
Concept explainers
Complete the following concept map to test your knowledge of gene regulation.
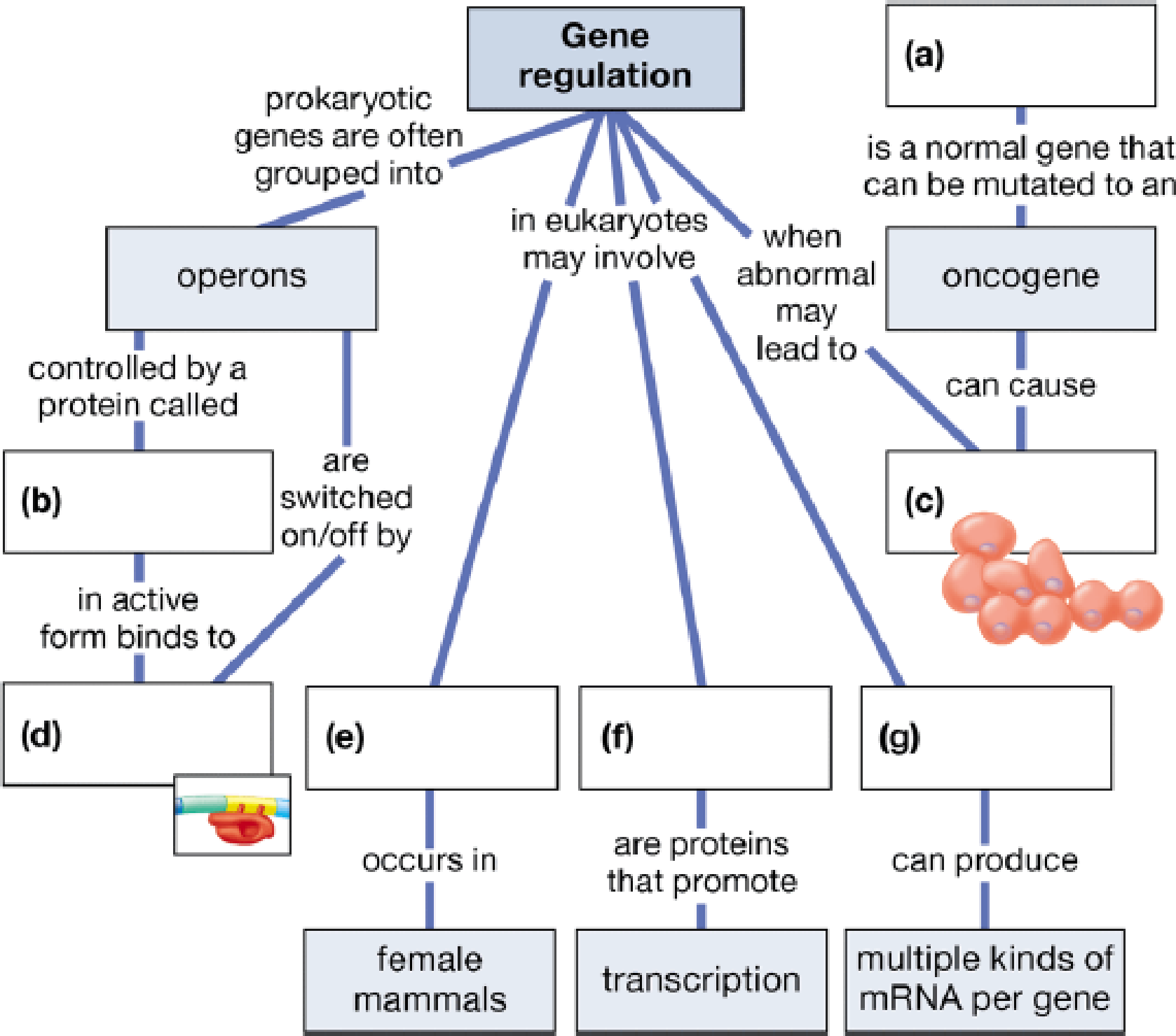
To complete: The given map showing a process of gene regulation.
Introduction: Gene regulation is a process where the expression of genes are controlled for the synthesis of specified gene products (usually RNA or proteins).
Answer to Problem 1CC
Pictorial representation: Figure 1 shows the completed map of the gene regulation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
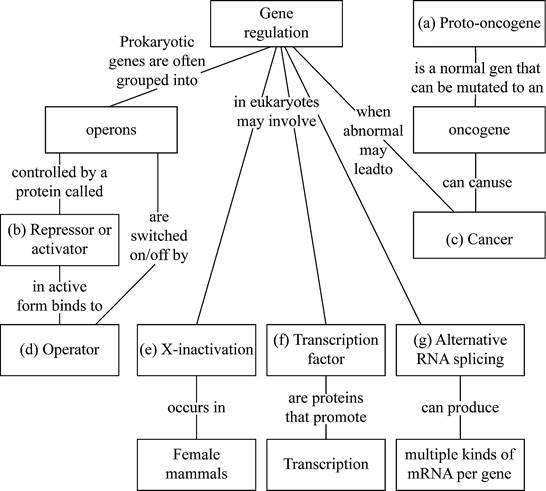
Fig. 1: Gene regulation in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Explanation of Solution
(a)
Correct answer: Proto-oncogenes.
Explanation: Proto-oncogenes are the common genes which are transformed into oncogenes (malignant genes) during mutation. These mutations can lead to indefinite proliferation of cells.
(b)
Correct answer: Repressor or activator.
Explanation: They are the molecules which regulates the transcription. Activators are transcription factors that activate or boost a gene to express and the repressors are the molecules that stop the expression of a gene.
(c)
Correct answer: Cancer.
Explanation: Cancer is a diseased condition where the normal cells get converted to abnormal cells through undifferentiated and uncontrolled growth.
(d)
Correct answer: Operator.
Explanation: Operator is a part of the operons which regulates the binding of a repressor molecule to it. The transcription is stopped when the repressor binds to the operator, thereby it blocks the further binding of RNA polymerase to initiate the transcription.
(e)
Correct answer: X-inactivation.
Explanation: The process of inactivation of single copy of X chromosomes in female mammals is called as X-inactivation.
(f)
Correct answer: Transcription factors.
Explanation: The proteins that are associated with the transcription of DNA to mRNA are called as transcription.
(g)
Correct answer: Alternative RNA splicing.
Explanation: Alternative splicing (differential splicing) is the process of regulation during a gene expression to produce a single gene which can code for different proteins. Final product of alternative splicing will be a processed mRNA.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- What is behavioral adaptarrow_forward22. Which of the following mutant proteins is expected to have a dominant negative effect when over- expressed in normal cells? a. mutant PI3-kinase that lacks the SH2 domain but retains the kinase function b. mutant Grb2 protein that cannot bind to RTK c. mutant RTK that lacks the extracellular domain d. mutant PDK that has the PH domain but lost the kinase function e. all of the abovearrow_forwardWhat is the label ?arrow_forward
- Can you described the image? Can you explain the question as well their answer and how to get to an answer to an problem like this?arrow_forwardglg 112 mid unit assignment Identifying melting processesarrow_forwardGive only the mode of inheritance consistent with all three pedigrees and only two reasons that support this, nothing more, (it shouldn't take too long)arrow_forward
- Oarrow_forwardDescribe the principle of homeostasis.arrow_forwardExplain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward

 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





