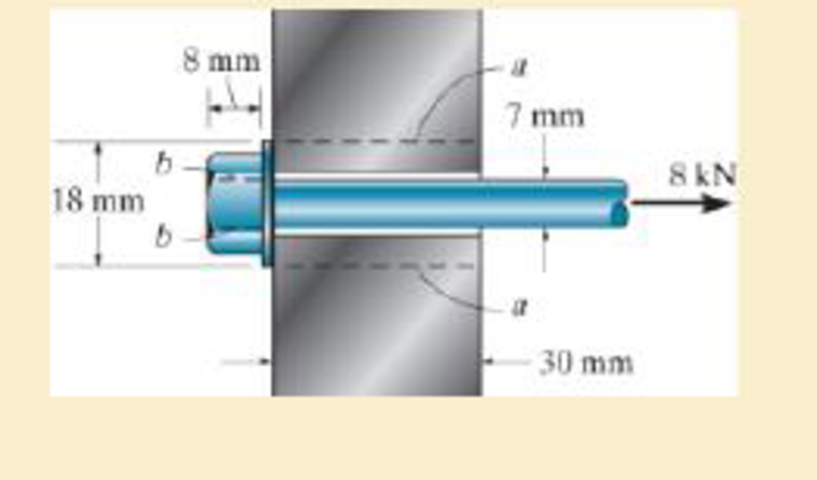
The long bolt passes through the 30-mm-thick plate. If the force in the bolt shank is 8 kN, determine the average normal stress in the shank, the average shear stress along the cylindrical area of the plate defined by the section lines a–a, and the average shear stress in the bolt head along the cylindrical area defined by the section lines b–b.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 1 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, Student Value Edition Plus Mastering Engineering with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (10th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Modern Database Management
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
- Please stop screenshoting ai solution,it always in accurate solve normalarrow_forwardResearch and select any different values for the Ratio of connecting rod length to crank radius from various engine models, then analyze how these changes affect instantaneous velocity and acceleration, presenting your findings visually using graphs.arrow_forwardPb 9) 4.44 bas gnibus& WX 002 grillimatul fred bail (e) For the simply supported I-beam, a load of 1000 lb in center. Find the maximum transverse shear stress. Compare your answer with the approximation obtained by dividing the shear load by the area of the web only with the web considered to extend for the full 8-in depth. - 3½ in. 12 bas in 0% to tolerabib tormi no grived in. 8 in. 38 in. 12 ½ in.arrow_forward
- Pb 12) 4.61 Draw the Mohr circle for the stresses experienced by the surface of an internally pressurized steel tube that is subject to the tangential and axial stresses in the outer surface of 45 ksi and 30 ksi, respectively, and a torsional stress of 18 ksi. yx 18 45 30arrow_forwardPb 8) 4.39 For the C-clamp shown, what force F can be exerted by the screw if the maximum tensile stress in the clamp is to be limited to 30 ksi? F 2 in. სის 3436 16 13 blos 0101 alos12 nodus 121A (s 3 in. in. 16 in. 16 web leonas OFF elson yollA (d 016 (& d of bolow-bloo ai 15912 020112LA sue) vilisub 22 bal.90 Swman a bris ctxibasqqA) laste is tools?arrow_forwardQuiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1 = 6mm, for w2 h2 = 5mm, and for w3 is h3 =5.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=22 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E90xx). 140 S Find the centroid I want university professor solutions O REDMI NOTE 8 PRO CAI QUAD CAMERA 101.15 Farrow_forward
- Pb 6) 4.31 do = 25 mm 4.31 What bending moment is required to produce a maximum normal stress of 400 MPa: (a) In a straight round rod of 40-mm diameter? (b) In a straight square rod, 40 mm on a side (with bending about the X axis as shown for a rectangular section in Appendix B-2)?arrow_forwardPb 13) 4.73 Find the maximum value of stress at the hole and semicircular notch. 45000 N 50 mm 100 mm 15 mm 25 mm 45000 Narrow_forwardPb 11) 4.53 Consider the 1-in solid round shaft supported by self-aligning bearings at A and B. Attached to the shaft are two chain sprockets that are loaded as shown. Treat this as a static loading problem and identify the specific shat location subjected to the most severe state of stress and make a Mohr circle representation of this stress state. 1-in.-dia. shaft 500 lb 2 in. 1000 lb 3 in. 3 in.arrow_forward
- Pb 5) 4.19 Estimate the torque required to produce a maximum shear stress of 570 MPa in a hollow shaft having an inner diameter of 20 mm and an outer diameter of 25 mm. d; = 20 mm T d = 25 mm Tmax = 570 MPaarrow_forwardQuiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1 = 6mm, for w2 h2 = 5mm, and for w3 is h3 =5.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=22 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E90xx). I want university professor solutions O REDMI NOTE 8 PRO CAI QUAD CAMERA 140 S 101.15 Farrow_forwardResearch and select different values for the R ratio from various engine models, then analyze how these changes affect instantaneous velocity and acceleration, presenting your findings visually using graphsarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





