
a) NaBH4 and H3O+
Interpretation:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated first with NaBH4 and then with H3O+ are to be given.
Concept introduction:
NaBH4, either in water or in alcohol reduce
To give:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated first with NaBH4 and then with H3O+.
Answer to Problem 58AP
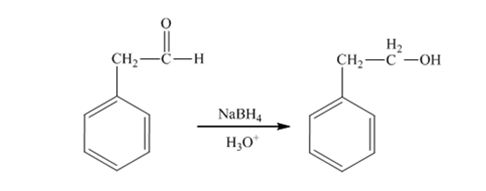
The product produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde is treated first with NaBH4 and then with H3O+ is 2-phenylethanol.
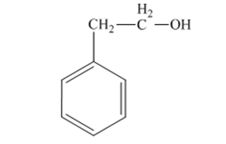
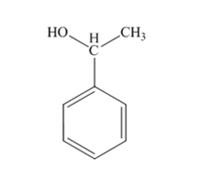
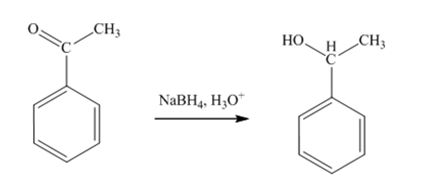
The product produced when acetophenone is treated first with NaBH4 and then with H3O+ is 1-phenylethanol.
Explanation of Solution
Phenylacetaldehyde, being an aldehyde is reduced by NaBH4 to a primary alcohol, 2-phenylethanol.
Acetophenone, being a ketone is reduced by NaBH4 to a secondary alcohol, 1-phenylethanol.
The product produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde is treated first with NaBH4 and then with H3O+ is 2-phenylethanol.

The product produced when acetophenone is treated first with NaBH4 and then with H3O+ is 1-phenylethanol.

b) Dess-Martin reagent
Interpretation:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with Dess-Martin reagent are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones are not oxidized by Dess-Martin reagent.
To give:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with Dess-Martin reagent.
Answer to Problem 58AP
Phenylacetaldehyde does not react with Dess-Martin reagent.
Acetophenone does not react with Dess-Martin reagent.
Explanation of Solution
Aldehydes and ketones are not oxidized by Dess-Martin reagent.
Phenylacetaldehyde does not react with Dess-Martin reagent.
Acetophenone does not react with Dess-Martin reagent.
c) NH2OH, HCl catalyst
Interpretation:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalyst are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones react with hydroxyl amne in the presence of an acid catalyst to yield aloximes and ketoximes respectively.
To give:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalyst.
Answer to Problem 58AP
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is
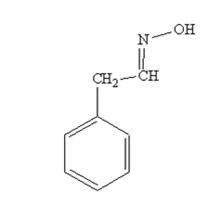
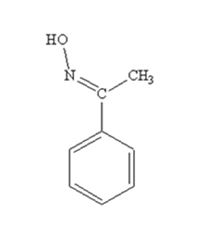
The product produced when acetophenone is treated with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is
Explanation of Solution
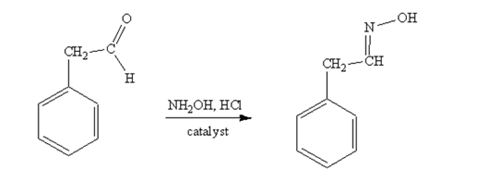
phenylacetaldehyde reacts with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalystto yield phenylacetaldoxime.
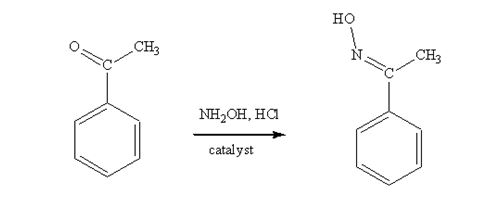
Acetophenone reacts with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalyst to give acetophenoneoxime.
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is

The product produced when acetophenone is treated with NH2OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is

d) CH3MgBr and H3O+
Interpretation:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+ are to be given.
Concept introduction:
On treatment with Grignard reagents followed by acidification, aldehydes other than formaldehyde yield secondary alcohols and ketones give tertiary alcohols.
To give:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+.
Answer to Problem 58AP
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+ is
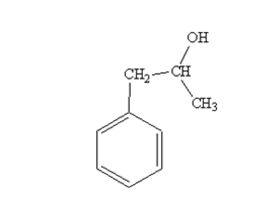
The products produced when acetophenone is treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+ is
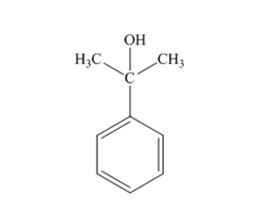
Explanation of Solution
When phenylacetaldehyde is treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+ the product produced is 1-phenyl-2-propanol, a secondary alcohol.
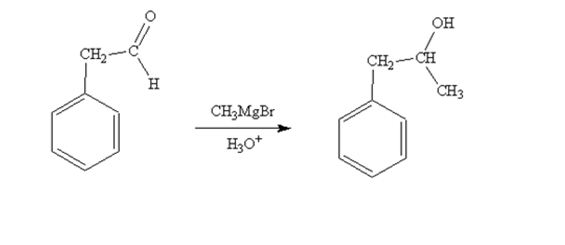
When acetophenone is treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+ the product produced is 2-phenyl-2-propanol, a tertiary alcohol.
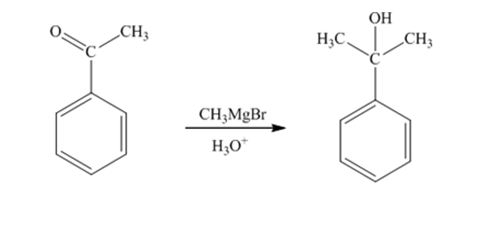
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+ is

The products produced when acetophenone is treated first with CH3MgBr and then with H3O+ is

e) CH3OH, HCl catalyst
Interpretation:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes react reversibley with two equivalents of an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst to yield acetals and ketones react to give ketals.
To give:
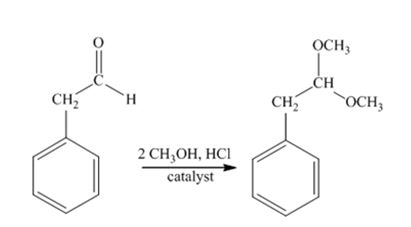
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst.
Answer to Problem 58AP
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is
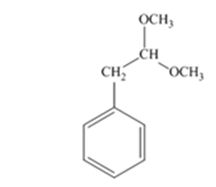
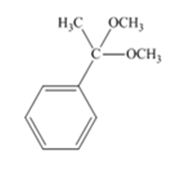
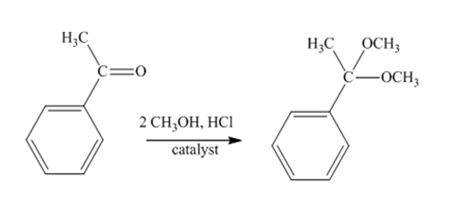
The product produced when acetophenone is treated with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is
Explanation of Solution
Phenylacetaldehyde reacts with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst to yield an acetal.
Acetophenone reacts with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst to yield a ketal.
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is

The product produced when acetophenone is treated with two equivalents of CH3OH in the presence of HCl catalyst is

f) NH2NH2, KOH
Interpretation:
The product produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with NH2NH2 in the presence of KOH are to be given.
Concept introduction:
The aldehydes and ketones undergo Wolff-Kishner reduction to yield
To give:
The product produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated first with NH2NH2 and KOH.
Answer to Problem 58AP
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with NH2NH2 and KOH is
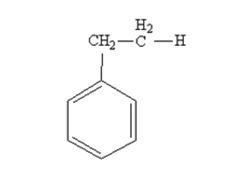
The product produced when acetophenone is treated with NH2NH2 and KOH is
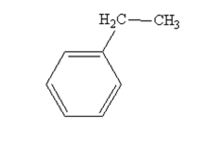
Explanation of Solution
Phenylacetaldehyde is reduced by NH2NH2 and KOH to ethylbenzene.
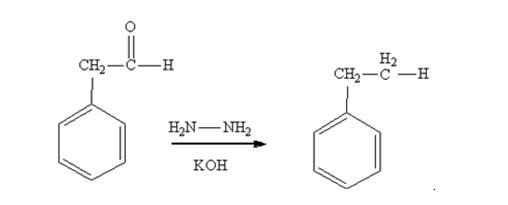
Acetophenone also is reduced by NH2NH2 and KOH to ethylbenzene.
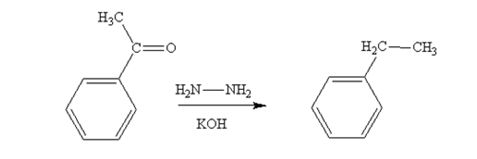
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with NH2NH2 and KOH is

