
Concept explainers
The
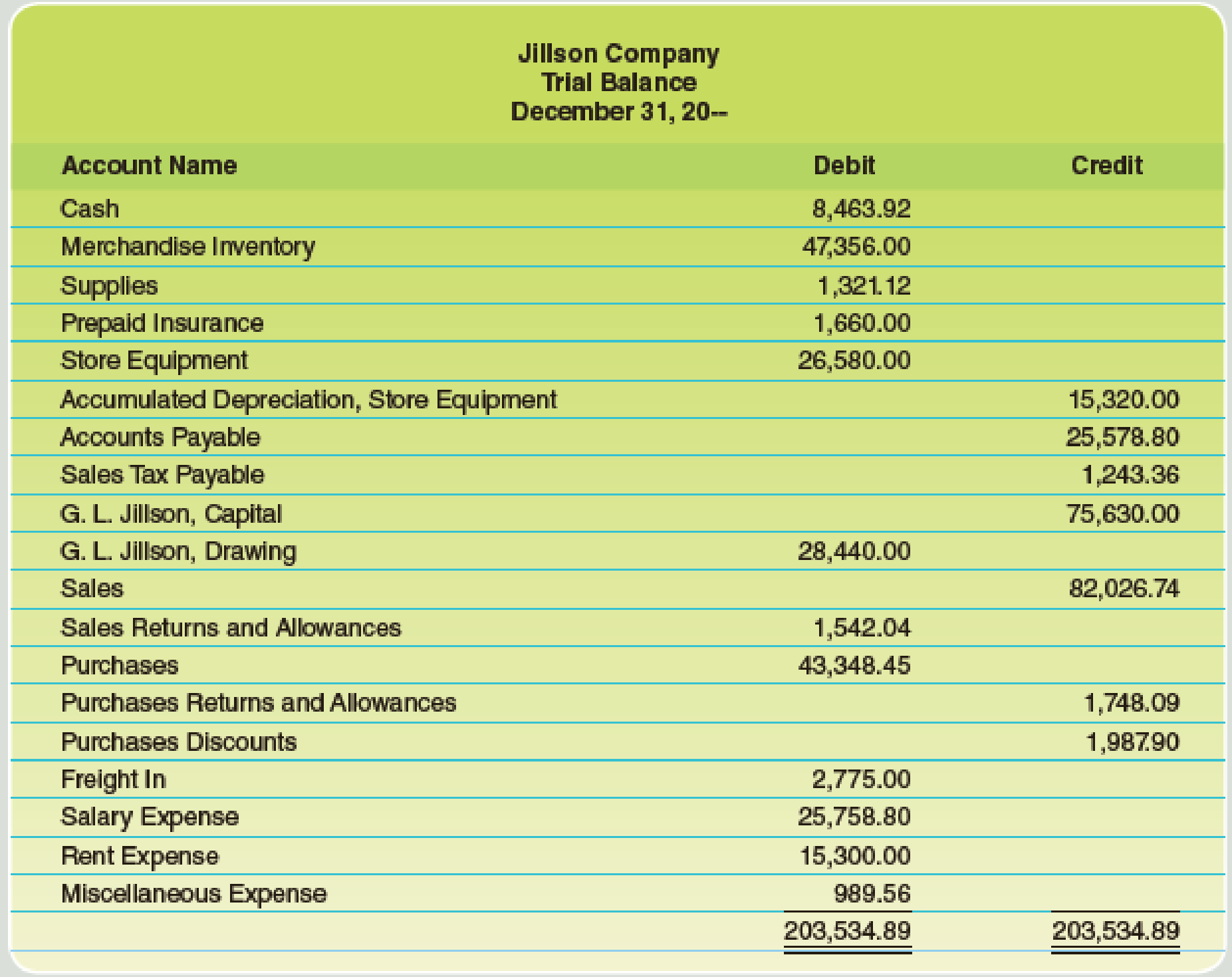
Here are the data for the adjustments.
a–b. Merchandise Inventory at December 31, $54,845.00.
c. Store supplies inventory (on hand), $488.50.
d. Insurance expired, $680.
e. Salaries accrued, $692.
f.
Required
Complete the work sheet after entering the account names and balances onto the work sheet.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 11 Solutions
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career Approach
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Foundations Of Finance
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
Macroeconomics
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
- What is predetermined standard variable manufacturing overhead rate?arrow_forwardGiven answer general accountingarrow_forwardCrescent Manufacturing produces a single product. Last year, the company had a net operating income of $102,400 using absorption costing and $94,100 using variable costing. The fixed manufacturing overhead cost was $5 per unit. There were no beginning inventories. If 32,000 units were produced last year, then sales last year were_. (a) 21,750 units (b) 29,820 units (c) 30,440 units (d) 35,600 units MCQarrow_forward
 College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning

