
Calculate the power absorbed at t = 0−, t = 0+, and t = 200 ms by each of the elements in the circuit of Fig. 11.27 if vs is equal to (a) −10u(−t) V; (b) 20 + 5u(t) V.
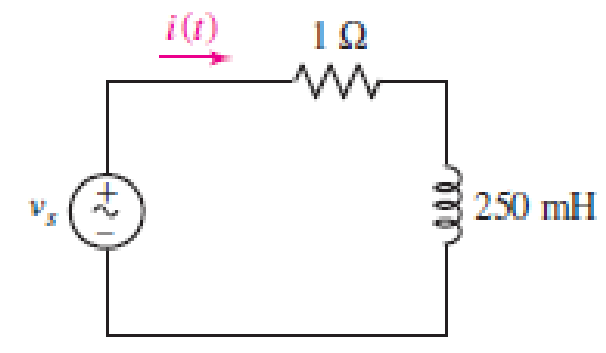
■ FIGURE 11.27
(a)
Find the power absorbed at
Answer to Problem 3E
The power absorbed at
The power absorbed at
The power absorbed at
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure 11.27 in the textbook for the given circuit.
The circuit parameters are given as follows:
Formula used:
Write the expression for power absorbed by the voltage source as follows:
Here,
Write the expression for power absorbed by the resistor in the given circuit as follows:
Here,
Write the expression for conservation power in the circuit as follows:
Here,
Calculation:
Find the source voltage at
Write the expression for current through each element in the given circuit as follows:
Here,
Write the expression for time constant in the given circuit as follows:
Substitute
From the given circuit, the initial value of the current is determined as follows:
From the given data, substitute
Substitute
Find the current
Modify the expression in Equation (1) for
Substitute
Modify the expression in Equation (2) for
Substitute
Rewrite the expression in Equation (3) as follows:
Here,
Rewrite the expression in Equation (6) for the power absorbed by the inductor as follows:
Modify the expression for
Substitute
Find the source voltage at
Substitute
Modify the expression in Equation (1) for
Substitute 0 V for
Modify the expression in Equation (2) for
Substitute
Modify the expression in Equation (7) for
Substitute 0 W for
Find the source voltage at
Substitute
Modify the expression in Equation (1) for
Substitute 0 V for
Modify the expression in Equation (2) for
Substitute
Modify the expression in Equation (7) for
Substitute 0 W for
Conclusion:
Thus, the power absorbed at
The power absorbed at
The power absorbed at
(b)
Find the power absorbed at
Answer to Problem 3E
The power absorbed at
The power absorbed at
The power absorbed at
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The source voltage is given as follows:
Calculation:
Find the source voltage at
Write the expression for current through each element in the given circuit as follows:
From Part (a), substitute 0.25 s for
Find the current
Modify the expression in Equation (1) for
Substitute 20 V for
Modify the expression in Equation (2) for
Substitute 20 A for
Substitute
Find the source voltage at
Substitute
Modify the expression in Equation (1) for
Substitute 25 V for
Modify the expression in Equation (2) for
Substitute 20 A for
Modify the expression in Equation (7) for
Substitute
Find the source voltage at
Substitute
Modify the expression in Equation (1) for
Substitute 25 V for
Modify the expression in Equation (2) for
Substitute 22.7533 A for
Modify the expression in Equation (7) for
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the power absorbed at
The power absorbed at
The power absorbed at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
- Not use ai pleasearrow_forward49. For the circuit below, what is the best connection of the capacitor to filte voltage? ბი DO A O BO wwwww wwwww M m H E LOADarrow_forward5.25. Determine the corner frequency resulting from Cin in Fig. 5.47(d). For simplicity, assume C₁ is a short circuit. TVDD C₁ M2 RF Vin H w - Vout Cin M₁arrow_forward
- In the below circuit, find out the value of equivalent Thevenin's voltage and Thevenin's resistance at the terminal. 2000 0.25 A 400 2 800 2 0.1 Aarrow_forwardQ1: For the circuit shown in Figure-1, (a) Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit, RAB at the terminals A and B. [10] (b) When 50V dc source is switched at terminals A-B, solve for the voltage V₁ at the location shown. [10] 50V www 12Ω 10Ω 5Ω www www A + B 200 Figure-1 www 10Ω ww 25Ω 100arrow_forwarda. Write a PLC ladder diagram that allows the teacher to teach AND, OR, and XOR logic gates through using three PLC's digital input points and only one digital output point.arrow_forward
- rately by PRACTICE 4.2 For the circuit of Fig. 4.5, compute the voltage across each curren source. 202 ww 3A 30 ww 4Ω S 50 www Reference node FIGURE 4.5 Ans: V3A =5.235 V; 7A = 11.47 V. 7 Aarrow_forwardQ2) a) design and show me your steps to convert the following signal from continuous form to digital form: s(t)=3sin(3πt) -1 373 Colesarrow_forwardA sequence is defined by the relationship r[n] = [h[m]h[n+m]=hn*h-n where h[n] is a minimum-phase sequence and r[n]= 4 4 (u[n]+ 12" [n-1] 3 (a) Find R(z) and sketch the pole-zero diagram. (b) Determine the minimum-phase sequence h[n] to within a scale factor of ±1. Also, determine the z-transform H(z) of h[n].arrow_forward
- usıng j-k and D flipflop design a counter that counts 0,2,1 again as shown below ın the tablearrow_forwardfind the minterms of the followıng boolean expressıon desıgn F's cırcuit using one of the approciate decoders given below and a NOR gateF(A,B,C,D)=(A+'BC)(B 'C+'A 'D + CD)arrow_forward64) answer just two from three the following terms: A) Design ADC using the successive method if the Vmax=(3) volt, Vmin=(-2) volt, demonstrate the designing system for vin-1.2 volt. Successive Approximation ADC Input Voltage-1.1 V -4-3.5-3 -2.5 -2 -1.5 +1 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 1 T -8 -7 -6 -5 -3 +2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 X=1??? 1st guess: -0.25 V (too high) X=11?? 2nd guess: -2.25 V (too low) 3rd guess: -1.25 V (too low) X=1110 X=111? 4th guess: -0.75 V (too high) Make successive guesses and use a comparator to tell whether your guess is too high or too low. Each guess determines one bit of the answer and cuts the number of remaining possibilities in half.arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





