
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the alloy is hypoeutectic or hypereutectic needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Eutectic alloy is defined as a mixture of metals having a melting point lower than that of any of components. An alloy which has composition that lies to the left of the eutectic point present on the phase diagram is termed as hypoeutectic alloy. The hyper-eutectic alloy is defined as the alloy which consist of composition that lies to the extreme right of the eutectic point.
Answer to Problem 11.31P
The Ai-
Explanation of Solution
The Al-
Therefore, Al-
The hyper-eutectic alloy is defined as the alloy which consist of composition that lies to the extreme right of the eutectic point.
Hence, as per the hyper-eutectic alloy conditions, the given Ai-
(b)
Interpretation:
The value of composition of the first solid formed during the solidification process needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Solidification is the method which is also known as freezing process. Solidification process is defined as the phase change of matters. The phase change of matter that results in the production of solid phase. Regularly, this occurs when the temperature of the liquid is lowered below the freezing point. Undercooling of liquid takes place in the process of solidification. Solidification can yield metastable product structures at high undercooling. The constituents of the metastable products are the result of kinetic competition.
Answer to Problem 11.31P
The value of composition is
Explanation of Solution
During solidification the first solid formed has some amount of composition. The value of composition of the first solid formed during solidification of Al-
Therefore, composition where the first solid phase occurs as
(c)
Interpretation:
The amount and composition of each phase of temperature of
Concept Introduction:
Solidification is the method which is also known as freezing process. Solidification process is defined as the phase change of matters. The phase change of matter that results in the production of solid phase. Regularly, this occurs when the temperature of the liquid is lowered below the freezing point. Undercooling of liquid takes place in the process of solidification. Solidification can yield metastable product structures at high undercooling. The constituents of the metastable products are the result of kinetic competition.
Answer to Problem 11.31P
The amount of the phase obtained is
Explanation of Solution
The given temperature is
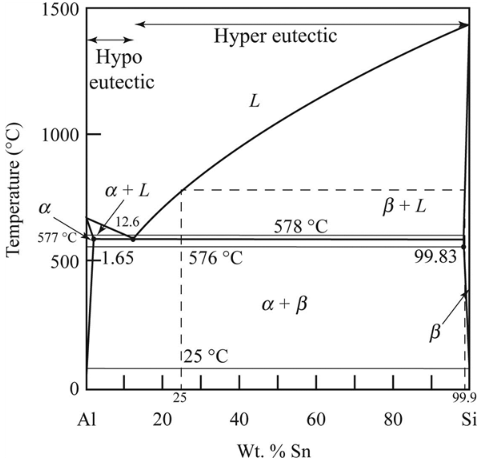
So, we can calculate the weight percentage of eutectic phase
Thus, we obtained the amount and composition of phase from the above standard phase diagram as
(d)
Interpretation:
The amount and composition of each phase at temperature of
Concept Introduction:
Solidification is the method which is also known as freezing process. Solidification process is defined as the phase change of matters. The phase change of matter that results in the production of solid phase. Regularly, this occurs when the temperature of the liquid is lowered below the freezing point. Undercooling of liquid takes place in the process of solidification. Solidification can yield metastable product structures at high undercooling. The constituents of the metastable products are the result of kinetic competition.
Answer to Problem 11.31P
The amount of phase obtained is
Explanation of Solution
The given temperature is
The amount of each phase at
To calculate the composition of each phase at
To calculate the composition of phase, we have the expression,
So, we can calculate the weight percentage of eutectic phase
(e)
Interpretation:
The amount and composition of each micro constituent at the temperature of
Concept Introduction:
Solidification is the method which is also known as freezing process. Solidification process is defined as the phase change of matters. The phase change of matter that results in the production of solid phase. Regularly, this occurs when the temperature of the liquid is lowered below the freezing point. Undercooling of liquid takes place in the process of solidification. Solidification can yield metastable product structures high undercooling. The constituents of the metastable products are the result of kinetic competition.
Answer to Problem 11.31P
The amount of eutectic phase and phase is calculated at
Explanation of Solution
The phases present at eutectic phase and phase is calculated as
The phases present at the
From the diagram mentioned above at
To calculate the composition of eutectic phase at
To calculate the composition of primary phase −
So, the weight percentage of eutectic phase
(f)
Interpretation:
The amount and composition of each phase at
Concept Introduction:
Solidification is the method which is also known as freezing process. Solidification process is defined as the phase change of matters. The phase change of matter that results in the production of solid phase. Regularly, this occurs when the temperature of the liquid is lowered below the freezing point. Undercooling of liquid takes place in the process of solidification. Solidification can yield metastable product structures at high undercooling. The constituents of the metastable products are the result of kinetic competition.
Answer to Problem 11.31P
The number of phases present in Al-
Explanation of Solution
The phases present at
From the diagram mentioned above the amount of the phases calculated are
To calculate the composition of phase at
So, one can calculate the weight percentage of eutectic phase
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Essentials Of Materials Science And Engineering
- i need helppp pleasearrow_forward3) (30pts) An application requires a bit rate of 18.2 Kbps and an error rate of less than 104. The channel has a noise power spectral density of 10-8 W/Hz. The channel attenuates the power in the signal by 5 dB. The system uses binary PAM baseband digital communication system with the minimum required bandwidth and a roll-off factor of 0.319. a) (10 pts) What is the estimated minimum required signal power (Pt) at the transmitter?arrow_forwardA common measure of transmission for digital data is the baud rate, defined as the number of bits transmitted per second. Generally, transmission is accomplished in packets consisting of starting bit, a byte of information, and a stop bit. Using this approach, answer the following. a) How many minutes would it take to transmit a 512×512 image with 128 grey Levels at 300 baud? b) What would the time be at 9600 baud? c) Repeat (a) and (b) for a 1024×1024 image 128 grey levelsarrow_forward
- 1a) (5pts) Suppose X is a Gaussian random variable with a mean of 2 and a variance of 9. What is the probability X is greater than 2. 1b) (5pts) Suppose X is a Gaussian random variable with a mean of 2 and a variance of 9. Using the Q-function, determine Prob{-4-2} Leave your answer in terms of the Q-function; do not evaluate it.arrow_forwardchemical engineering. Only focus on H(3), which is the nitrogen gas. Start with the reference state to the process state. Be thorough to the fullestarrow_forwardText Book Problem 7.82 (page 261) Consider the total head-loss in the system forthis flow is 18.56 ft (head-losses in first and second pipe are 13.83 ft and 4.73 ftrespectively). Please show numerical values for EGL/HGL at the beginning/end/intermediatechange point. (Point distribution: elevation determination 5 points, EGL, HGL lines 4points).(I think we are just using the values provided for head losses to solve this problem)arrow_forward
- Calculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the moment distribution method, and draw the Shear force diagram and Bending moment diagram for the beam shown. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forwardCalculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the Slope deflection method. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forward2. Express the following complex numbers in rectangular form. (a) z₁ = 2еjл/6 (b) Z2=-3e-jπ/4 (c) Z3 = √√√3e-j³/4 (d) z4 = − j³arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





