
Practical Management Science, Loose-leaf Version
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781305631540
Author: WINSTON, Wayne L.; Albright, S. Christian
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Chapter 11, Problem 44P
Summary Introduction
To estimate: The probability that Person X would reach the goal with the betting strategy.
Introduction: Simulation model is the digital prototype of the physical model that helps to
Expert Solution & Answer
Explanation of Solution
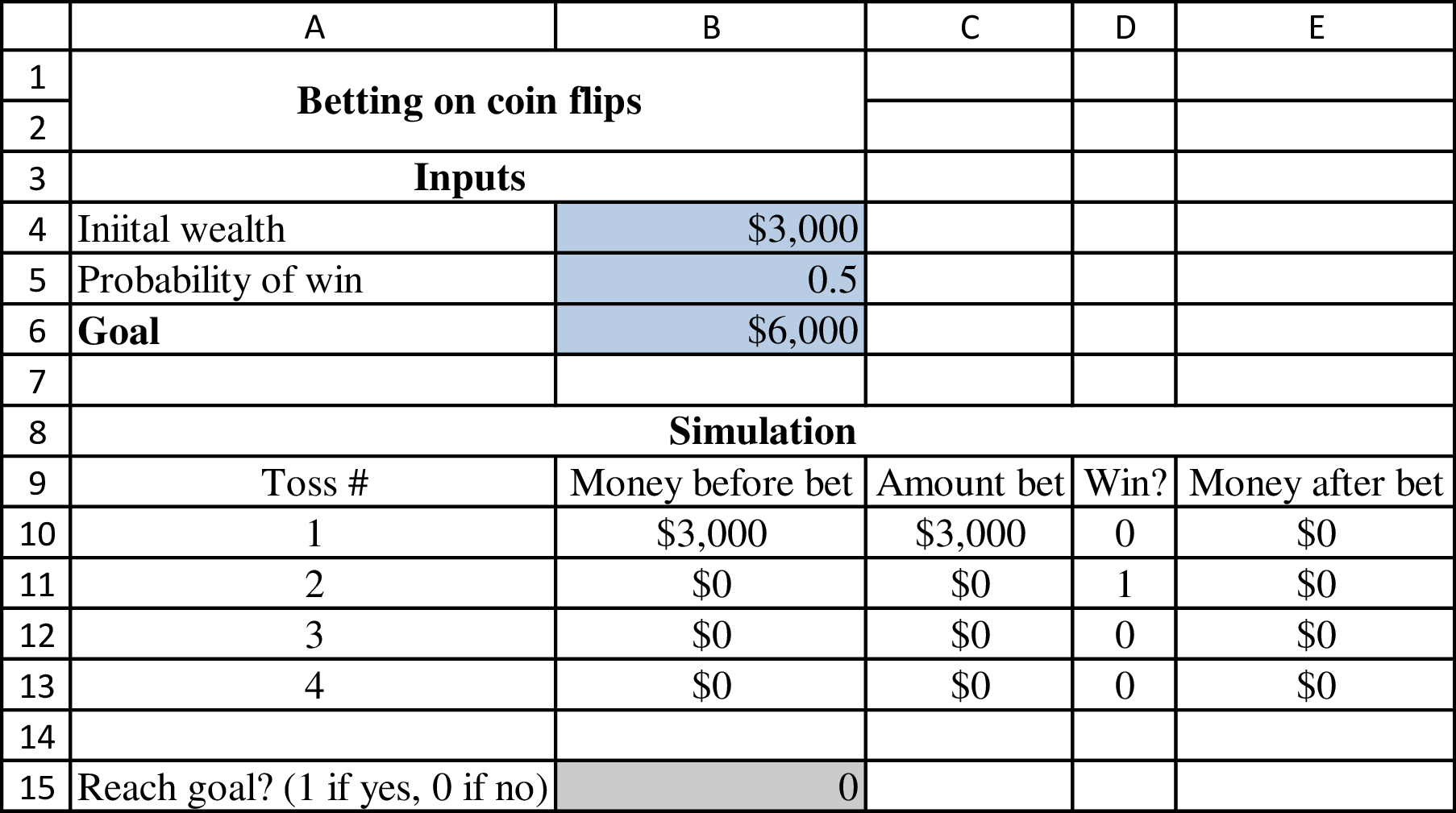
Formulae to determine the above table:
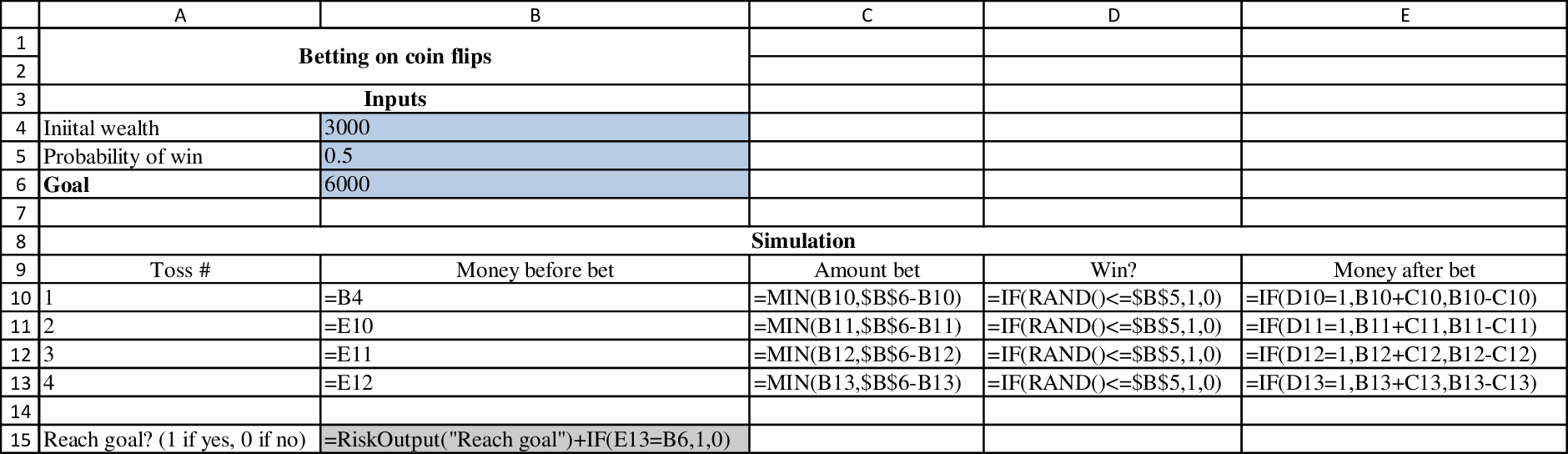
Output results:
The following table is attained by running the simulation @RISK by placing the cursor at B15:
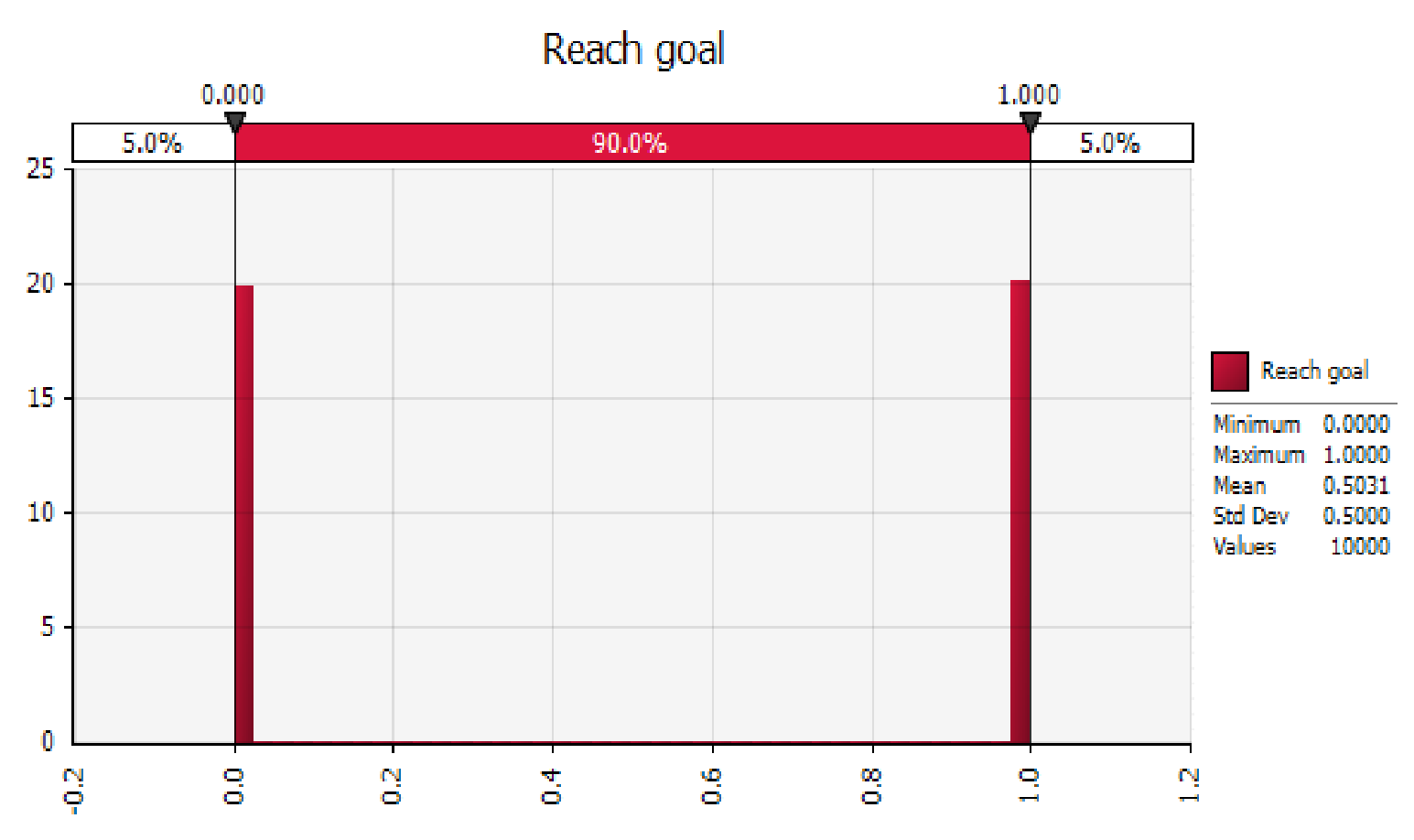
The gambler reaches the goal about 31.5% of the time
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Students have asked these similar questions
What are the obstacles to incorporating stress management techniques?
How can we overcome these obstacles?
In the 2016, "ATB: digital disruption in the parking meter industry" perform a finanacial analysis and make a chart similar to this one
2013
2014
Current Ratio
1.88
1.41
Quick Ratio
0.49
0.29
Debt to Equity
0.95
1.92
Return on Assets
5.47%
2.76%
Net Profit Margin
2.71%
1.89%
Perform a VRIO Analysis on the 2016 "ATB: Digital disruption in the parking meter industry" and make a chart similar to this one
V
R
I
O
Topic
Y
Y
Y
Y
Relations with John Deere and Paccar
Y
N
N
Y
Customer Relations
Y
Y
Y
Y
Acquisition and Integration Process
Y
Y
Y
N
Cervus Leadership University
Y
Y
N
Y
Proactive Management
Y
Y
N
Y
Financial Position
Y
N
N
N
Scale of Organization
Chapter 11 Solutions
Practical Management Science, Loose-leaf Version
Ch. 11.2 - If the number of competitors in Example 11.1...Ch. 11.2 - In Example 11.1, the possible profits vary from...Ch. 11.2 - Referring to Example 11.1, if the average bid for...Ch. 11.2 - See how sensitive the results in Example 11.2 are...Ch. 11.2 - In Example 11.2, the gamma distribution was used...Ch. 11.2 - Prob. 6PCh. 11.2 - In Example 11.3, suppose you want to run five...Ch. 11.2 - In Example 11.3, if a batch fails to pass...Ch. 11.3 - Rerun the new car simulation from Example 11.4,...Ch. 11.3 - Rerun the new car simulation from Example 11.4,...
Ch. 11.3 - In the cash balance model from Example 11.5, the...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 12PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 13PCh. 11.3 - The simulation output from Example 11.6 indicates...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 15PCh. 11.3 - Referring to the retirement example in Example...Ch. 11.3 - A European put option allows an investor to sell a...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 18PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 19PCh. 11.3 - Based on Kelly (1956). You currently have 100....Ch. 11.3 - Amanda has 30 years to save for her retirement. At...Ch. 11.3 - In the financial world, there are many types of...Ch. 11.3 - Suppose you currently have a portfolio of three...Ch. 11.3 - If you own a stock, buying a put option on the...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 25PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 26PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 27PCh. 11.3 - Prob. 28PCh. 11.4 - Prob. 29PCh. 11.4 - Seas Beginning sells clothing by mail order. An...Ch. 11.4 - Based on Babich (1992). Suppose that each week...Ch. 11.4 - The customer loyalty model in Example 11.9 assumes...Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 33PCh. 11.4 - Suppose that GLC earns a 2000 profit each time a...Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 35PCh. 11.5 - A martingale betting strategy works as follows....Ch. 11.5 - The game of Chuck-a-Luck is played as follows: You...Ch. 11.5 - You have 5 and your opponent has 10. You flip a...Ch. 11.5 - Assume a very good NBA team has a 70% chance of...Ch. 11.5 - Consider the following card game. The player and...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 42PCh. 11 - Prob. 44PCh. 11 - You now have 10,000, all of which is invested in a...Ch. 11 - Prob. 46PCh. 11 - Prob. 47PCh. 11 - Based on Marcus (1990). The Balboa mutual fund has...Ch. 11 - Prob. 50PCh. 11 - Prob. 52PCh. 11 - The annual demand for Prizdol, a prescription drug...Ch. 11 - Prob. 54PCh. 11 - The DC Cisco office is trying to predict the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 56PCh. 11 - Prob. 58PCh. 11 - You are considering a 10-year investment project....Ch. 11 - Prob. 61PCh. 11 - An automobile manufacturer is considering whether...Ch. 11 - Prob. 63PCh. 11 - Prob. 65PCh. 11 - Rework the previous problem for a case in which...Ch. 11 - Prob. 68PCh. 11 - The Tinkan Company produces one-pound cans for the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 70PCh. 11 - In this version of dice blackjack, you toss a...Ch. 11 - Prob. 76PCh. 11 - It is January 1 of year 0, and Merck is trying to...Ch. 11 - Suppose you are an HR (human resources) manager at...Ch. 11 - You are an avid basketball fan, and you would like...Ch. 11 - Suppose you are a financial analyst and your...Ch. 11 - Software development is an inherently risky and...Ch. 11 - Health care is continually in the news. Can (or...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, operations-management and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How do incorporated stress management techniques impact future emotional strength and wellness? What are the lesson learned from incorporating stress management techniques in the past that reflects developing emotional resilience?arrow_forwardIn the 2016 "ATB: digital disruption in the parking meter industry" 1. Identification + use of suitable decision criteriato rank options▪ Development of practical options in relation toidentified issue(s) + prior analysis▪ Qualitative + financial evaluation andcomparison of options 2 2. Detailed + practical action to putrecommendations in place (both short & long-run)▪ Timeline of sequence of actions, e.g. Ganttchart▪ Controls + timeline to measure if plan is ontrack▪ Contingency planarrow_forwardIn the 2016, "ATB: digital disruption in the parking meter industry" case provide a financial analysis of firmarrow_forward
- Several disadvantages are associated with lying in negotiation which include all of the following except _____. Group of answer choices the liar can be caught and face criminal charges increased risk of a bidding war cultural cost in terms of people being suspicious about others within the organization personal reputation and trustworthiness is damagedarrow_forwardA major obstacle to reaching integrative negotiation agreements is negotiators' beliefs about the outcome of some future event. A _____ is a type of agreement in which parties leverage differences of opinion to form an integrative agreement. Group of answer choices compromise contract fixed contract speculative agreement contingent contractarrow_forwardHow can trust be measured? Many surveys are available that measure trust based on behavioral and interpersonal traits. Find a measuring tool for trust and list the following. What is the tool (be sure to use APA guidelines when citing the author and list the complete reference at the end of the post)? How does the tool measure trust? Could the tool provide an accuracy of truth? Why did you select this particular tool?arrow_forward
