1 Tension, Compression, And Shear 2 Axially Loaded Members 3 Torsion 4 Shear Forces And Bending Moments 5 Stresses In Beams (basic Topics) 6 Stresses In Beams (advanced Topics) 7 Analysis Of Stress And Strain 8 Applications Of Plane Stress (pressure Vessels, Beams, And Combined Loadings) 9 Deflections Of Beams 10 Statically Indeterminate Beams 11 Columns expand_more
Chapter Questions expand_more
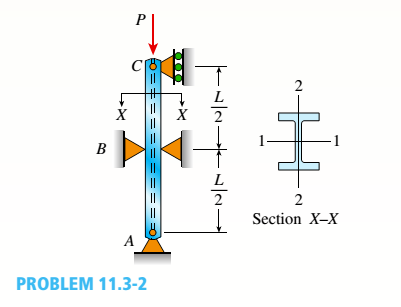
Problem 11.2.1P: A rigid bar of length L is supported by a linear elastic rotational spring with rotational stiffness... Problem 11.2.2P: The figure shows an idealized structure consisting of a rigid bar with pinned connections and... Problem 11.2.3P: -2-3. Two rigid bars are connected with a rotational spring, as shown in the figure. Assume that the... Problem 11.2.4P: Repeat Problem 11.2-3 assuming that R= 10 kN · m/rad and L = 2 m. Problem 11.2.5P: The figure shows an idealized structure consisting of two rigid bars with pinned connections and... Problem 11.2.6P: An idealized column consists of rigid bar ABCD with a roller support at B and a roller and spring... Problem 11.2.7P: An idealized column is made up of rigid segments ABC and CD that are joined by an elastic connection... Problem 11.2.8P: The figure shows an idealized structure consisting of bars AB and BC that are connected using a... Problem 11.2.9P: The figure shows an idealized structure consisting of two rigid bars joined by an elastic connection... Problem 11.2.10P: The figure shows an idealized structure consisting of rigid bars ABC And DEF joined by a linearly... Problem 11.2.11P: The figure shows an idealized structure consisting of an L-shaped rigid bar structure supported by... Problem 11.2.12P: Rigid column ABCD has an elastic support at B with translational stiffness ß. Find an expression for... Problem 11.2.13P: An idealized column is made up of rigid bars ABC and CD that are joined by a rotational elastic... Problem 11.2.14P: An idealized column is composed of rigid bars ABC and CD joined by an elastic connection with... Problem 11.2.15P: Repeat Problem 11.2-14 using L = 12 ft, ß = 0.25 kips/in., ßRl= 1.5ßL2, and ßR2= 2 ßR1. Problem 11.2.16P: An idealized column is composed of rigid bars ABC and CD joined by an elastic connection with... Problem 11.3.1P: Column AB has a pin support at A,a roller support at B, and is compressed by an axial load P (see... Problem 11.3.2P: Slender column ABC is supported at A and C and is subjected to axial load P. Lateral support is... Problem 11.3.3P: Calculate the critical load PCTfor a W 8 × 35 steel column (see figure) having a length L = 24 ft... Problem 11.3.4P: Solve the preceding problem for a W 250 × 89 steel column having a length L = 10 m. Let E = 200 GPa. Problem 11.3.5P: Solve Problem 11.3-3 for a W 10 × 45 steel column having a length L = 28 ft. Problem 11.3.6P: A horizontal beam AB is pin-supported at end A and carries a clockwise moment M at joint B, as shown... Problem 11.3.7P: A column ABC is supported at ends A and C and compressed by an axial load P (figure a). Lateral... Problem 11.3.8P: Find the controlling buckling load (kN) for the steel column shown in the figure. The column is... Problem 11.3.9P: A column, pinned at top and bottom, is made up of two C 6 x 13 steel shapes (see figure) that act... Problem 11.3.10P: Repeat Problem 11.3-9. Use two C 150 × 12.2 steel shapes and assume that E = 205 GPa and L = 6 m. Problem 11.3.11P: A horizontal beam AB is pin-supported at end A and carries a load Q at joint B, as shown in the... Problem 11.3.12P: -12 A horizontal beam AB is supported at end A and carries a load Q at joint B, as shown in the... Problem 11.3.13P: A horizontal beam AB has a sliding support at end A and carries a load Q at end B, as shown in the... Problem 11.3.14P: A slender bar AB with pinned ends and length L is held between immovable supports (see figure). What... Problem 11.3.15P: A rectangular column with cross-sectional dimensions b and h is pin-supported at ends A and C (see... Problem 11.3.16P: .16 Three identical, solid circular rods, each of radius r and length L, are placed together to form... Problem 11.3.17P: Three pinned-end columns of the same material have the same length and the same cross-sectional area... Problem 11.3.18P: A long slender column ABC is pinned at ends A and C and compressed by an axial force F (sec figure).... Problem 11.3.19P: The roof over a concourse at an airport is