
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
7th Edition
ISBN: 8220100257063
Author: BEER
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10.4, Problem 93P
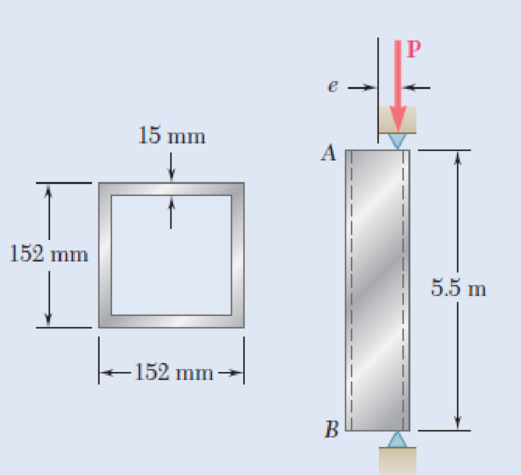
A column of 5.5-m effective length is made of the aluminum alloy 2014-T6 for which the allowable stress in bending is 220 MPa. Using the interaction method, determine the allowable load P, knowing that the eccentricity is (a) e = 0, (b) e = 40 mm.
Fig. P10.93
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Problem 13:
F₁ =
A
=250 N 30%
Determine the moment of each of the three forces about point B.
F₂ = 300 N
60°
2 m
-3 m
B
4 m
F3=500 N
3 kN
3 kN
1.8 kN/m
80 mm
B
300 mm
D
an
1.5 m-1.5 m--1.5 m-
PROBLEM 5.47
Using the method of Sec. 5.2, solve Prob. 5.16
PROBLEM 5.16 For the beam and loading shown, determine the
maximum normal stress due to bending on a transverse section at C.
300 mm
3 kN
3 kN
450 N-m
D
E
200 mm
300 mm
PROBLEM 5.12
Draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the beam and loading
shown, and determine the maximum absolute value (a) of the shear,
(b) of the bending moment.
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
Ch. 10.1 - Knowing that the spring at A is of constant k and...Ch. 10.1 - Two rigid bars AC and BC are connected by a pin at...Ch. 10.1 - 10.3 and 10.4 Two rigid bars AC and BC are...Ch. 10.1 - 10.3 and 10.4 Two rigid bars AC and BC are...Ch. 10.1 - The steel rod BC is attached to the rigid bar AB...Ch. 10.1 - The rigid rod AB is attached to a hinge at A and...Ch. 10.1 - The rigid bar AD is attached to two springs of...Ch. 10.1 - A frame consists of four L-shaped members...Ch. 10.1 - Determine the critical load of a pin-ended steel...Ch. 10.1 - Determine the critical load of a pin-ended wooden...
Ch. 10.1 - A column of effective length L can be made by...Ch. 10.1 - A compression member of 1.5-m effective length...Ch. 10.1 - Determine the radius of the round strut so that...Ch. 10.1 - Determine (a) the critical load for the square...Ch. 10.1 - A column with the cross section shown has a...Ch. 10.1 - A column is made from half of a W360 216...Ch. 10.1 - A column of 22-ft effective length is made by...Ch. 10.1 - A single compression member of 8.2-m effective...Ch. 10.1 - Knowing that P = 5.2 kN, determine the factor of...Ch. 10.1 - Members AB and CD are 30-mm-diameter steel rods,...Ch. 10.1 - The uniform brass bar AB has a rectangular cross...Ch. 10.1 - A 1-in.-square aluminum strut is maintained in the...Ch. 10.1 - A 1-in.-square aluminum strut is maintained in the...Ch. 10.1 - Column ABC has a uniform rectangular cross section...Ch. 10.1 - Column ABC has a uniform rectangular cross section...Ch. 10.1 - Column AB carries a centric load P of magnitude 15...Ch. 10.1 - Each of the five struts shown consists of a solid...Ch. 10.1 - A rigid block of mass m can be supported in each...Ch. 10.2 - An axial load P = 15 kN is applied at point D that...Ch. 10.2 - An axial load P is applied to the 32-mm-diameter...Ch. 10.2 - The line of action of the 310-kN axial load is...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 32PCh. 10.2 - An axial load P is applied to the 32-mm-square...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 34PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 35PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 36PCh. 10.2 - Solve Prob. 10.36, assuming that the axial load P...Ch. 10.2 - The line of action of the axial load P is parallel...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 39PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 40PCh. 10.2 - The steel bar AB has a 3838-in. square cross...Ch. 10.2 - For the bar of Prob. 10.41, determine the required...Ch. 10.2 - A 3.5-m-long steel tube having the cross section...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 44PCh. 10.2 - An axial load P is applied to the W8 28...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 46PCh. 10.2 - A 100-kN axial load P is applied to the W150 18...Ch. 10.2 - A 26-kip axial load P is applied to a W6 12...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 49PCh. 10.2 - Axial loads of magnitude P = 84 kN are applied...Ch. 10.2 - An axial load of magnitude P = 220 kN is applied...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 52PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 53PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 54PCh. 10.2 - Axial loads of magnitude P = 175 kN are applied...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 56PCh. 10.3 - Using allowable stress design, determine the...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 58PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 59PCh. 10.3 - A column having a 3.5-m effective length is made...