
Concept explainers
Chemical/Bio Engineering
An irreversible, first-order reaction takes place in four well mixed reactors (Fig. P12.10),
Thus, the rate at which A is transformed to B can be represented as
The reactors have different volumes, and because they are operated at different temperatures, each has a different reaction rate:
| Reactor | V, L |
|
| 1 | 25 | 0.05 |
| 2 | 75 | 0.1 |
| 3 | 100 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 25 | 0.1 |
Determine the concentration of A and B in each of the reactors at steady state.
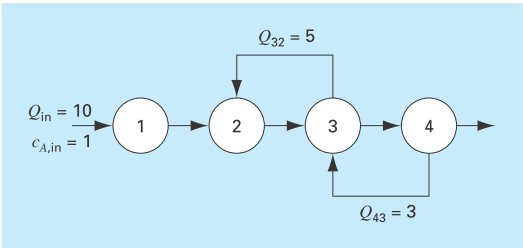
FIGURE P12.10
To calculate:
Answer to Problem 10P
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Write the provided values of the volume and rate of reaction.
Formula used:
Write system of linear equations in matrix form.
And,
The term
Calculation:
Consider the provided diagram for an irreversible first order reaction takes place in four will-mixed reactors.
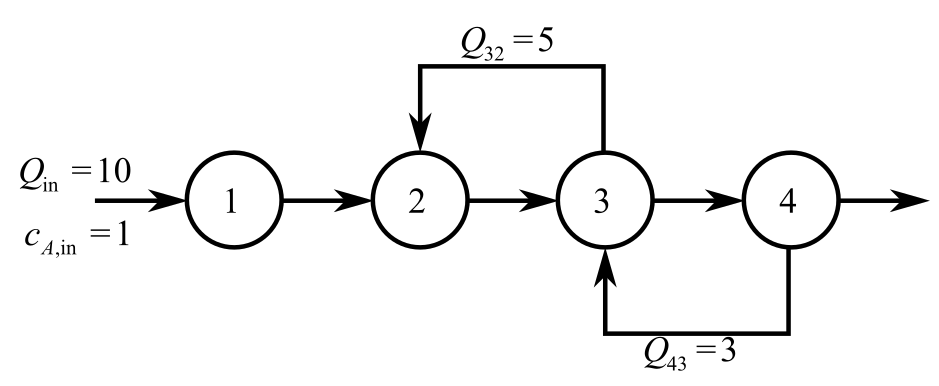
Balance the mass for A in reactor 1 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Balance the mass for A in reactor 2 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Balance the mass for A in reactor 3 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Balance the mass for A in reactor 4 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Balance the mass for B in reactor 1 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Balance the mass for B in reactor 2 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Balance the mass for B in reactor 3 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Balance the mass for B in reactor 4 at steady-state.
Substitute
Further solve.
Now, write all the equations, to find linear system of equations.
Write the above linear equations in matrix form as written in symbolized form.
Here, coefficient matrix A is,
Column matrix
Column matrix B is,
Substitute the values in the matrix equation form.
Solve for
Code:
Type the above code into MATLAB command window and press enter to find the result.
Result is obtained as follows:
Hence,
Hence, the concentration of A and B is,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Numerical Methods for Engineers
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus (Standalone Book)
Elementary Statistics ( 3rd International Edition ) Isbn:9781260092561
Precalculus
Intermediate Algebra (13th Edition)
- Golden Ratio search Method f(x) = 2x^3 - 3x^2 - 12x + 1 Golden ratio search rules 1.If f(x) < f(x2): 1. Eliminate all x values less than x2 2. X2 becomes the new a 3. x, becomes the new x2 4. no change in b If f(x) > f(x2): 1. Eliminate all x values greater than x 2. x, becomes the new b 3. x2 becomes the new x 4. no change in aquesion=Narrow the interval in which the minimizer of the function f is located using the golden search method, starting with the initial interval (0,6], until its width is less than 2. Then, accept the midpoint of this interval as an approximate value of the minimizer of the function fand determine it. (ф=0.62)According to the question above, fill in the table below using the algorithm until the appropriate place.please write every step by step in a verry comprehensive wayarrow_forwardIn preparing for the upcoming holiday season, Fresh Toy Company (FTC) designed a new doll called The Dougie that teaches children how to dance. The fixed cost to produce the doll is $100,000. The variable cost, which includes material, labor, and shipping costs, is $31 per doll. During the holiday selling season, FTC will sell the dolls for $39 each. If FTC overproduces the dolls, the excess dolls will be sold in January through a distributor who has agreed to pay FTC $10 per doll. Demand for new toys during the holiday selling season is extremely uncertain. Forecasts are for expected sales of 60,000 dolls with a standard deviation of 15,000. The normal probability distribution is assumed to be a good description of the demand. FTC has tentatively decided to produce 60,000 units (the same as average demand), but it wants to conduct an analysis regarding this production quantity before finalizing the decision. (a) Determine the equation for computing FTC's profit for given values of the…arrow_forwardFor all integers a and b, (a + b)^4 ≡ a^4 + b^4 (mod 4).arrow_forward
- Let Χ be a real-valued character (mod k). Let k S = Σnx(n). n=1 If (a, k) = 1, ax(a)S = S (mod k). (iii) Write k = 2ºq where q is odd. Show that there is an integer a with (a, k) = 1 such that a = 3 (mod 2ª) and a = 2 (mod q). Deduce that 12S = 0 (mod k).arrow_forwardProve that (1) Σσς (α) μ(η/α) = n d/n (ii) Σσς(d) = η Σσο(α)/d d❘n d❘n (iii) σ (d) σ (n/d) = Σ d³oo(d) σo(n/d). d|n dnarrow_forwardhow to do part b,carrow_forward
- If p = 5 (mod 8), where p is prime, show that p|2 (P-1)/2 + 1. State and prove the corresponding result when p = 7 (mod 8). Deduce that 250 + 1 and 251 1 are composite. -arrow_forwardWhy the character no change for my remark?arrow_forwardIn preparing for the upcoming holiday season, Fresh Toy Company (FTC) designed a new doll called The Dougie that teaches children how to dance. The fixed cost to produce the doll is $100,000. The variable cost, which includes material, labor, and shipping costs, is $31 per doll. During the holiday selling season, FTC will sell the dolls for $39 each. If FTC overproduces the dolls, the excess dolls will be sold in January through a distributor who has agreed to pay FTC $10 per doll. Demand for new toys during the holiday selling season is extremely uncertain. Forecasts are for expected sales of 60,000 dolls with a standard deviation of 15,000. The normal probability distribution is assumed to be a good description of the demand. FTC has tentatively decided to produce 60,000 units (the same as average demand), but it wants to conduct an analysis regarding this production quantity before finalizing the decision. (a) Determine the equation for computing FTC's profit for given values of the…arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning


