
(a)
Interpretation: The galvanic cells based on given overall reaction needs to be sketched and the value of
Concept Introduction: A galvanic cell is an electro chemical cell that drives electrical energy from
In a galvanic cell the oxidation and the reduction half cells are separated by a connecting wire so that electrons can flow through the wire.
(a)
Answer to Problem 19E
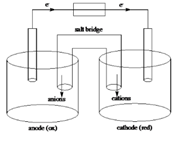
Sketch of a galvanic cell is as follows:
Values of
Explanation of Solution
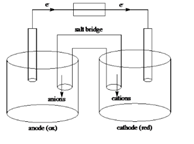
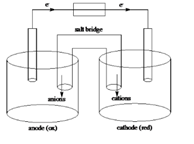
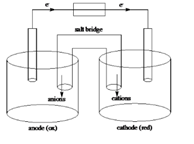
Below is a sketch of a galvanic cell where electrons flow from anode to cathode with a salt bridge between two to supply the required ions and complete the circuit. Cations will always flow to the anode and anions will always flow to the cathode.
By examining oxidation number of atoms in the reaction determine which compound is oxidized and which being reduced.
In above reaction Cr has +3 oxidation state and Cl has 0 oxidation state and in products Cr has +6 oxidation state and Cl has -1 oxidation state. Oxidation number increased for Cr, it is oxidized. This means that
Determine actual half reactions that have occurred.
Cr has lost three electrons because Cr atom has gone from +3 to +6. Add six electrons to the products. The half reaction is now change balanced as well.
It has been converted to
Each Cl atom required one electron because they have gone from 0 to -1, thus add two electrons in reactants for a change balance.
Add two half reactions together and cancel out the electrons to determine overall process. Because Cr half reaction has six electrons multiply Cl half reaction by three before adding two together.
Determine the standard reduction potential from reference table to calculate
Add these values together to give
(b)
Interpretation: The galvanic cells based on given overall reaction needs to be sketched and the value of
Concept Introduction: A galvanic cell is an electro chemical cell that drives electrical energy from chemical reactions taking place within a particular cell.
In a galvanic cell the oxidation and the reduction half cells are separated by a connecting wire so that electrons can flow through the wire.
(b)
Answer to Problem 19E
Sketch of a galvanic cell is as follows:
Values of
Explanation of Solution
By examining oxidation number of atoms in the reaction determine which compound is oxidized and which being reduced.
In above reaction Cu has +2 oxidation state and Mg has 0 oxidation state and in products Cu has 0 oxidation state and Mg has +2oxidation state. Oxidation number increased for Mg, it is oxidized. This means that Mg is at the anode. For Cu oxidation number decreased, it was reduced. This means that
Add two half reactions together and cancel out electrons determine overall process.
Determine the standard reduction potential from reference table to calculate
Add these values together to give
(c)
Interpretation: The galvanic cells based on given overall reaction needs to be sketched and the value of
Concept Introduction: A galvanic cell is an electro chemical cell that drives electrical energy from chemical reactions taking place within a particular cell.
In a galvanic cell the oxidation and the reduction half cells are separated by a connecting wire so that electrons can flow through the wire.
(c)
Answer to Problem 19E
Sketch of a galvanic cell is as follows:
Values of
Explanation of Solution
By examining oxidation number of atoms in the reaction determine which compound is oxidized and which being reduced.
In above reaction I has +5 oxidation state and Fe has +2 oxidation state and in products I has 0 oxidation state and Fe has +3oxidation state. Oxidation number increased for Fe, it is oxidized. This means that
Determine actual half reactions that have occurred
Each I atom has gone from +5 to 0 oxidation state, thus it has gained five electrons. Add ten electrons to reactants. Half-reaction is now charge balanced as well.
To determine overall process add two half reactions together and cancel out electrons. Because I half-reaction has ten electrons, multiply Fe half-reaction by ten before adding two together.
Determine standard reduction potentials from reference table to calculate
Add these values together to give
(d)
Interpretation: The galvanic cells based on given overall reaction needs to be sketched and the value of
Concept Introduction: A galvanic cell is an electro chemical cell that drives electrical energy from chemical reactions taking place within a particular cell.
In a galvanic cell the oxidation and the reduction half cells are separated by a connecting wire so that electrons can flow through the wire.
(d)
Answer to Problem 19E
Sketch of a galvanic cell is as follows:
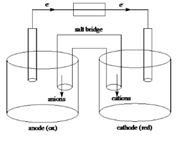
Values of
Explanation of Solution
By examining oxidation number of atoms in the reaction determines which compound is oxidized and which being reduced.
In above reaction Ag has +1 oxidation state and Zn has 0 oxidation state and in products Ag has 0 oxidation state and Zn has +2 oxidation state. This means Zn is at anode. Because oxidation number decrease for Ag. It is reduced. This means that
Determine actual-half reactions that have occurred. Zn has only been converted to
Zn loses two electrons so add two electrons to products to charge balance half-reaction.
Determine standard reduction potentials from reference table to calculate
Add these values together to give
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK WEBASSIGN FOR ZUMDAHL'S CHEMICAL PR
- An expression for the root mean square velocity, vrms, of a gas was derived. Using Maxwell’s velocity distribution, one can also calculate the mean velocity and the most probable velocity (mp) of a collection of molecules. The equations used for these two quantities are vmean=(8RT/πM)1/2 and vmp=(2RT/M)1/2 These values have a fixed relationship to each other.(a) Arrange these three quantities in order of increasing magnitude.(b) Show that the relative magnitudes are independent of the molar mass of the gas.(c) Use the smallest velocity as a reference for establishing the order of magnitude and determine the relationship between the larger and smaller values.arrow_forwardThe reaction of solid dimethylhydrazine, (CH3)2N2H2, and liquefied dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4, has been investigated for use as rocket fuel. The reaction produces the gases carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), and water vapor (H2O), which are ejected in the exhaust gases. In a controlled experiment, solid dimethylhydrazine was reacted with excess dinitrogen tetroxide, and the gases were collected in a closed balloon until a pressure of 2.50 atm and a temperature of 400.0 K were reached.(a) What are the partial pressures of CO2, N2, and H2O?(b) When the CO2 is removed by chemical reaction, what are the partial pressures of the remaining gases?arrow_forwardOne liter of chlorine gas at 1 atm and 298 K reacts completely with 1.00 L of nitrogen gas and 2.00 L of oxygen gas at the same temperature and pressure. A single gaseous product is formed, which fills a 2.00 L flask at 1.00 atm and 298 K. Use this information to determine the following characteristics of the product:(a) its empirical formula;(b) its molecular formula;(c) the most favorable Lewis formula based on formal charge arguments (the central atom is N);(d) the shape of the molecule.arrow_forward
- How does the square root mean square velocity of gas molecules vary with temperature? Illustrate this relationship by plotting the square root mean square velocity of N2 molecules as a function of temperature from T=100 K to T=300 K.arrow_forwardDraw product B, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CF3 NH2 Me O .N. + B OMearrow_forwardBenzimidazole E. State its formula. sState the differences in the formula with other benzimidazoles.arrow_forward
- Draw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CN CF3 K2CO3, DMSO, H₂O2 Aarrow_forward19) Which metal is most commonly used in galvanization to protect steel structures from oxidation? Lead a. b. Tin C. Nickel d. Zinc 20) The following molecule is an example of a: R₁ R2- -N-R3 a. Secondary amine b. Secondary amide c. Tertiary amine d. Tertiary amidearrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





