
Concept explainers
Instructions: You may use Excel, MegaStat, Minitab, JMP, or another computer package of your choice. Attach appropriate copies of the output or capture the screens, tables, and relevant graphs and include them in a written report. Try to state your conclusions succinctly in language that would be clear to a decision maker who is a nonstatistician. Exercises marked * are based on optional material. Answer the following questions, or those your instructor assigns.
- a. Choose an appropriate ANOVA model. State the hypotheses to be tested.
- b. Display the data visually (e.g., dot plots or line plots by factor). What do the displays show?
- c. Do the ANOVA calculations using the computer.
- d. State the decision rule for α = .05 and make the decision. Interpret the p-value.
- e. In your judgment, are the observed differences in treatment means (if any) large enough to be of practical importance?
- f. Given the nature of the data, would more data collection be practical?
- g. Perform Tukey multiple comparison tests and discuss the results.
- h. Perform a test for homogeneity of variances. Explain fully.
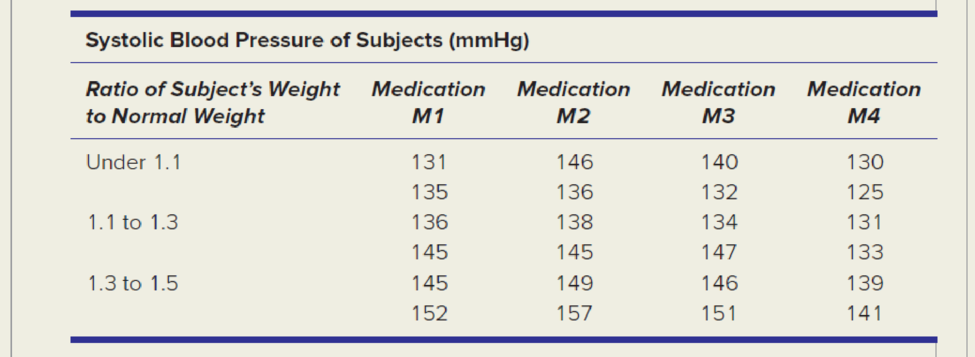
To check pain-relieving medications for potential side effects on blood pressure, it is decided to give equal doses of each of four medications to test subjects. To control for the potential effect of weight, subjects are classified by weight groups. Subjects are approximately the same age and are in general good health. Two subjects in each category are chosen at random from a large group of male prison volunteers. Subjects’ blood pressures 15 minutes after the dose are shown below. Research question: Is
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Applied Statistics in Business and Economics
- Compute the median of the following data. 32, 41, 36, 42, 29, 30, 40, 22, 25, 37arrow_forwardTask Description: Read the following case study and answer the questions that follow. Ella is a 9-year-old third-grade student in an inclusive classroom. She has been diagnosed with Emotional and Behavioural Disorder (EBD). She has been struggling academically and socially due to challenges related to self-regulation, impulsivity, and emotional outbursts. Ella's behaviour includes frequent tantrums, defiance toward authority figures, and difficulty forming positive relationships with peers. Despite her challenges, Ella shows an interest in art and creative activities and demonstrates strong verbal skills when calm. Describe 2 strategies that could be implemented that could help Ella regulate her emotions in class (4 marks) Explain 2 strategies that could improve Ella’s social skills (4 marks) Identify 2 accommodations that could be implemented to support Ella academic progress and provide a rationale for your recommendation.(6 marks) Provide a detailed explanation of 2 ways…arrow_forwardQuestion 2: When John started his first job, his first end-of-year salary was $82,500. In the following years, he received salary raises as shown in the following table. Fill the Table: Fill the following table showing his end-of-year salary for each year. I have already provided the end-of-year salaries for the first three years. Calculate the end-of-year salaries for the remaining years using Excel. (If you Excel answer for the top 3 cells is not the same as the one in the following table, your formula / approach is incorrect) (2 points) Geometric Mean of Salary Raises: Calculate the geometric mean of the salary raises using the percentage figures provided in the second column named “% Raise”. (The geometric mean for this calculation should be nearly identical to the arithmetic mean. If your answer deviates significantly from the mean, it's likely incorrect. 2 points) Starting salary % Raise Raise Salary after raise 75000 10% 7500 82500 82500 4% 3300…arrow_forward
- I need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)arrow_forward310015 K Question 9, 5.2.28-T Part 1 of 4 HW Score: 85.96%, 49 of 57 points Points: 1 Save of 6 Based on a poll, among adults who regret getting tattoos, 28% say that they were too young when they got their tattoos. Assume that six adults who regret getting tattoos are randomly selected, and find the indicated probability. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. a. Find the probability that none of the selected adults say that they were too young to get tattoos. 0.0520 (Round to four decimal places as needed.) Clear all Final check Feb 7 12:47 US Oarrow_forward
- how could the bar graph have been organized differently to make it easier to compare opinion changes within political partiesarrow_forwardDraw a picture of a normal distribution with mean 70 and standard deviation 5.arrow_forwardWhat do you guess are the standard deviations of the two distributions in the previous example problem?arrow_forward
- Please answer the questionsarrow_forward30. An individual who has automobile insurance from a certain company is randomly selected. Let Y be the num- ber of moving violations for which the individual was cited during the last 3 years. The pmf of Y isy | 1 2 4 8 16p(y) | .05 .10 .35 .40 .10 a.Compute E(Y).b. Suppose an individual with Y violations incurs a surcharge of $100Y^2. Calculate the expected amount of the surcharge.arrow_forward24. An insurance company offers its policyholders a num- ber of different premium payment options. For a ran- domly selected policyholder, let X = the number of months between successive payments. The cdf of X is as follows: F(x)=0.00 : x < 10.30 : 1≤x<30.40 : 3≤ x < 40.45 : 4≤ x <60.60 : 6≤ x < 121.00 : 12≤ x a. What is the pmf of X?b. Using just the cdf, compute P(3≤ X ≤6) and P(4≤ X).arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL


