
Concept explainers
MCAT-Style Passage Problems
Kangaroo Locomotion

Kangaroos have very stout tendons in their legs that can be used to store energy. When a kangaroo lands on its feet, the tendons stretch, transforming kinetic energy of motion to elastic potential energy. Much of this energy can be transformed back into kinetic energy as the kangaroo takes another hop. The kangaroo’s peculiar hopping gait is not very efficient at low speeds but is quite efficient at high speeds.
Figure P11.68 shows the energy cost of human and kangaroo locomotion. The graph shows oxygen uptake (in mL/s) per kg of body mass, allowing a direct comparison between the two species.
Figure P11.68 Oxygen uptake (a measure of energy use per second) for a running human and a hopping kangaroo.
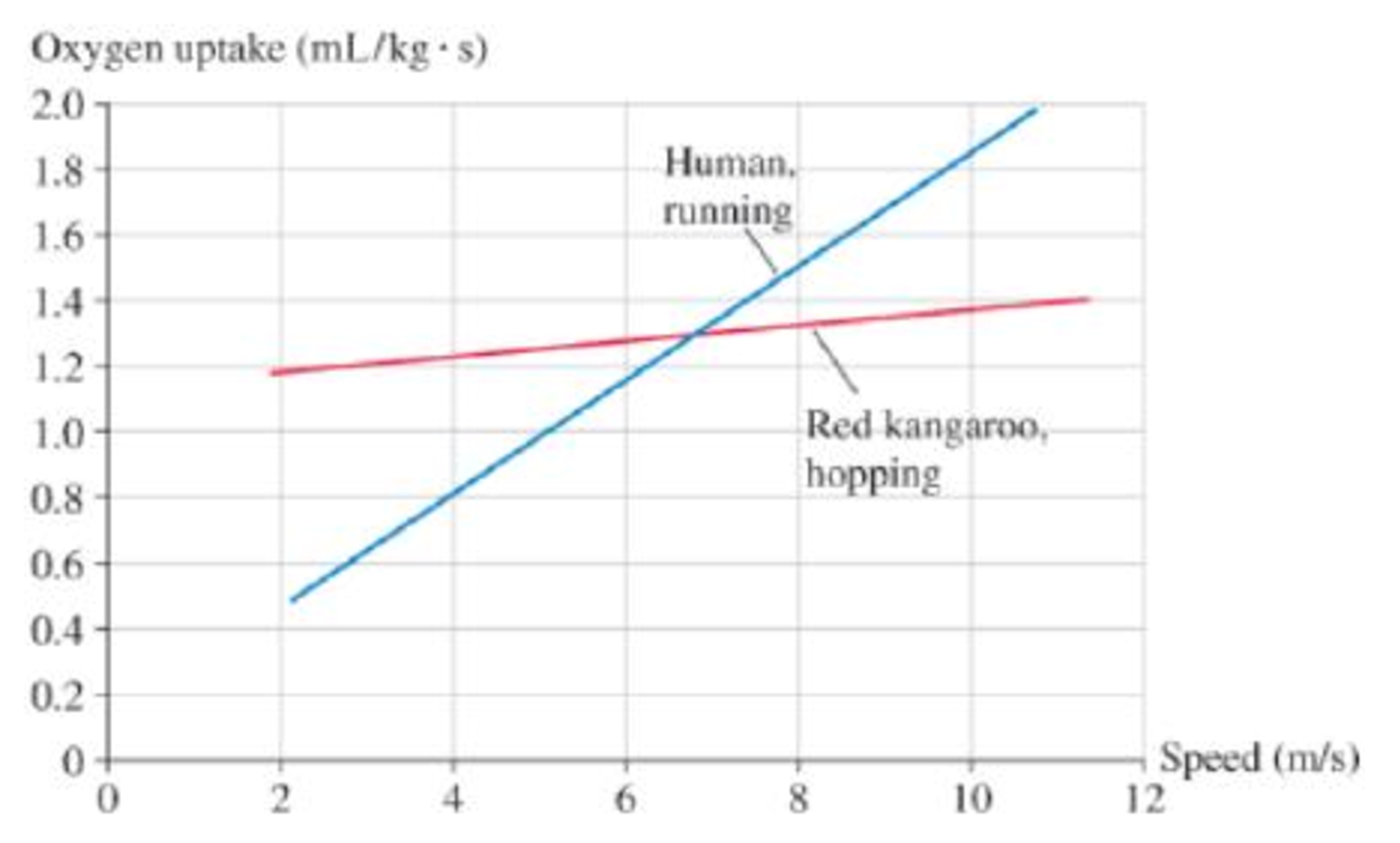
For humans, the energy used per second (i.e., power) is proportional to the speed. That is, the human curve nearly passes through the origin, so running twice as fast takes approximately twice as much power. For a hopping kangaroo, the graph of energy use has only a very small slope. In other words, the energy used per second changes very little with speed. Going faster requires very little additional power. Treadmill tests on kangaroos and observations in the wild have shown that they do not become winded at any speed at which they are able to hop. No matter how fast they hop, the necessary power is approximately the same.