supported by the use of pretensioned cables. At a typical... Problem 11.3.20P: The hoisting arrangement for lifting a large pipe is shown in the figure. The spreader is a steel... Problem 11.3.21P: A pinned-end strut of aluminum (E = 10,400 ksi) with a length L = 6 ft is constructed of circular... Problem 11.3.22P: The cross section of a column built up of two steel I-beams (S 150 × 25.7 sections) is shown in the... Problem 11.3.23P: The truss ABC shown in the figure supports a vertical load W at joint B. Each member is a slender... Problem 11.3.24P: A truss ABC supports a load W at joint B, as shown in the figure. The length L, of member Aß is... Problem 11.3.25P: An S6 × 12.5 steel cantilever beam AB is supported by a steel tic rod at B as shown. The tie rod is... Problem 11.3.26P: The plane truss shown in the figure supports vertical loads F at joint D, 2F at joint C, and 3F at... Problem 11.3.27P: A space truss is restrained at joints O, A,B, and C as shown in the figure. Load F is applied at... Problem 11.4.1P: A fixed-end column with circular cross section is acted on by compressive axial load P. The... Problem 11.4.2P: A cantilever aluminum column has a square tube cross section with an outer dimension of 150 mm. The... Problem 11.4.3P: An aluminum pipe column (E = 10,400 ksi) with a length L = 10.0 ft has inside and outside diameters... Problem 11.4.4P: Solve the preceding problem for a steel pipe column (E = 210 GPa) with length L = 1.2 m, inner... Problem 11.4.5P: A wide-flange steel column (E = 30 × l06 psi) of W12 × 87 shape (see figure) h as a length L = 28... Problem 11.4.6P Problem 11.4.7P: The upper end of a WE × 21 wide-flange steel column (E = 30 × 103ksi) is supported laterally between... Problem 11.4.8P: A vertical post AB is embedded in a concrete foundation and held at the top by two cables (see... Problem 11.4.9P: The horizontal beam ABC shown in the figure is supported by columns BD and CE. The beam is prevented... Problem 11.4.10P: The roof beams of a warehouse are supported by pipe columns (see figure) having an outer diameter... Problem 11.4.11P: Determine the critical load Pcrand the equation of the buckled shape for an ideal column with ends... Problem 11.4.12P: A fixed-pinned column is a W310 × 21 steel shape and is designed to carry an axial load of 125 kN.... Problem 11.4.13P: Find the Controlling buckling load (kips) for the steel column shown in the figure. The column is... Problem 11.4.14P Problem 11.4.15P: A rigid L-shaped frame is supported by a steel pipe column AB (sec figure) and is subjected to a... Problem 11.4.16P: An aluminum tube AB with a circular cross section has a sliding support at the base and is pinned at... Problem 11.4.17P: The frame ABC consists of two members AB and BC that are rigidly connected at joint B, as shown in... Problem 11.5.1P: An aluminum bar having a rectangular cross section (2.0 in. × 1.0 in.) and length L = 30 in. is... Problem 11.5.2P: ‘11.5-2 A steel bar having a square cross section (50 mm × 50 mm)and length L = 2.0 in is compressed... Problem 11.5.3P: A simply supported slender column is subjected to axial load P = 175 kips applied at distance e =... Problem 11.5.4P: A brass bar of a length L = 0.4 m is loaded at end B by force P = 10 kN with an eccentricity e =... Problem 11.5.5P: Determine the bending moment M in the pinned-end column with eccentric axial loads shown in the... Problem 11.5.6P: Plot the load-deflection diagram for a pinned-end column with eccentric axial loads (see figure) if... Problem 11.5.7P: Solve the preceding problem for a column with e = 0.20 in,, L = 12 ft, I = 2L7in4, and E = 30 ×... Problem 11.5.8P: A wide-flange member (W200 × 22.5) is compressed by axial loads that have a resultant P acting at... Problem 11.5.9P: A wide-f hinge member (W 10 × 30) is compressed by axial loads that have a resultant P = 20 kips... Problem 11.5.10P: Solve the preceding problem (W 250 × 44.8) if the resultant force P equals 110 kN and E = 200 GPa. Problem 11.5.11P: The column shown in the figure is fixed at the base and free at the upper end. A compressive load P... Problem 11.5.12P: An aluminum box column with a square cross section is fixed at the base and free at the top (sec... Problem 11.5.13P: Solve the preceding problem for an aluminum column with b = 6,0 in., t = 0.5 in., P = 10 kips, and E... Problem 11.5.14P: A steel post /t if with a hollow circular cross section is fixed at the base and free at the top... Problem 11.5.15P: A frame ABCD is constructed of steel wide-flange members (W8 x 21; E = 30 x ID6 psi) and subjected... Problem 11.6.1P: A steel bar has a square cross section of width b = 2.0 in. (sec figure). The bar has pinned... Problem 11.6.2P: ]11.6-2 A brass bar (E = 100 GPa) with a square cross section is subjected to axial forces having a... Problem 11.6.3P: A square aluminum bar with pinned ends carries a load P = 25 kips acting at distance e = 2,0 in.... Problem 11.6.4P: A pinned-and column of a length L = 2A m is constructed of steel pipe (E = 210GPa) having an inside... Problem 11.6.5P: A pinned-end strut of a length L = 5.2 ft is constructed of steel pipe (E = 30 × 103 ksi) having an... Problem 11.6.6P: A circular aluminum tube with pinned ends supports a load P = 18 kN acting at a distance e = 50 mm... Problem 11.6.7P: A steel W 12 × 35 column is pin-supported at the ends. The column carries an axial load p = 150 kips... Problem 11.6.8P: A steel W 310 x 52 column is pin-supported at the ends and has a length L = 4 m. The column supports... Problem 11.6.9P: A steel column (E = 30 x 103 ksi) with pinned ends is constructed of a W10 x 60 wide-flange shape... Problem 11.6.10P: A W410 × S5 steel column is compressed by a force P = 340 kN acting with an eccentricity e = 38 mm,... Problem 11.6.11P: A steel column ( E = 30 X 103 ksi) that is fixed at the base and free at the top is constructed of a... Problem 11.6.12P: AW310 × 74 wide-flange steel column with length L = 3.8 m is fixed at the base and free at the top... Problem 11.6.13P: A pinned-end column with a length L = 18 ft is constructed from a W12 x 87 wide-flange shape (sec... Problem 11.6.14P: The wide-flange, pinned-end column shown in the figure carries two loads: a force P1= 450 kN acting... Problem 11.6.15P: A W14 × 53 wide-flange column of a length L = 15 ft is fixed at the base and free at the top (see... Problem 11.6.16P: A wide-flange column with a bracket is fixed at the base and free at the top (see figure). The... Problem 11.9.1P: Determine the allowable axial load Pallowa W 10 X 45 steel wide-flange column with pinned ends (see... Problem 11.9.2P: Determine the allowable axial load Pallowfor a W 310 × 129 steel wide-flange column with pinned ends... Problem 11.9.3P: Determine the allowable axial load Pallowfor a W 10 × 129 steel wide-flange column with pinned ends... Problem 11.9.4P: Select a steel wide-flange column of a nominal depth of 250 mm (W 250 shape) to support an axial... Problem 11.9.5P Problem 11.9.6P: Select a steel wide-flange column of a nominal depth of 360 mm (W 360 shape) to support an axial... Problem 11.9.7P Problem 11.9.8P: Determine the allowable axial load Pallowfor a steel pipe column with pinned ends having an outside... Problem 11.9.9P: Determine the allowable axial load Pallowfor a steel pipe column that is fixed at the base and free... Problem 11.9.10P: Determine the allowable axial load Pallowfor a steel pipe column that is fixed at the base and free... Problem 11.9.11P: -11 Determine the maximum permissible length Lmaxfor a steel pipe column that is fixed at the base... Problem 11.9.12P: Determine the maximum permissible length Lmaxfor a steel pipe column that is fixed at the base and... Problem 11.9.13P: A steel pipe column with pinned ends supports an axial load P = 21 kips. The pipe has outside and... Problem 11.9.14P: The steel columns used in a college recreation center are 16.75 m long and arc formed by welding... Problem 11.9.15P: A W8 × 28 steel wide-flange column with pinned ends carries an axial load P. What is the maximum... Problem 11.9.16P Problem 11.9.17P Problem 11.9.18P Problem 11.9.19P Problem 11.9.20P Problem 11.9.21P Problem 11.9.22P: An aluminum pipe column (alloy 2014-T6) with pinned ends has an out side diameter d2= 120 mm and... Problem 11.9.23P Problem 11.9.24P Problem 11.9.25P Problem 11.9.26P Problem 11.9.27P Problem 11.9.28P Problem 11.9.29P Problem 11.9.30P Problem 11.9.31P: A wood column with, a rectangular cross section (see figure) is constructed of 4 in. × 8 im... Problem 11.9.32P Problem 11.9.33P Problem 11.9.34P: A square wood column with side dimensions b (see figure) is constructed of a structural grade of... Problem 11.9.35P: A square wood column with side dimensions b (see figure) is constructed of a structural grade of... Problem 11.9.36P format_list_bulleted


 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning