
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism for the reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
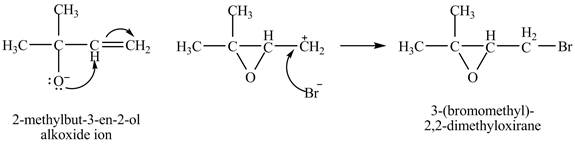
The given reaction is shown below.
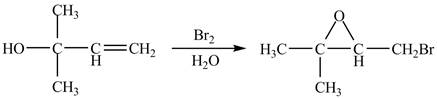
Figure 1
The oxygen atom of the alkoxide ion attack carbon of double bond to form

Figure 2
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is -the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the speed of the reaction. It is also known as anchimeric assistance.
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
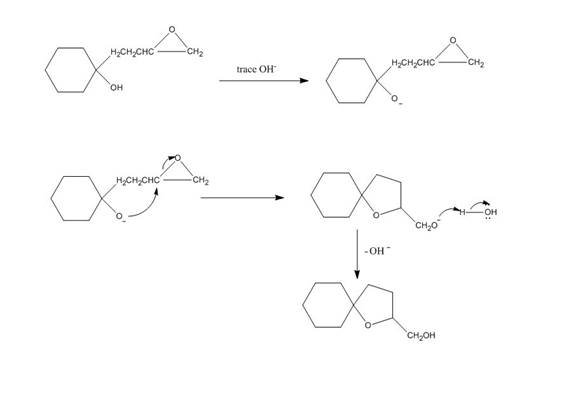
The given reaction is shown below.
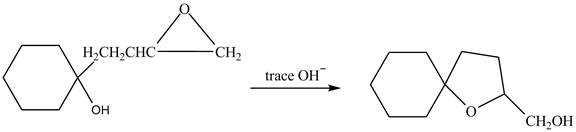
Figure 3
Hydroxide ion abstract the proton from hydroxyl group of given compound. The oxide attacks the carbon of epoxide ring to form a five membered ring. The alkoxide ion formed is protonated in presence of water. The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
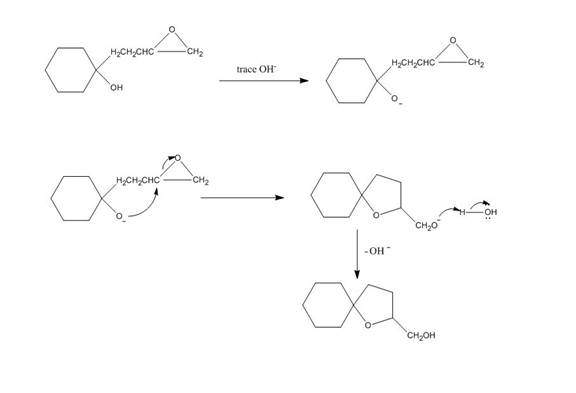
Figure 4
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 4.
(c)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is -the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the speed of the reaction. It is also known as anchimeric assistance.
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
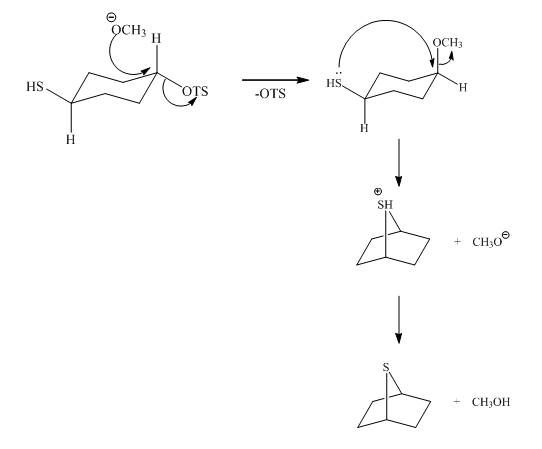
The given reaction is shown below.
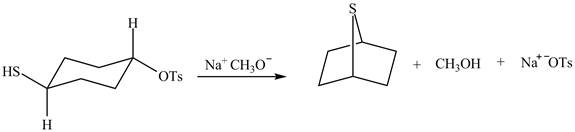
Figure 5
The methoxy group attacks the carbon containing sulfonate ester group. The nucleophilic displacement reaction occurs. The sulfonate ester group is displaced by methoxy group. Then neighbouring group participation of sulfur atom displaces the methoxy group. The sulfonium ion formed undergoes deprotonation to form the product. The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.