A person runs 1 km. How does his speed affect the total energy needed to cover this distance?
A. A faster speed requires less total energy.
B. A faster speed requires more total energy.
C. The total energy is about the same for a fast speed and a slow speed.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- In general it is best to conceptualize vectors as arrows in space, and then to make calculations with them using their components. (You must first specify a coordinate system in order to find the components of each arrow.) This problem gives you some practice with the components. Let vectors A = (1,0, −3), B = (-2, 5, 1), and C = (3,1,1). Calculate the following, and express your answers as ordered triplets of values separated by commas.arrow_forwardOnly Part C.) is necessaryarrow_forwardOnly Part B.) is necessaryarrow_forward
- A (3.60 m) 30.0°- 70.0° x B (2.40 m)arrow_forwardIn general it is best to conceptualize vectors as arrows in space, and then to make calculations with them using their components. (You must first specify a coordinate system in order to find the components of each arrow.) This problem gives you some practice with the components. Let vectors A = (1,0, -3), B = (-2, 5, 1), and C = (3,1,1). Calculate the following, and express your answers as ordered triplets of values separated by commas.arrow_forwardfine the magnitude of the vector product express in sq meters what direction is the vector product in -z or +zarrow_forward
- 4) Three point charges of magnitude Q1 = +2.0 μC, Q2 = +3.0 μС, Q3 = = +4.0 μС are located at the corners of a triangle as shown in the figure below. Assume d = 20 cm. (a) Find the resultant force vector acting on Q3. (b) Find the magnitude and direction of the force. d Q3 60° d Q1 60° 60° Q2 darrow_forwardThree point charges of magnitudes Q₁ = +6.0 μС, Q₂ = −7.0 μС, Qз = −13.0 μC are placed on the x-axis at x = 0 cm, x = 40 cm, and x = 120 cm, respectively. What is the force on the Q3 due to the other two charges?arrow_forwardTwo point charges of +30.0 μС and -9.00 μC are separated by a distance of 20.0 cm. What is the intensity of electric field E midway between these two charges?arrow_forward
- Two point charges of +7.00 μС and +10.0 μС are placed inside a cube of edge length 0.100 m. What is the net electric flux due to these charges?arrow_forwardA conducting hollow sphere has a charge density of σ = 12.2 μC/m². If the sphere has a radius of 25 cm, what net charge is on the sphere?arrow_forward9) Consider an electric field right Ĕ = 21+3ĵ. What is the magnitude of the flux of this field through a 4.0 m² square surface whose corners are located at (x,y,z) = (0, 2, 1), (2, 2, 1), (2, 2, −1), (0, 2, −1)? Ꮓ ту x (0,2,1) Surface 2 Surface (2,2,1) y Ē (0,2,-1) (2,2,-1) 2 xarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
 An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





