
Concept explainers
Suggest reasonable explanations for each of the following observations:
The first-order rate constant for solvolysis of
After a solution of
in aqueous sulfuric acid had been allowed to stand for
and
Treatment of
with hydrogen bromide gave the same mixture of
Treatment of
The major product in parts (c) and (d) was
Interpretation:
The reasonable explanations for each of the given observations are to be suggested.
Concept introduction:
The allyl group contains the unit
In substitution reactions, allylic halides react faster than the corresponding alkyl halides.
The primary or secondary allylic carbocations are less stable than tertiary allylic carbocations.
In allylic carbocations that are not symmetrically substituted, the two resonance structures are not equivalent and do not contribute equally to the resonance hybrid. A more stable resonance form contributes more to the resonance hybrid.
Two non-equivalent resonance forms of the allylic carbocation yield two different products.
Reactions that occur via
The regioselectivity of an
A more substituted alkene is stable and forms more readily than a less substituted alkene.
Answer to Problem 52P
Solution:
a) Resonance stabilization of the carbocation formed by the removal of chloride ion from
b) The resonance stabilization of the carbocation formed by the reaction of
c) The resonance stabilization of the carbocation formed by the reaction of
d) The resonance stabilization of the carbocation formed by the reaction of both
e)
Explanation of Solution
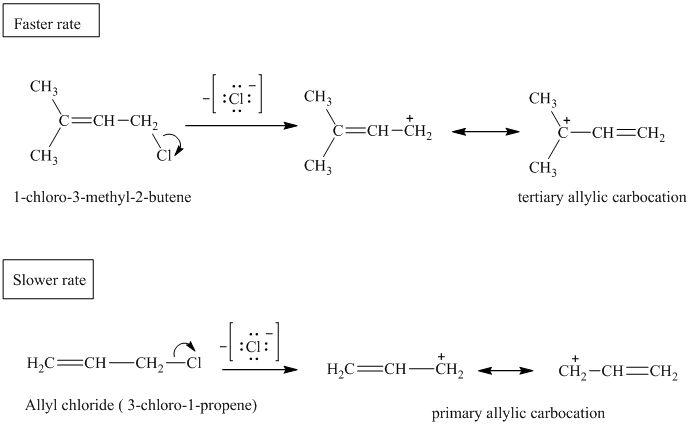
a) The comparison of rate constant of solvolysis of the given allylic chlorides.
The expanded structures for the two given allylic chlorides are shown below:
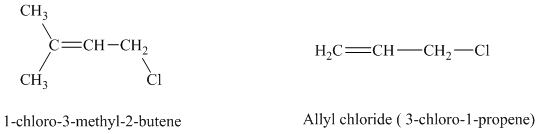
Both the allylic chlorides follow the
b) Reaction of
The expanded structure for
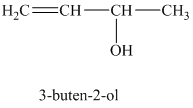
When a solution of
c) Treatment of the given compound with hydrogen bromide.
The structure for
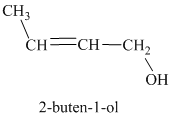
When
resonance stabilized. However, the two resonance forms for this allylic carbocation are not equivalent. Each allylic carbocation will undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction to form two different allylic bromides as shown below.
