
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given compound
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structure:
The representation of valence shell electrons around the atom is known as Lewis structure or Lewis dot structure. Electrons are represented as a dot in Lewis structures, a single dot represents unpaired electron and paired of dots represents paired electrons.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound,
The total number of valence electrons in
The skeletal structure of
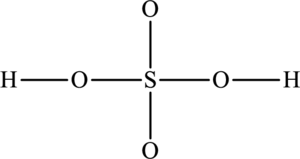
The total number of 12 electrons are used for bonding. Remaining 22 electrons can be distributed over oxygen atoms to get the octet.
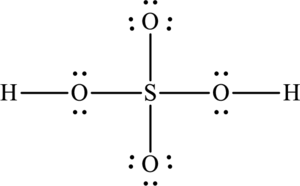
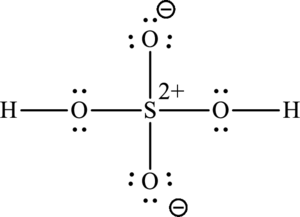
The Lewis structure of compound showing charges can be given as follows:
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given compound
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a)
(b)
Explanation of Solution
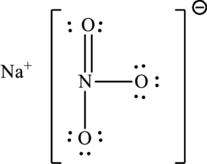
Given compound,
The total number of valence electrons in
The skeletal structure of
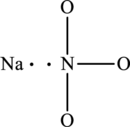
The total number of 8 electrons are used for bonding. Remaining 16 electrons can be distributed over oxygen atoms to get the octet.
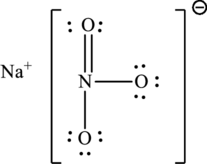
The Lewis structure of compound showing charges can be given as follows:
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given compound
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a)
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound,
The total number of valence electrons in
The skeletal structure of
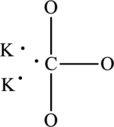
The total number of 6 electrons are used for bonding. Remaining 18 electrons can be distributed over oxygen atoms to get the octet.
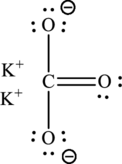
The Lewis structure of compound showing charges can be given as follows:
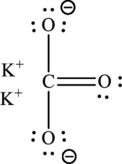
(d)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given compound
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a)
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound,
The total number of valence electrons in
The skeletal structure of
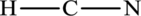
The total number of four electrons are used for bonding. Remaining 6 electrons can be distributed over nitrogen and carbon atoms to get the octet.
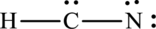
The Lewis structure of compound showing charges can be given as follows:
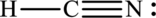
(e)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given compound
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a)
(e)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound,
The total number of valence electrons in
The skeletal structure of
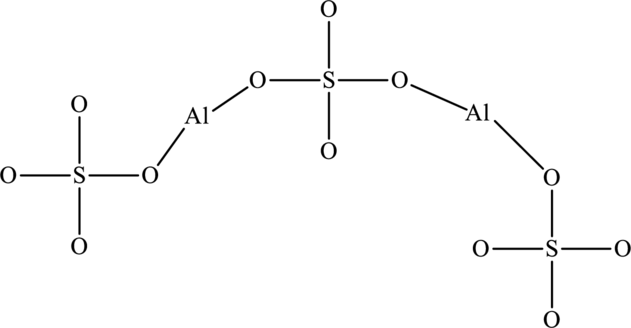
The total number of 32 electrons are used for bonding. Remaining 64 electrons can be distributed over oxygen atoms to get the octet.
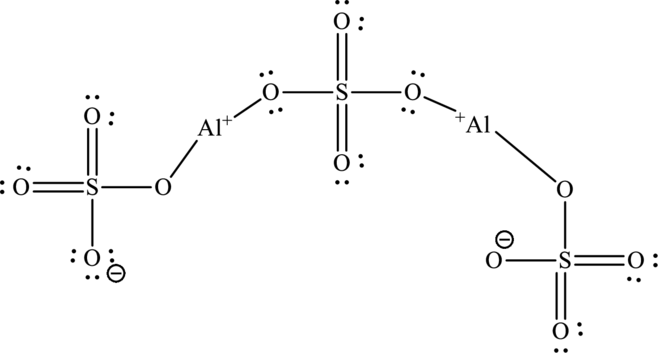
The Lewis structure of compound showing charges can be also be represented as follows:
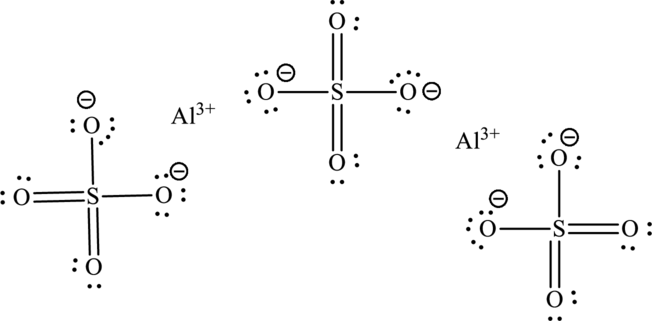
(f)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the given compound
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a)
(f)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound,
The total number of valence electrons in
The skeletal structure of
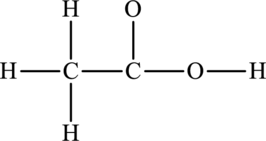
The total number of 14 electrons are used for bonding. Remaining 10 electrons can be distributed over oxygen and carbon atoms to get the octet.
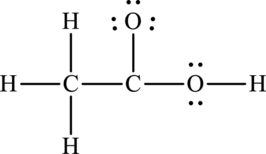
Here octet of carbon attached to oxygen is not completed. Therefore, the Lewis structure of compound can be given as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
FOUNDATIONS OF COLLEGE CHEM +KNEWTONALTA
- What is single-point calibration? Provide an example.arrow_forwardDraw the major product formed via an E1 pathway.arrow_forwardPart 9 of 9 Consider the products for the reaction. Identify the major and minor products. HO Cl The E stereoisomer is the major product and the Z stereoisomer is the minor product ▼ S major product minor productarrow_forward
- Consider the reactants below. Answer the following questions about the reaction mechanism and products. HO Clarrow_forwardjulietteyep@gmail.com X YSCU Grades for Juliette L Turner: Orc X 199 A ALEKS - Juliette Turner - Modul X A ALEKS - Juliette Turner - Modul x G butane newman projection - Gox + www-awa.aleks.com/alekscgi/x/Isl.exe/10_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IBxzaplnN4HsoQggFsejpgqKoyrQrB2dKVAN-BcZvcye0LYa6eXZ8d4vVr8Nc1GZqko5mtw-d1MkNcNzzwZsLf2Tu9_V817y?10Bw7QYjlb il Scribbr citation APA SCU email Student Portal | Main Ryker-Learning WCU-PHARM D MySCU YSCU Canvas- SCU Module 4: Homework (Ch 9-10) Question 28 of 30 (1 point) | Question Attempt: 1 of Unlimited H₂SO heat OH The mechanism of this reaction involves two carbocation intermediates, A and B. Part 1 of 2 KHSO 4 rearrangement A heat B H₂O 2 OH Draw the structure of A. Check Search #t m Save For Later Juliet Submit Assignm 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessarrow_forwardThe electrons flow from the electron-rich atoms of the nucleophile to the electrons poor atoms of the alkyl halide. Identify the electron rich in the nucleophile. Enter the element symbol only, do not include any changes.arrow_forward
- Hello, I am doing a court case analysis in my Analytical Chemistry course. The case is about a dog napping and my role is prosecution of the defendant. I am tasked in the Area of Expertise in Neutron Activation and Isotopic Analysis. Attached is the following case study reading of my area of expertise! The landscaping stone was not particularly distinctive in its decoration but matched both the color and pattern of the Fluential’s landscaping stone as well as the stone in the back of the recovered vehicle. Further analysis of the stone was done using a technique called instrumental neutron activation analysis. (Proceed to Neutron Activation data) Photo Notes: Landscaping stone recovered in vehicle. Stone at Fluential’s home is similar inappearance. Finally, the white paint on the brick was analyzed using stable isotope analysis. The brick recovered at the scene had smeared white paint on it. A couple of pieces of brick in the back of the car had white paint on them. They…arrow_forwardCite the stability criteria of an enamine..arrow_forwardCalculate the pH of a 0.01m solution of acetic acid use pka of 4.75arrow_forward
- What is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