Figure 6
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 6.
(d)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is -the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the speed of the reaction. It is also known as anchimeric assistance.
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
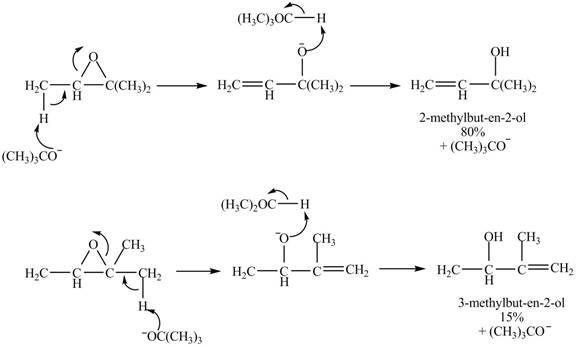
The given reaction is shown below.
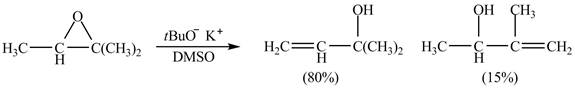
Figure 7
A strong base is used in the reaction; hence elimination reaction will take place. The given compound contains two
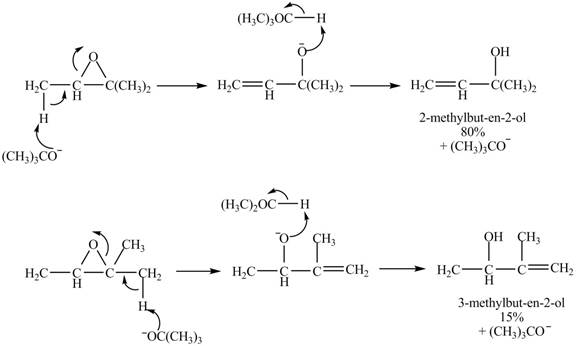
Figure 8
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 8.
(e)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is -the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the speed of the reaction. It is also known as anchimeric assistance.
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
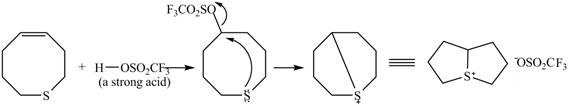
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
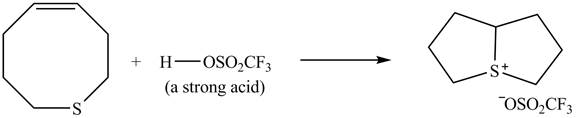
Figure 9
The
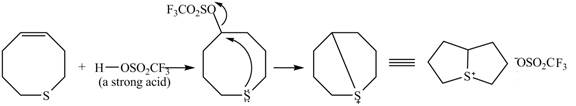
Figure 10
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 10.
(f)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is -the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the speed of the reaction. It is also known as anchimeric assistance.
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
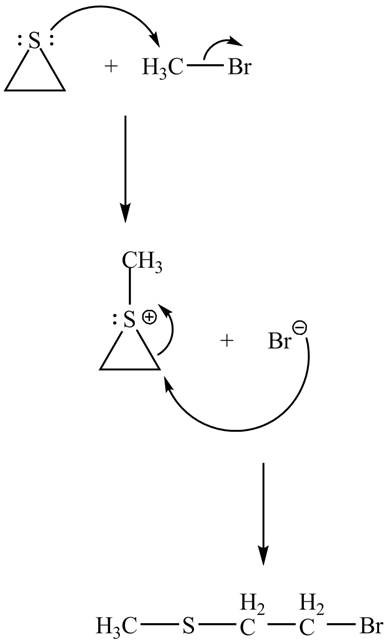
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
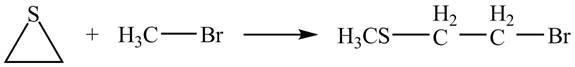
Figure 11
The lone pair of sulphur atom attacks the carbon of methyl bromide. The sulfur atom of the ring gets methylated. Then bromide ion attacks the carbon atom of ring which results in ring opening to form the desired product. The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.

Figure 12
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 12.
(g)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is -the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the speed of the reaction. It is also known as anchimeric assistance.
