
(a)
Interpretation:
The sketch of galvanic cell along with cathode and anode and the direction of electron flow, the direction of flow of ions through salt bridge, the balanced chemical equation and the E0cell should be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
In galvanic cell chemical energy converted into electrical energy.
At anode oxidation takes place which means loss of electrons.
At cathode reduction takes place which means gain of electrons.
(a)
Answer to Problem 21E
The E0cell is0.27 V
Reaction at anode:
Reaction at cathode:
Overall reaction:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The diagram of cell is shown below:
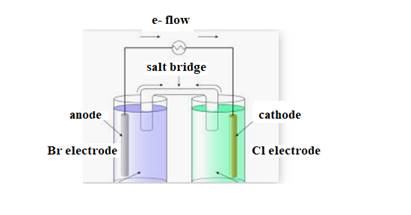
The direction of flow of electrons is from anode to cathode.
Negative ions flow towards anode.
At anode oxidation takes place
At cathode reduction takes place.
The cell representation is shown below:
The oxidation half-cell reaction is shown below:
The reduction half-cell reaction is shown below:
The overall reaction is shown below:
The calculation of E0cell is shown below:
E0cell = E0cathode − E0anode
= 1.36 − (-1.09)
= 0.27 V
(b)
Interpretation:
The sketch of galvanic cell along with cathode and anode and the direction of electron flow, the direction of flow of ions through salt bridge, the balanced chemical equation and the E0cell should be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
In galvanic cell chemical energy converted into electrical energy.
At anode oxidation takes place which means loss of electrons.
At cathode reduction takes place which means gain of electrons.
(b)
Answer to Problem 21E
The E0cell is 0.09 V
Reaction at anode:
Reaction at cathode:
Overall reaction:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The diagram is shown below:
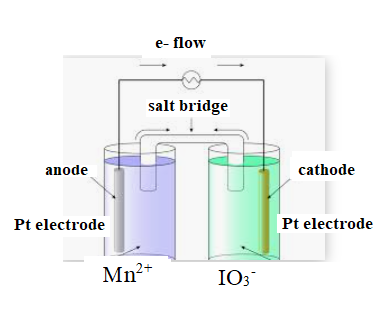
The direction of flow of electrons is from anode to cathode.
Negative ions flow towards anode.
At anode oxidation takes place
At cathode reduction takes place.
The oxidation half-cell reaction is shown below:
The reduction half-cell reaction is shown below:
The overall reaction is shown below:
The calculation of E0cell is shown below:
E0cell = E0cathode − E0anode
= 1.60 − 1.51
= 0.09 V
(c)
Interpretation:
The sketch of galvanic cell along with cathode and anode and the direction of electron flow, the direction of flow of ions through salt bridge, the balanced chemical equation and the E0cell should be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
In galvanic cell chemical energy converted into electrical energy.
At anode oxidation takes place which means loss of electrons.
At cathode reduction takes place which means gain of electrons.
(c)
Answer to Problem 21E
The E0cell is 1.10 V
Reaction at anode:
Reaction at cathode:
Overall reaction:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The diagram is shown below:
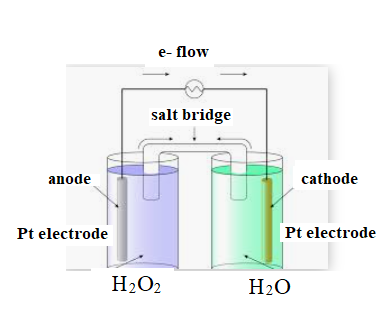
The direction of flow of electrons is from anode to cathode.
Negative ions flow towards anode.
At anode oxidation takes place
At cathode reduction takes place.
The oxidation half-cell reaction is shown below:
The reduction half-cell reaction is shown below:
The overall reaction is shown below:
The calculation of E0cell is shown below:
E0cell = E0cathode − E0anode
= 1.78 − 0.68
= 1.10 V
(d)
Interpretation:
The sketch of galvanic cell along with cathode and anode and the direction of electron flow, the direction of flow of ions through salt bridge, the balanced chemical equation and the E0cell should be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
In galvanic cell chemical energy converted into electrical energy.
At anode oxidation takes place which means loss of electrons.
At cathode reduction takes place which means gain of electrons.
(d)
Answer to Problem 21E
The E0cell is 1.14 V
Reaction at anode:
Reaction at cathode:
Overall reaction:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The diagram is shown below:
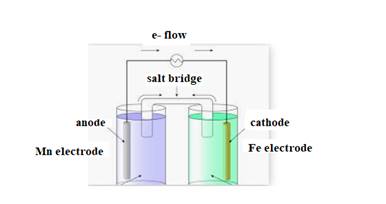
The direction of flow of electrons is from anode to cathode.
Negative ions flow towards anode.
At anode oxidation takes place
At cathode reduction takes place.
The oxidation half-cell reaction is shown below:
The reduction half-cell reaction is shown below:
The overall reaction is shown below:
The calculation of E0cell is shown below:
E0cell = E0cathode − E0anode
= - 0.036- (-1.18)
= 1.14 V
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK WEBASSIGN FOR ZUMDAHL'S CHEMICAL PR
- Please complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forwardWhat would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forwardWhat would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forward
- For benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forward
- Which of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forwardWhich of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? O O OH OH 1. BH 2. H₂O₂, NaOH OH OHarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





