
Concept explainers
(a)
The magnitude of the velocity of the parasailer as a function of time.
Answer to Problem 11.164P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:

Length of rope is defined as,
Constant velocity of the boat is
The angle is increasing at
The velocity in radial and transverse components,
The acceleration in radial and transverse components,
Calculation:

According to given information,
Convert,
We know that,
Therefore,
According to the explanation, the relative velocity of parasailer with respect to boat is,
The relative co-ordinates of the relative velocity is equal to,
Therefore the velocity of parasailer is equal to,
We can rewrite this as,
Where,
To find the magnitude,
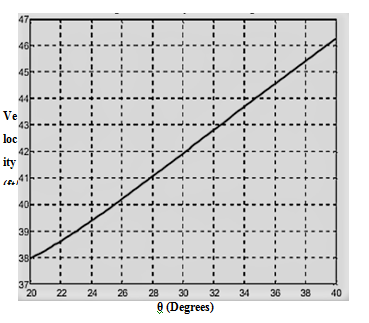
Now, plot the graph,

Conclusion:
The magnitude of velocity of the parasailer is equal to,
The relevant graph is shown above.
(b)
The magnitude of acceleration of parasailer at
Answer to Problem 11.164P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:

Length of rope is defined as,
Constant velocity of the boat is
The angle is increasing at
The velocity in radial and transverse components,
The acceleration in radial and transverse components,
Calculation:

According to given information,
Convert,
We know that,
Therefore,
According to the explanation, the relative acceleration of parasailer with respect to boat is,
The acceleration of parasailer is equal to,
At,
Therefore the magnitude is equal to,
Conclusion:
The magnitude of acceleration of the parasailer is equal to,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
- please help me to solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardplease help me to solve this problem and determine the stress for each point i like to be explained step by step with the correct answerarrow_forwardplease solve this problem for me the best way that you can explained to solve please show me the step how to solvearrow_forward
- plese solbe this problem and give the correct answer solve step by step find the forces and line actionarrow_forwardplease help me to solve this problems first write the line of action and them find the forces {fx=0: fy=0: mz=0: and them draw the shear and bending moment diagram. please explain step by steparrow_forwardplease solve this problem step by step like human and give correct answer step by steparrow_forward
- PROBLEM 11: Determine the force, P, that must be exerted on the handles of the bolt cutter. (A) 7.5 N (B) 30.0 N (C) 52.5 N (D) 300 N (E) 325 N .B X 3 cm E 40 cm cm F = 1000 N 10 cm 3 cm boltarrow_forwardUsing the moment-area theorems, determine a) the rotation at A, b) the deflection at L/2, c) the deflection at L/4. (Hint: Use symmetry for Part a (θA= - θB, or θC=0), Use the rotation at A for Parts b and c. Note that all deformations in the scope of our topics are small deformation and for small θ, sinθ=θ).arrow_forwardDistilled water is being cooled by a 20% propylene glycol solution in a 1-1/U counter flow plate and frame heat exchanger. The water enters the heat exchanger at 50°F at a flow rate of 86,000 lbm/h. For safety reasons, the water outlet temperature should never be colder than 35°F. The propylene glycol solution enters the heat exchanger at 28°F with a flow rate of 73,000 lbm/h. The port distances on the heat exchanger are Lv = 35 in and Lh = 18 in. The plate width is Lw = 21.5 2 in. The plate thickness is 0.04 in with a plate pitch of 0.12 in. The chevron angle is 30° and the plate enlargement factor is 1.17. All ports have a 2 in diameter. The fouling factor of the propylene glycol solution can be estimated as 2 ×10−5 h-ft2-°F/Btu. a. Determine the maximum number of plates the heat exchanger can have while ensuring that the water outlet temperature never drops below 35°F. b. Determine the thermal and hydraulic performance of the heat exchanger with the specified number of plates.…arrow_forward
- Liquid pentane is flowing in the shell of a shell and tube heat exchanger at a rate of 350,000lbm/hr and an average temperature of 20°F. The shell has a diameter of 27 in and a length of 16ft. The tubes in the heat exchanger are ¾-in 15 BWG tubes on a 1-in triangular pitch. The purposeof this problem is to investigate how the number of baffles impacts the heat transfer and thepressure drop on the shell side of the heat exchanger. Calculate the shell-side convective heattransfer coefficient and pressure drop for the case where the heat exchanger has 10 baffles. Repeatthe calculation for 20 baffles. Then determine thea. Ratio of the shell-side convective heat transfer coefficient for the 20-baffle heat exchangerto the 10-baffle heat exchangerb. Ratio of the shell-side pressure drop for the 20-baffle heat exchanger to the 10-baffle heatexchangerc. If the optimum baffle spacing is somewhere between 0.4Ds and 0.6Ds, how many baffleswould you recommend for this heat exchanger? What are the…arrow_forwardThe evaporator of a vapor compression refrigeration cycle utilizing R-123 as the refrigerant isbeing used to chill water. The evaporator is a shell and tube heat exchanger with the water flowingthrough the tubes. The water enters the heat exchanger at a temperature of 54°F. The approachtemperature difference of the evaporator is 3°R. The evaporating pressure of the refrigeration cycleis 4.8 psia and the condensing pressure is 75 psia. The refrigerant is flowing through the cycle witha flow rate of 18,000 lbm/hr. The R-123 leaves the evaporator as a saturated vapor and leaves thecondenser as a saturated liquid. Determine the following:a. The outlet temperature of the chilled waterb. The volumetric flow rate of the chilled water (gpm)c. The UA product of the evaporator (Btu/h-°F)d. The heat transfer rate between the refrigerant and the water (tons)arrow_forwardThe blade support of a hacksaw is subject to compression when a blade is installed and tightened. What is the state of stress (total combined stress) at A in MPa if the compression in the support is 1,524 N. Note: pay close attention to what is compression and what is tension and use a negative sign for the former. 100 mm 8 mm 3 mm 75 mm A 8 mm 3 mm B 50 mmarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





