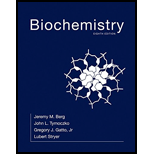
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of D-Allose: Epimeric at C-3 should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Carbohydrates are a large group of organic compounds that are present in foods, living tissues. These include sugars, cellulose, and starch. Anomers are the glycosides or cyclic monosaccharides that are epimers. These are different from each other in the configuration of C-1 (aldoses) or at C-2 if (ketoses).
Answer to Problem 6P
The structure of D-Allose:
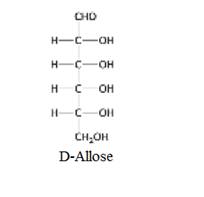
Explanation of Solution
When two sugars vary in their configuration around one carbon atom then those sugars are known as epimers of each other.
The structure of D-Allose: Epimeric at C-3 is given below:
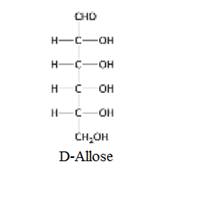
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of D-Altrose: Isomeric at C-2 and C-3 should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Carbohydrates are a large group of organic compounds that are present in foods, living tissues. These include sugars, cellulose, and starch. These are comprised of hydrogen and oxygen in a similar ratio as in water (2:1). They are usually broken down to release the energy in the animal body. These are of three types: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Answer to Problem 6P
The structure of D-Altrose:
Explanation of Solution
Glucose is an aldose as it contains one
The structure of D-Altrose: Isomeric at C-2 and C-3 is given below:
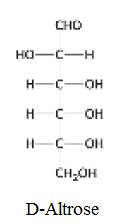
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of D-Mannose: Eplmeric at C-2 should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Carbohydrates are a large group of organic compounds that are present in foods, living tissues. These include sugars, cellulose, and starch. These are comprised of hydrogen and oxygen in a similar ratio as in water (2:1). They are usually broken down to release the energy in the animal body. These are of three types: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Answer to Problem 6P
The structure of D-Mannose:
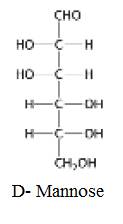
Explanation of Solution
Anomers are the glycosides or cyclic monosaccharides that are epimers. These are different from each other in the configuration of C-1 (aldoses) or at C-2 if (ketoses). In a pair of anomers, the anomer containing the alkoxy group or hydroxy group is pointing up on the anomeric carbon is known as the ß-anomer.
The structure of D-Mannose: Eplmeric at C-2 is given below:
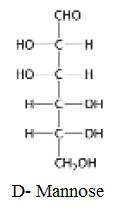
(d)
Interpretation:
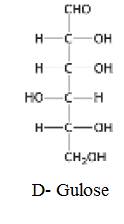
The structure of D- Gulose: Isomeric at C-3 and C-4
should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Carbohydrates are a large group of organic compounds that are present in foods, living tissues. These include sugars, cellulose, and starch. These are comprised of hydrogen and oxygen in a similar ratio as in water (2:1). They are usually broken down to release the energy in the animal body. These are of three types: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Answer to Problem 6P
The structure of D- Gulose:
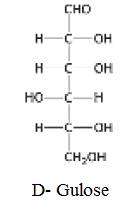
Explanation of Solution
Glucose is an aldose as it contains one aldehyde group per molecule in its acyclic form. Mannose is a sugar of the hexose group. It occurs as a constituent of several natural polysaccharides.
The structure of D- Gulose: Isomeric at C-3 and C-4 is given below:
(e)
Interpretation:
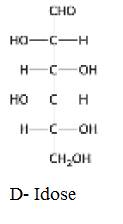
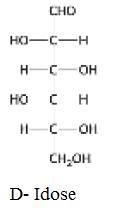
The structure of D-Idose: Isomeric at C-2, C-3, and C-4 should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Carbohydrates are a large group of organic compounds that are present in foods, living tissues. These include sugars, cellulose, and starch. These are comprised of hydrogen and oxygen in a similar ratio as in water (2:1). They are usually broken down to release the energy in the animal body. These are of three types: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Answer to Problem 6P
The structure of D-Idose:
Explanation of Solution
Glucose is an aldose as it contains one aldehyde group per molecule in its acyclic form. Mannose is a sugar of the hexose group. It occurs as a constituent of several natural polysaccharides.
The structure of D-Idose: Isomeric at C-2, C-3, and C-4 is given below:
(f)
Interpretation:
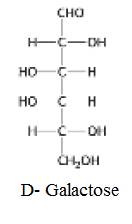
The structure of D-Galactose: Epimeric at C-4 should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Carbohydrates are a large group of organic compounds that are present in foods, living tissues. These include sugars, cellulose, and starch. These are comprised of hydrogen and oxygen in a similar ratio as in water (2:1). They are usually broken down to release the energy in the animal body. These are of three types: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Answer to Problem 6P
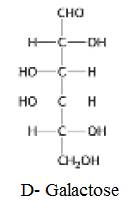
The structure of D-Galactose:
Explanation of Solution
Glucose is an aldose as it contains one aldehyde group per molecule in its acyclic form. When two sugars vary in their configuration around one carbon atom then those sugars are known as epimers of each other.
The structure of D-Galactose: Epimeric at C-4 is given below:
(g)
Interpretation:
The structure of D-Talose: Isomeric at C-2 and C-4 should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Carbohydrates are a large group of organic compounds that are present in foods, living tissues. These include sugars, cellulose, and starch. These are comprised of hydrogen and oxygen in a similar ratio as in water (2:1). They are usually broken down to release the energy in the animal body. These are of three types: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Answer to Problem 6P
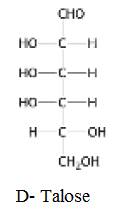
The structure of D-Talose:
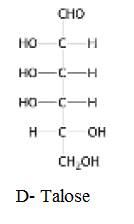
Explanation of Solution
Glucose is an aldose as it contains one aldehyde group per molecule in its acyclic form. When two sugars vary in their configuration around one carbon atom then those sugars are known as epimers of each other.
The structure of D-Talose: Isomeric at C-2 and C-4 is given below:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Biochemistry
- 2. Which one is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction sequence? HO A OH 1. NaOEt, EtOH 1. LiAlH4 EtO OEt 2. H3O+ 2. H3O+ OH B OH OH C -OH HO -OH OH D E .CO₂Etarrow_forwardwhat is a protein that contains a b-sheet and how does the secondary structure contributes to the overall function of the protein.arrow_forwarddraw and annotate a b-sheet and lable the hydrogen bonding. what is an example that contains the b-sheet and how the secondary structure contributes to the overall function of your example protein.arrow_forward
- Four distinct classes of interactions (inter and intramolecular forces) contribute to a protein's tertiary and quaternary structures. Name the interaction then describe the amino acids that can form this type of interaction. Draw and annotate a diagram of the interaction between two amino acids.arrow_forwardExamine the metabolic pathway. The enzymes that catalyze each step are identified as "e" with a numeric subscript. e₁ e3 e4 A B с 1° B' 02 e5 e6 e7 E F Which enzymes catalyze irreversible reactions? ப e ez ☐ ez e4 ☐ ப es 26 5 e7 Which of the enzymes is likely to be the allosteric enzyme that controls the synthesis of G? €2 ез e4 es 26 5 e7arrow_forwardAn allosteric enzyme that follows the concerted model has an allosteric coefficient (T/R) of 300 in the absence of substrate. Suppose that a mutation reversed the ratio. Select the effects this mutation will have on the relationship between the rate of the reaction (V) and substrate concentration, [S]. ㅁㅁㅁ The enzyme would likely follow Michaelis-Menten kinetics. The plot of V versus [S] would be sigmoidal. The enzyme would mostly be in the T form. The plot of V versus [S] would be hyperbolic. The enzyme would be more active.arrow_forward
- Penicillin is hydrolyzed and thereby rendered inactive by penicillinase (also known as ẞ-lactamase), an enzyme present in some penicillin-resistant bacteria. The mass of this enzyme in Staphylococcus aureus is 29.6 kDa. The amount of penicillin hydrolyzed in 1 minute in a 10.0 mL. solution containing 1.00 x 10 g of purified penicillinase was measured as a function of the concentration of penicillin. Assume that the concentration of penicillin does not change appreciably during the assay. Plots of V versus [S] and 1/V versus 1/[S] for these data are shown. Vo (* 10 M minute"¹) 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 20 1.0 0.0 о 10 20 30 1/Vo (* 10 M1 minute) 20 103 90 BO 70 50 [S] (* 100 M) 40 50 60 y=762x+1.46 × 10" [Penicillin] (M) Amount hydrolyzed (uM) 1 0.11 3 0.25 5 0.34 10 0.45 30 0.58 50 0.61arrow_forwardConsider the four graphs shown. In each graph, the solid blue curve represents the unmodified allosteric enzyme and the dashed green curve represents the enzyme in the presence of the effector. Identify which graphs correctly illustrate the effect of a negative modifier (allosteric inhibitor) and a positive modifier (allosteric activator) on the velocity curve of an allosteric enzyme. Place the correct graph in the set of axes for each type of modifier. Negative modifier Reaction velocity - Positive modifier Substrate concentration - Reaction velocity →→→→ Substrate concentration Answer Bankarrow_forwardConsider the reaction: phosphoglucoisomerase Glucose 6-phosphate: glucose 1-phosphate After reactant and product were mixed and allowed to reach at 25 °C, the concentration of each compound at equilibrium was measured: [Glucose 1-phosphate] = 0.01 M [Glucose 6-phosphate] = 0.19 M Calculate Keq and AG°'. Код .0526 Incorrect Answer 7.30 AG°' kJ mol-1 Incorrect Answerarrow_forward
- Classify each phrase as describing kinases, phosphatases, neither, or both. Kinases Phosphatases Neither Both Answer Bank transfer phosphoryl groups to acidic amino acids in eukaryotes may use ATP as a phosphoryl group donor remove phosphoryl groups from proteins catalyze reactions that are the reverse of dephosphorylation reactions regulate the activity of other proteins catalyze phosphorylation reactions PKA as an example turn off signaling pathways triggered by kinasesarrow_forwardConsider the reaction. kp S P kg What effects are produced by an enzyme on the general reaction? AG for the reaction increases. The rate constant for the reverse reaction (kr) increases. The reaction equilibrium is shifted toward the products. The concentration of the reactants is increased. The activation energy for the reaction is lowered. The formation of the transition state is promoted.arrow_forwardThe graph displays the activities of wild-type and several mutated forms of subtilisin on a logarithmic scale. The mutations are identified as: • The first letter is the one-letter abbreviation for the amino acid being altered. • The number identifies the position of the residue in the primary structure. ⚫ The second letter is the one-letter abbreviation for the amino acid replacing the original one. • Uncat. refers to the estimated rate for the uncatalyzed reaction. Log₁(S-1) Wild type S221A H64A -5 D32A S221A H64A D32A -10 Uncat. How would the activity of a reaction catalyzed by a version of subtilisin with all three residues in the catalytic triad mutated compare to the activity of the uncatalyzed reaction? It would have more activity, because the reaction catalyzed by the triple mutant is approximately three-fold faster than the uncatalyzed reaction. It would have less activity, because the reaction catalyzed by the triple mutant is approximately 1000-fold slower than the…arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning