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
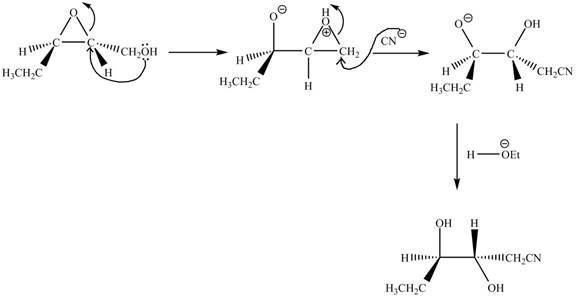
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is shown below.
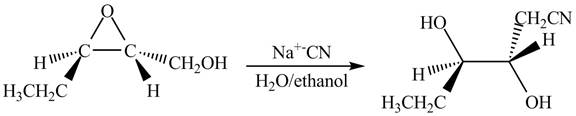
Figure 13
The neighbouring group participation of oxygen atom takes place in the given reaction. The oxygen atom of hydroxyl group attacks the electrophilic carbon atom of the epoxide ring which results in the formation of new epoxide ring. Then cyanide ion attacks at the electrophilic carbon of epoxide which results in ring opening. The oxide ion takes proton form ethanol to form desired product. The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown below.

Figure 14
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 14.
(h)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Neighbouring group participation is -the interaction of the lone pair electrons of an atom (hetero) or electron present in sigma and pi bond with the parent molecule to increase the speed of the reaction. It is also known as anchimeric assistance.
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
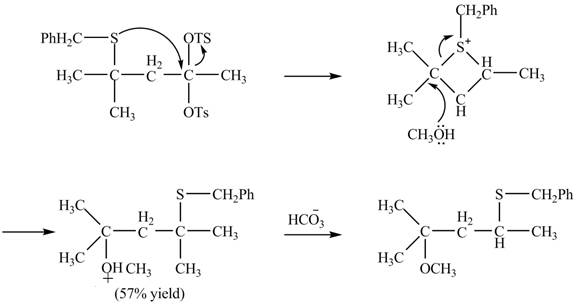
The given reaction is shown below.
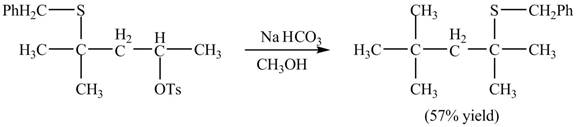
Figure 15
The sulfur atom attacks at the electrophilic carbon atom to form a four membered ring. The nucleophilic attack by methanol at the ring results in ring opening. Then the base abstracts proton from the protonated hydroxyl group to form the desired product. The curved-arrow mechanism for the given reaction is shown below.
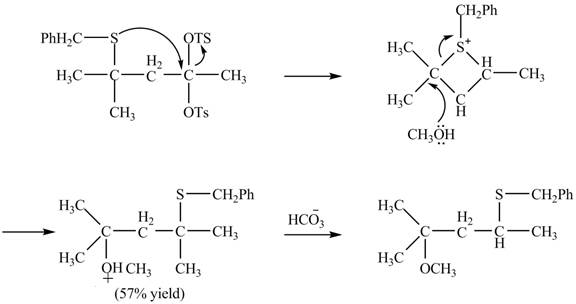
Figure 16
The curved arrow mechanism for given rearrangement is shown in Figure 16.
(i)
Interpretation:
The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
The vicinal
Answer to Problem 11.77AP
The curved arrow mechanism of the given reaction is shown below.
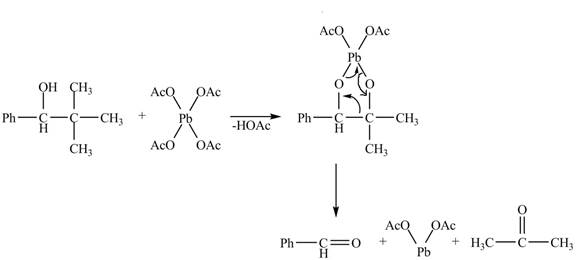
Explanation of Solution
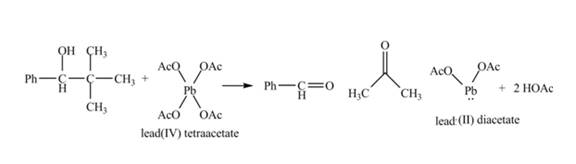
Figure 17
The given compound is a vicinal diol. It will react with the lead tetraacetate to form five membered ring intermediate. The intermediate formed rearranges to form acetone, benzaldehyde and lead diacetate. The curved arrow mechanism for the given reaction is shown below.
