
Concept explainers
Interpretation: A real estate firm wishes to open four new offices in Boston area and they are having six potential sites available. Based on the number of employees in each office and the location of the properties that each employee will manage, the firm estimated the total travel time in hours per day for each office and each location. The optimal assignment of offices to sites to minimize employee travel time needs to be determined.
| Offices | |||||
| A | B | C | D | ||
| 1 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 8 | |
| 2 | 13 | 5 | 2 | 6 | |
| Sites | 3 | 12 | 9 | 9 | 4 |
| 4 | 14 | 2 | 7 | 7 | |
| 5 | 17 | 7 | 4 | 3 | |
| 6 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 5 | |
Concept Introduction: A discrete facility location problem is considered, when a balance has to be achieved between the minimum and maximum number of customers, wherein there is a difference that arises between the allocation of these customers made to every plant.
Answer to Problem 46AP
The optimal travel time has been derived as 17.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Offices | |||||
| A | B | C | D | ||
| 1 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 8 | |
| 2 | 13 | 5 | 2 | 6 | |
| Sites | 3 | 12 | 9 | 9 | 4 |
| 4 | 14 | 2 | 7 | 7 | |
| 5 | 17 | 7 | 4 | 3 | |
| 6 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 5 | |
When there are no inter-departmental interactions and a discrete set of alternative locations could be considered, then assignment problems can be considered to be appropriate. Following are the procedure for solution for assignment problems:
- The smallest number in row 1 needs to be identified and it should be subtracted from all the entries in that row. This procedure needs to be repeated for all the rows in cost matrix.
- Similarly, the smallest number in column 1 needs to be identified and it should be subtracted from all the entries in column 1. This procedure needs to be repeated for all the columns in cost matrix.
- At a certain point, each column and each row will have at least a zero. If there is possibility for making a zero assignment, then the same can be done, which in turn will be the optimal solution, and if not, then proceed to the next step.
- The maximum number of zero cost assignments needs to be determined, which will be equal to smallest number of lines adequate to cover all zeros. These lines are not necessarily unique and are found by inspection. The number of lines drawn should be less than the maximum number of zero cost assignments.
- The smallest uncovered number should be identified and proceed with the following steps:
- Subtract smallest uncovered number from all the other uncovered numbers.
- Add this to the step at the point where the line crosses.
- Return back to step 3
Step 1: The below shown matrix, not being a square matrix, dummy rows to balance the sites and offices are added.
| Offices | ||||
| Sites | A | B | C | D |
| 1 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 8 |
| 2 | 13 | 5 | 2 | 6 |
| 3 | 12 | 9 | 9 | 4 |
| 4 | 14 | 2 | 7 | 7 |
| 5 | 17 | 7 | 4 | 3 |
| 6 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 5 |
By adding the dummy rows the matrix has been modified as shown below:
| Offices | ||||||
| Sites | A | B | C | D | E | F |
| 1 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 13 | 5 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 12 | 9 | 9 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 14 | 2 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 17 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
Step 2: The row reducing matrix needs to be performed by subtracting the smallest number from each row. Since in this case, the resultant zero assignment has been achieved for each office, further column reduction matrix is not performed.
| Offices | ||||||
| Sites | A | B | C | D | E | F |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 2 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
Step 3: From each site identifying of the zero assignment gives the following matrix
| Offices | ||||||
| Sites | A | B | C | D | E | F |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| 3 | 2 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 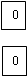 | 0 |
| 4 | 4 | 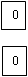 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 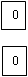 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 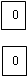 |
Thus the optimal solution for travel time will be
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS ANALYSIS
- There was a most recent poll for which 571 adults that flew in the past year had info collected. This info was their number 1 complaints about flying. A - small cramped seat - 45 complaints B - cost - 18 complaints C - fear or dislike - 81 complaints D - security - 123 complaints E - Poor service - 12 complaints F - Conntected flight issue - 8 complaints G - overcrowded - 41 complaints H - Late and wait - 81 complaints I - Food - 5 complaints J - Lost/missing luggage - 5 complaints K - Other - 51 complaints What percentage of those surveyed found nothing they didnt dislike?arrow_forwardCan you help me with this, and explain what a product by value analysis is? Thanks in advancearrow_forwardOperations Management Questionarrow_forward
- can you explain and breakdown the "ATB: digital disruption in the parking meter industry" case in detail outlining the key issuesarrow_forwardAt Quick Car Wash, the wash process is advertised to take less than 6 minutes. Consequently, management has set a target average of 330 seconds for the wash process. Suppose the average range for a sample of 7 cars is 10 seconds. Use the accompanying table to establish control limits for sample means and ranges for the car wash process. Click the icon to view the table of factors for calculating three-sigma limits for the x-chart and R-chart. The UCLR equals seconds and the LCLR equals seconds. (Enter your responses rounded to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardIf Jeremy who is the VP for the operations, proceeds with their existing prototype (which is option a), the firm can then expect sales to be 120,000 units at $550 each. And with a probability of 0.52 and a 0.48 probability of 65,000 at $550. we However, he uses his value analysis team (option b), the firm expects sales of 75,000 units at $770, with a probability of 0.78 and a 0.22 probability of 65,000 units at $770. Value engineering, at a cost of $100,000, is only used in option b. Which option for this has the highest expected monetary value (EMV)? The EMV for option a is $? The EMV for option b is $? Which has the highest expected monetary value. A or B?arrow_forward
- Part 1 of 2 Jim's Outfitters, Inc., makes custom western shirts. The shirts could be flawed in various ways, including flaws in the weave or color of the fabric, loose buttons or decorations, wrong dimensions, and uneven stitches. Jim randomly examined 10 shirts, with the following results shown to the right. Shirt Defects 1 7 2 1 4 13 3 10 2 8 5 9 10 8 7 a. Assuming that 10 observations are adequate for these purposes, determine the three-sigma control limits for defects per shirt. The UCLC equals and the LCL equals (Enter your responses rounded to two decimal places. If your answer for LCL is negative, enter this value as 0.)arrow_forwardManagement at Webster Chemical Company is concerned as to whether caulking tubes are being properly capped. If a significant proportion of the tubes are not being sealed, Webster is placing its customers in a messy situation. Tubes are packaged in large boxes of 144. Several boxes are inspected, and the following numbers of leaking tubes are found: Sample Tubes Sample Tubes Sample Tubes 1 7 8 7 15 7 2 7 9 8 16 9 3 6 10 7 17 3 4 4 11 1 18 7 5 8 12 8 19 7 6 7 2 9 13 14 1 20 6 7 Total 121 Calculate p-chart three-sigma control limits to assess whether the capping process is in statistical control. The UCLp equals and the LCLp equals (Enter your responses rounded to three decimal places. If your answer for LCLp is negative, enter this value as 0.)arrow_forwardAspen Plastics produces plastic bottles to customer order. The quality inspector randomly selects four bottles from the bottle machine and measures the outside diameter of the bottle neck, a critical quality dimension that determines whether the bottle cap will fit properly. The dimensions (in.) from the last six samples are Bottle Sample 1 2 3 4 1 0.624 0.586 0.602 0.591 2 0.613 0.599 0.578 0.618 3 0.606 0.585 0.587 0.623 4 0.581 0.623 0.571 0.610 5 0.609 0.610 0.623 0.617 6 0.605 0.573 0.570 0.602 Click the icon to view the table of factors for calculating three-sigma limits for the x-chart and R-chart. Suppose that the specification for the bottle neck diameter is 0.600 ± 0.050 in. and the population standard deviation is 0.014 in. a. What is the process capability index? The Cpk is (Enter your response rounded to two decimal places.)arrow_forward
- How would you handle the Apple 'batterygate' scandal as an operations manager? What quality measures would you take to fix the problem and prevent it from happening again? When would you implement these measures and communicate with the stakeholders?arrow_forwardPerosnal Thoughts about the articlearrow_forwardRevenue retrieval for Brew Mini= $ round response to two decimal places What would be the best design alternative? Brew master or brew miniarrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub


