
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of 1-Hexanol with chromic acid has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation of alcohols: Oxidation of primary alcohol gives an
Chromic acid Oxidation of an Alcohol:
Step 1: Reaction of alcohol and chromic acid gives an alkyl chromate. No change in oxidation state of both Carbon and Chromium.
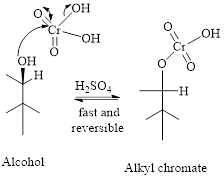
Step 2: Take a proton away and simultaneously break bonds to give stable molecules or ions. Reaction of the alkyl chromate with a base (here water molecule) results in cleavage of a
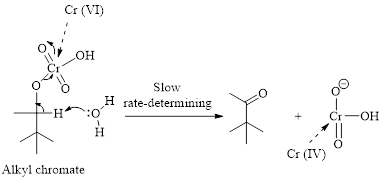
(b)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of 2-Hexanol with chromic acid has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation of alcohols: Oxidation of primary alcohol gives an aldehyde or a carboxylic acid, depending on experimental conditions.
Chromic acid Oxidation of an Alcohol:
Step 1: Reaction of alcohol and chromic acid gives an alkyl chromate. No change in oxidation state of both Carbon and Chromium.

Step 2: Take a proton away and simultaneously break bonds to give stable molecules or ions. Reaction of the alkyl chromate with a base (here water molecule) results in cleavage of a

(c)
Interpretation:
The product formed in the reaction of Cyclohexanol with chromic acid has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation of alcohols: Oxidation of primary alcohol gives an aldehyde or a carboxylic acid, depending on experimental conditions.
Chromic acid Oxidation of an Alcohol:
Step 1: Reaction of alcohol and chromic acid gives an alkyl chromate. No change in oxidation state of both Carbon and Chromium.

Step 2: Take a proton away and simultaneously break bonds to give stable molecules or ions. Reaction of the alkyl chromate with a base (here water molecule) results in cleavage of a

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 10 Solutions
Student Study Guide and Solutions Manual for Brown/Iverson/Anslyn/Foote's Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition
- The two pKa values of oxalic acid are 1.25 and 3.81. Why are they not the same value? Show the protontransfer as part of your explanation. *see imagearrow_forwardасть Identify all the bonds that gauche interact with C-OMe in the most stable conformation of the above compound.arrow_forwardPredict the reactants used in the formation of the following compounds using Acid-Catalyzed dehydration reactionarrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this?arrow_forward.. Give the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show ll relevant stereochemistry [3 ONLY]. A H Br 1. NaCN 2 NaOH, H₂O, heat 3. H3O+ B. CH₂COOH 19000 1. LiAlH4 THF, heat 2 H₂O* C. CH Br 1. NaCN, acetone 2 H3O+, heat D. Br 1. Mg. ether 3. H₂O+ 2 CO₂ E. CN 1. (CH) CHMgBr, ether 2 H₂O+arrow_forwardAssign this COSY spectrumarrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this?arrow_forward1. Draw structures corresponding to each of the following names [3 ONLY]: A. 2,2,2-trichloroethanal (chloral). B. trans-3-isopropylcyclohexanecarbaldehyde C. What is the correct structure for 2-hydroxyacetophenone? Circle the letter of your response. a C 0 OH OH OH HO b. H3C CH 0 H d OH D. Provide IUPAC names for each structure below. 0 H C-H 0 0 CH3 H NO₂ E. The substance formed on addition of water to an aldehyde or ketone is called a hydrate or a/an: a. vicinal diol b. geminal diol C. acetal d. ketalarrow_forwardAssign this spectrumarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