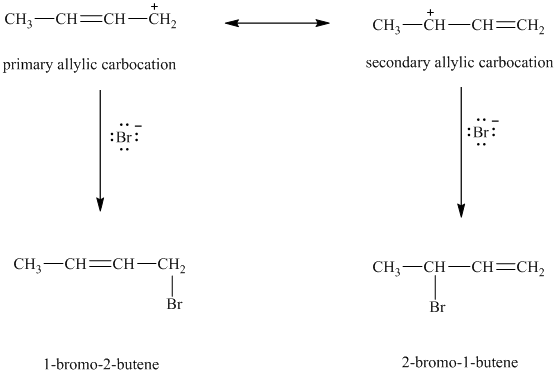
d) Treatment of
The structure for
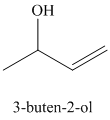
When
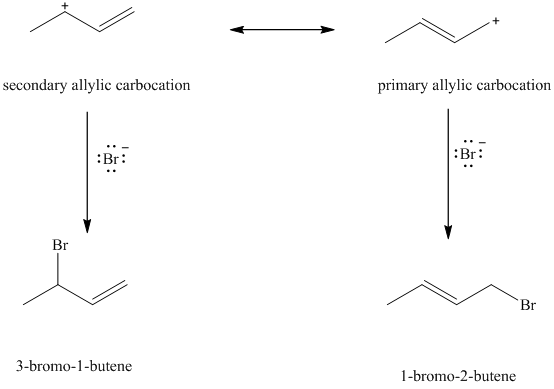
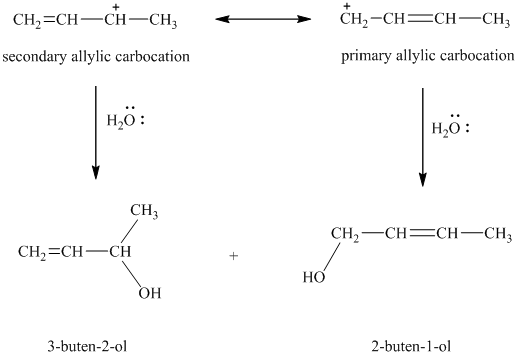
e) Major products obtained in part (c) and (d).
The products obtained in part (c) and (d) are as follows:
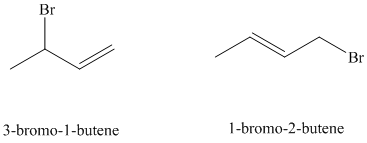
This is because this reaction follows
The major product formed in the reaction is governed by the fact that a more substituted alkene is stable and forms readily than a less substituted alkene. The bromine atom bonds to the carbon that carries the positive charge, giving
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-W/SOLN.>CUSTOM<
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Organic Chemistry
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
- What is the formula of the compound 3-isopropylcyclopentane-1-carbonyl chloride?arrow_forwardIndicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COONa (Sodium acetoacetate) and BrCH2COOC2H5arrow_forwardIndicate whether the product of the reaction between Naphthalene and CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºC is 1,4 naphthoquinone or phthalic anhydride.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products of the reaction between CH3COCH2COOC2H5 and Na+-OC2H5.arrow_forwardPrimary, Secondary, and Tertiary Alcohols O-H O-H O-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-H R₁-C-R₁ H R₂ R₂ Primary Alcohol Secondary Alcohol ChemistryLearner.com R stands for Carbon group like ethyl methyl propyl Tertiary Alcohol If 1 carbon group with two H attached to alcoholic carbon, then primary If 2 carbon group and 1 H are attached to alcoholic carbon, then secondary IF 3 carbon group and no H attach to alcoholic carbon then tertiary. The bottom line Starting "Weak" oxidant material PCC, DMP, Swern, etc Primary alcohol Aldehyde OH Secondary alcohol Ketone OH "Strong" oxidant KMnO4, H₂CrO4 (or equivalent) OH Carboxylic acid 요 Ketone No reaction No reaction Tertiary alcohol 1. Is ethanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of ethanol and any oxidation products of ethanol. If there is more than one oxidation product, give the structure of each of the products. 2. Is 2-propanol a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol? Write out the structures of 2-propanol and any…arrow_forwardFormulate the reaction: Naphthalene with CrO3 in acetic acid at 25ºCarrow_forward
- Complete the following equations please hand written pleasearrow_forwardUsing the Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 3+ 3Cu²+ (aq) +2Al(s) → 3 Cu(s)+2A1³* (aq) 2+ Suppose the cell is prepared with 5.29 M Cu in one half-cell and 2.49 M A1³+ in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. x10 μ ☑ 00. 18 Ar Иarrow_forwardPlease help me solve this homework problemarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