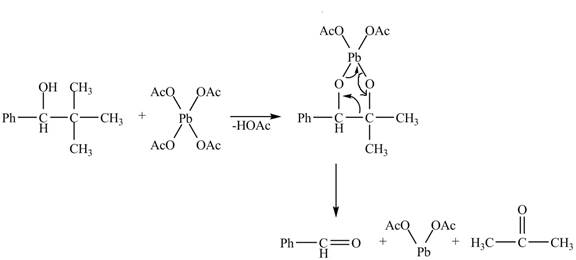
Figure 18
The curved arrow mechanism for given reaction is shown in Figure 18.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM +SG +SAPLING >IP<
- Draw the structure of serine at pH 6.8. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : d كarrow_forwardTake a look at this molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. CH2OH H H H OH OH OH CH2OH H H H H OH H H OH H OH Is this a reducing sugar? yes α β ロ→ロ no ☑ yes Does this molecule contain a glycosidic bond? If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the symbol describing it. O no 0+0 If you said this molecule does contain a glycosidic bond, write the common names (including anomer and enantiomer labels) of the molecules that would be released if that bond were hydrolyzed. If there's more than one molecule, separate each name with a comma. ☐arrow_forwardAnswer the questions in the table below about this molecule: H₂N-CH₂ -C—NH–CH–C—NH–CH—COO- CH3 CH CH3 What kind of molecule is this? 0= CH2 C If you said the molecule is a peptide, write a description of it using 3-letter codes separated ☐ by dashes. polysaccharide peptide amino acid phospolipid none of the above Хarrow_forward
- Draw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: CH₂OH C=O HO H H -OH H OH CH₂OH Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : ☐ Х S '☐arrow_forwardNucleophilic Aromatic Substitution 22.30 Predict all possible products formed from the following nucleophilic substitution reactions. (a) (b) 9 1. NaOH 2. HCI, H₂O CI NH₁(!) +NaNH, -33°C 1. NaOH 2. HCl, H₂Oarrow_forwardSyntheses 22.35 Show how to convert toluene to these compounds. (a) -CH,Br (b) Br- -CH3 22.36 Show how to prepare each compound from 1-phenyl-1-propanone. 1-Phenyl-1-propanone ہتی. Br. (b) Br (racemic) 22.37 Show how to convert ethyl benzene to (a) 2,5-dichlorobenzoic acid and (b) 2,4-dichlorobenzoic acid. 22.38 Show reagents and conditions to bring about the following conversions. (a) 9 NH2 8 CO₂H NH2 CO₂Et (d) NO2 NH2 S NH₂ NO2 CHS CHarrow_forward
- ive the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all rant stereochemistry. [10 only] A. B. NaN3 1. LiAlH4, ether Br 2. H₂O CH3 HNO3 H₂/Pt H₂SO ethanol C. 0 0 CH3CC1 NaOH NHCCH AICI H₂O . NH₂ CH3CH2 N CH2CH3 + HCI CH₂CH 3 1. LIAIH, THE 2. H₂Oarrow_forwardCalculate the stoichiometric amount of CaCl2 needed to convert all of the CuSO4 into CuCl2.arrow_forwardH CH تنی Cl 1. NaCN, DMF 2. LIAIH4, ether H₂O pyridine N NH₂ 5 CH H 1 HNO, H₂SO 2. Nal NH2 Br Br HNO₂ CuCl H₂SO HCI CH3 H3C NN HSO KCN CuCN 1. HNO₂, H₂SO O₂N NH2 2. OH ཀ་ལས། །ས་ཅན་ :i་དེ་མ་མ་སེ་ NH₂ CH3 1. HNO₂, H₂SO4 2. H3PO₂ 1 HNO2, H2SO4 2. Nalarrow_forward
- ive the major organic product(s) of each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show all rant stereochemistry. [10 only] A. B. NaN3 1. LiAlH4, ether Br 2. H₂O CH3 HNO3 H₂/Pt H₂SO ethanol C. 0 0 CH3CC1 NaOH NHCCH AICI H₂O . NH₂ CH3CH2 N CH2CH3 + HCI CH₂CH 3 1. LIAIH, THE 2. H₂Oarrow_forwardIf a pharmacy chain sold 65 million 500-mg tablets of aspirin, how many US tons of aspirin does this represent? Report your answer to 2 significant figures.arrow_forwardHere are the options: reducing a monosaccharide a non reducing disaccharide amylopectin cellulose 1,4' beta- glycosidearrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