The product produced when acetophenone is treated with NH2NH2 and KOH is

g) (C6H5)3P=CH2
Interpretation:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with (C6H5)3P=CH2 are to be given.
Concept introduction:
The reaction given is Wittig reaction. Aldehydes and ketones are converted into
To give:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with (C6H5)3P=CH2.
Answer to Problem 58AP
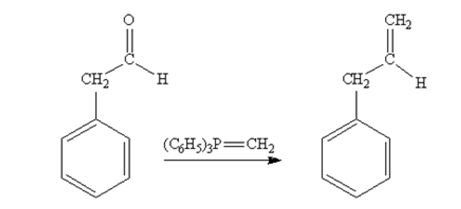
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with (C6H5)3P=CH2 is
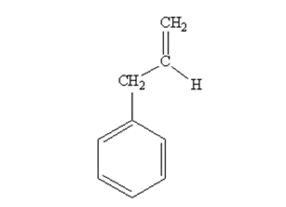
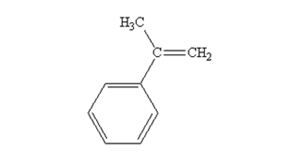
The product produced when acetophenone are treated with (C6H5)3P=CH2 is
Explanation of Solution
Phenylacetaldehyde reacts with with (C6H5)3P=CH2 to yield 3-phenylpropene.
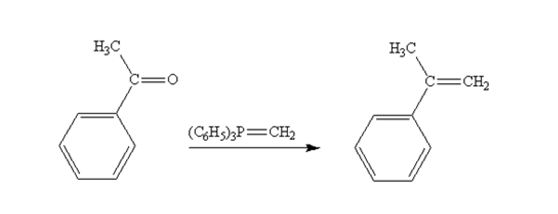
Acetophenone reacts with with (C6H5)3P=CH2 to yield 2-phenylpropene.
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with (C6H5)3P=CH2 is

The product produced when acetophenone are treated with (C6H5)3P=CH2 is

h) HCN, KCN
Interpretation:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated with HCN, KCN are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reaction.
To give:
The products produced when 1) phenylacetaldehyde and 2) acetophenone are treated first with HCN, KCN to yield their cyanohydrins.
Answer to Problem 58AP
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with HCN, KCN is
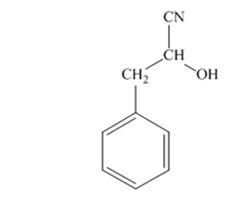
The products produced when acetophenone is treated with HCN, KCN is
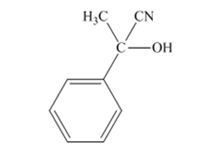
Explanation of Solution
When phenylacetaldehyde is treated with HCN, KCN, it gives phenylacetaldehydecyanohydrin.
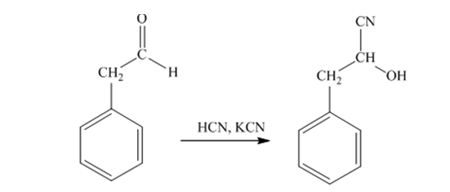
When acetophenone is treated with HCN, KCN, it gives acetophenonecyanohydrin.
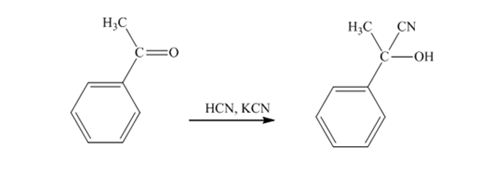
The product produced when phenylacetaldehyde is treated with HCN, KCN is

The products produced when acetophenone is treated with HCN, KCN is

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - With Access (Custom)
- Arrange the following compounds / ions in increasing nucleophilicity (least to most nucleophilic) CH3NH2 CH3C=C: CH3COO 1 2 3 5 Multiple Choice 1 point 1, 2, 3 2, 1, 3 3, 1, 2 2, 3, 1 The other answers are not correct 0000arrow_forwardcurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. using the provided starting and product structures, draw the cured electron-pushing arrows for thw following reaction or mechanistic steps. be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond making stepsarrow_forwardUsing the graphs could you help me explain the answers. I assumed that both graphs are proportional to the inverse of time, I think. Could you please help me.arrow_forward
- Synthesis of Dibenzalacetone [References] Draw structures for the carbonyl electrophile and enolate nucleophile that react to give the enone below. Question 1 1 pt Question 2 1 pt Question 3 1 pt H Question 4 1 pt Question 5 1 pt Question 6 1 pt Question 7 1pt Question 8 1 pt Progress: 7/8 items Que Feb 24 at You do not have to consider stereochemistry. . Draw the enolate ion in its carbanion form. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. ⚫ Separate multiple reactants using the + sign from the drop-down menu. ? 4arrow_forwardShown below is the mechanism presented for the formation of biasplatin in reference 1 from the Background and Experiment document. The amounts used of each reactant are shown. Either draw or describe a better alternative to this mechanism. (Note that the first step represents two steps combined and the proton loss is not even shown; fixing these is not the desired improvement.) (Hints: The first step is correct, the second step is not; and the amount of the anhydride is in large excess to serve a purpose.)arrow_forwardHi I need help on the question provided in the image.arrow_forward
- Draw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the following reaction: CH3 CH3 Et-OH Et Edit the reaction by drawing all steps in the appropriate boxes and connecting them with reaction arrows. Add charges where needed. Electron-flow arrows should start on the electron(s) of an atom or a bond and should end on an atom, bond, or location where a new bond should be created. H± EXP. L CONT. י Α [1] осн CH3 а CH3 :Ö Et H 0 N о S 0 Br Et-ÖH | P LL Farrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