- Respond to Adam; Agree or disagree The Trust Scale is perhaps the most famous tool for measuring trust, which was made by Mayer, Davis, and Schoorman (1995). It is based on the person's ability (competence), benevolence (intentions), and integrity (following principles). This tool is an assessment of other people's perceptions about their tests (competence), their beliefs (intentions), and their rules (integrity). A Likert-type scale questionnaire uses it; participants express their opinions on the above, and then data are summed in order to find out the general level of trust in the relationship. In organizational settings, where it is broadly used for measuring employee trust in leadership or peers, it also gives useful insights into workplace dynamics as well as potential barriers to collaboration (Mayer, Davis, & Schoorman, 1995). This tool is likely to render a true measurement of trust, especially in situations that are clearly structured so that trust behaviors are visible…arrow_forwardRespond to Lisa; Agree or disagree Trust is an essential trait required for relationships to thrive among individuals and even organizations. Employees are also expected to be trustworthy as a core value for building a robust and reliable corporate culture. Even though trust is a vital ingredient for human relationship and helps to understand organizational behaviors and interpersonal relationships, it is challenging measure the trust and its level (Evans & Revelle, 2008). However, several tools have been developed in an attempt to quantify trust but there is no known effectiveness in assessing its level based on interpersonal traits. Many studies have been conducted seeking to know how trust can be measured although they treated trust as situational construct. Some of the tools used include psychometric properties of a new trust inventory known as PTS (Propensity to Trust Survey) and Trust Style Inventory (TSI). PTS mostly relied on online survey data but has been increasingly…arrow_forward◄ Mail 18:09 5G CSTUDY_Jan25_BCOMHO...al_20241129091837.pdf.pdf FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT 1 Read the case study below and answer ALL of the questions that follow. Title: Upskilling and reskilling priorities for the gen Al era [100 MARKS] To realize the opportunity of generative Al, organizations should take a cross-collaborative, scaled approach to upskilling and reskilling workforces. The proliferation of generative artificial intelligence (gen Al) innovations necessitates a new approach to employee attraction, engagement, and retention. Our survey finds that compared to late adopters, companies adopting gen Al earlier place greater emphasis on talent development, with two-thirds already having a strategic approach to address their future talent and skill requirements. Organizations should think about a breadth of gen Al capability needs-from broad fluency supporting business goals, to deep technical and domain-specific capabilities-as well as the speed and scale at which they should be…arrow_forward
- Question 1 (25 Marks) Procurement is a key strategic function that directly impacts an organisation’s ability to create value, manage risks, and maintain a competitive advantage in the market. Critically analyse the strategic roles of procurement and how procurement practices in the fashion industry can strategically address complex challenges such as supply chain efficiency, sustainability, cost management, and global sourcing. Provide examples from the fashion industry to further your analysis. Question 2 (25 Marks) There are several enablers that need to be in place for a procurement and supply management function to implement a value-generating mode. Examine the extent of these enablers as they present themselves in the fashion industry. Question 3 (25 Marks) You are hired by local clothing chain Fashion World. The brand wants to instill a culture of professional purchasing. Construct a policy document which you would present at the next strategy meeting which inculcates the…arrow_forward◄ Files 18:11 5G CSTUDY_Jan25_SCMH_PS...Final_20241203151014.pdf FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT 1 Read the article below and answer ALL questions that follow Are your favourite fashion brands using forced labour? [100 MARKS] The global fashion and retail industry's reliance on producing quick-tumaround goods at a low cost through outsourcing and complex, globalised supply chains has allowed forced labour to thrive, workers' rights advocates war, claiming that major fashion brands profiting from the model seem reluctant to change. The apparel sector employs over 60 million workers worldwide, according to the World Bank Group. And while 97 percent of fashion and retail brands have codes of conduct and corporate social responsibility (CSR) standards, such policies are neither effective in preventing forced labour nor in ensuring remedy outcomes for workers, according to advocacy group KnowThe Chain KnowTheChain's 2021 Apparel and Footwear Benchmark Report (PDF) recently ranked 37 of the world's…arrow_forwardWhat does a Balanced Workout plan ensure comprehensive fitness? What are the obstacles involved in a Balanced Workout plan to ensure comprehensive Fitness? How does mental well-being entail implementing techniques such as mindfulness, therapy, physical activity, and social support to cultivate emotional resilience and mitigate stress?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:Cengage,
Single Exponential Smoothing & Weighted Moving Average Time Series Forecasting; Author: Matt Macarty;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IjETktmL4Kg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Introduction to Forecasting - with Examples; Author: Dr. Bharatendra Rai;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=98K7AG32qv8;License: Standard Youtube License