
Concept explainers
If a restriction enzyme cuts between the G and the A whenever it encounters the sequence GAATTC, how many fragments will be produced when the enzyme is digested with DNA with the following sequence? TGAGAATTCAACTGAATTCAAATTCGAATTCTTAGC
- a. Two
- b. Three
- c. Four
- d. Five
Introduction:
Restriction enzymes are the enzymes that digest the higher molecular weight DNA in to smaller fragments. They are also known as restriction endonucleases.
Answer to Problem 1MCQ
Correct answer:
There are three sequences of GAATTC present on the DNA fragment and the fragments formed after the cleavage of the DNA are four in numbers. Therefore, option (c) is correct.
Explanation of Solution
Reason for correct statement:
Restriction endonucleases digest a double stranded DNA at specific sites. These specific sites are also called recognition site that present as palindrome. If the restriction enzyme given cuts between the G and A whenever it encounters the sequence GAATTC on the given DNA with the following sequence TGAGAATTCTGAATTCAAATTCGAATTCTTAGC, the cleaving of the DNA will be given as follows:
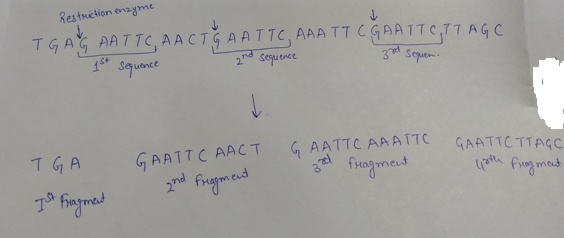
As shown, after the cleavage of the DNA by the help of the restriction enzyme, four fragments will be formed.
Option (c) is given as “Four”.
As, “the restriction enzyme recognizes three sequence on the given DNA, so it will make three cuts, that results in the production of the four DNA fragments,” is the right answer.
Hence, option (c) is correct.
Reasons for the incorrect statements:
Option (a), is given as “Two”.
The fragments of the DNA formed will be four after the action of the restriction enzyme. Hence, it is a wrong answer.
Option (b), is given as “Three”.
The DNA fragment formed after the cleavage will be four in numbers. Hence, it is a wrong answer.
Option (d), is given as “Five”.
For DNA fragments will be formed after the cutting action of the restriction enzyme at the given recognition site. Hence, it is a wrong answer.
Hence, options (a), (b), and (d), are incorrect.
Restriction enzymes are also known as molecular scissors that could cut double stranded DNA molecules at specific sites. It is an important tool that is used in the manipulation of DNA.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Biology: Concepts and Investigations
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- Identify the indicated tissue. (Tilia stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma xylem phloem none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the indicated structure. (Cucurbita stem l.s.) pit lenticel stomate tendril none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the specific cell? (Zebrina leaf peel) vessel element sieve element companion cell tracheid guard cell subsidiary cell none of thesearrow_forward
- What type of cells flank the opening on either side? (leaf x.s.) vessel elements sieve elements companion cells tracheids guard cells none of thesearrow_forwardWhat specific cell is indicated. (Cucurbita stem I.s.) vessel element sieve element O companion cell tracheid guard cell none of thesearrow_forwardWhat specific cell is indicated? (Aristolochia stem x.s.) vessel element sieve element ○ companion cell O O O O O tracheid O guard cell none of thesearrow_forward
- Identify the tissue. parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma ○ xylem O phloem O none of thesearrow_forwardPlease answer q3arrow_forwardRespond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: How might CRISPR-Cas 9 be used in research or, eventually, therapeutically in patients? What are some potential ethical issues associated with using this technology? Do the advantages of using this technology outweigh the disadvantages (or vice versa)? Explain your position.arrow_forward
- You are studying the effect of directional selection on body height in three populations (graphs a, b, and c below). (a) What is the selection differential? Show your calculation. (2 pts) (b) Which population has the highest narrow sense heritability for height? Explain your answer. (2 pts) (c) If you examined the offspring in the next generation in each population, which population would have the highest mean height? Why? (2 pts) (a) Midoffspring height (average height of offspring) Short Short Short Short (c) Short (b) Short Tall Short Tall Short Short Tall Midparent height (average height of Mean of population = 65 inches Mean of breading parents = 70 inches Mean of population = 65 inches Mean of breading parents = 70 inches Mean of population = 65 inches Mean of breading parents = 70 inchesarrow_forwardP You are studying a population of 100 flowers that has two alleles at a locus for flower color, blue (B) and green (G). There are 15 individuals with the BB genotype, 70 individuals with the BG genotype, and 15 individuals with the GG genotype. (a) What are the allele frequencies of B and G in the starting population? Show your calculations. (2 pts) (b) Is this population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? Show your calculations. (3 pts) 12pt v Paragraph BIU UA AV & VT2V f CO Varrow_forwardIn a natural population of outbreeding plants, the variance of the total number of seeds per plant is 16. From the natural population, 20 plants are taken into the laboratory and developed into separate true-breeding lines by self- fertilization-with selection for high, low, or medium number of seeds-for 10 generations. The average variance in the tenth generation in each of the 20 sets is about equal and averages 5.8 across all the sets. Estimate the broad-sense heritability for seed number in this population. (4 pts) 12pt v Paragraph BIUA V V T² v B ① O wordsarrow_forward
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