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 61PCh. 10.3 - Bar AB is free at its end A and fixed at its base...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 63PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 64PCh. 10.3 - A compression member of 8.2-ft effective length is...Ch. 10.3 - A compression member of 9-m effective length is...Ch. 10.3 - A column of 6.4-m effective length is obtained by...Ch. 10.3 - A column of 21-ft effective length is obtained by...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 69PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 70PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 71PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 72PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 73PCh. 10.3 - For a rod made of aluminum alloy 2014-T6, select...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 75PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 76PCh. 10.3 - A column of 4.6-m effective length must carry a...Ch. 10.3 - A column of 22.5-ft effective length must carry a...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 79PCh. 10.3 - A centric load P must be supported by the steel...Ch. 10.3 - A square steel tube having the cross section shown...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 82PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 83PCh. 10.3 - Two 89 64-mm angles are bolted together as shown...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 85PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 86PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 87PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 88PCh. 10.4 - An eccentric load is applied at a point 22 mm from...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 90PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 91PCh. 10.4 - Solve Prob. 10.91 using the interaction method and...Ch. 10.4 - A column of 5.5-m effective length is made of the...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 94PCh. 10.4 - A steel compression member of 9-ft effective...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 96PCh. 10.4 - Two L4 3 38-in. steel angles are welded together...Ch. 10.4 - Solve Prob. 10.97 using the interaction method...Ch. 10.4 - A rectangular column is made of a grade of sawn...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 100PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 101PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 102PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 103PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 104PCh. 10.4 - A steel tube of 80-mm outer diameter is to carry a...Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 106PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 107PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 108PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 109PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 110PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 111PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 112PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 113PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 114PCh. 10.4 - Prob. 115PCh. 10.4 - A steel column of 7.2-m effective length is to...Ch. 10 - Determine (a) the critical load for the steel...Ch. 10 - Prob. 118RPCh. 10 - Prob. 119RPCh. 10 - (a) Considering only buckling in the plane of the...Ch. 10 - Member AB consists of a single C130 3 10.4 steel...Ch. 10 - The line of action of the 75-kip axial load is...Ch. 10 - Prob. 123RPCh. 10 - Prob. 124RPCh. 10 - A rectangular column with a 4.4-m effective length...Ch. 10 - Prob. 126RPCh. 10 - Prob. 127RPCh. 10 - Prob. 128RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- CORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I REALLY NEED FBD. The cantilevered spandrel beam shown whose depth tapers from d1 to d2, has a constant width of 120mm. It carries a triangularly distributed end reaction.Given: d1 = 600 mm, d2 = 120 mm, L = 1 m, w = 100 kN/m1. Calculate the maximum flexural stress at the support, in kN-m.2. Determine the distance (m), from the free end, of the section with maximum flexural stress.3. Determine the maximum flexural stress in the beam, in MPa.ANSWERS: (1) 4.630 MPa; (2) 905.8688 m; (3) 4.65 MPaarrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I REALLY NEED FBD A concrete wall retains water as shown. Assume that the wall is fixed at the base. Given: H = 3 m, t = 0.5m, Concrete unit weight = 23 kN/m3Unit weight of water = 9.81 kN/m3(Hint: The pressure of water is linearly increasing from the surface to the bottom with intensity 9.81d.)1. Find the maximum compressive stress (MPa) at the base of the wall if the water reaches the top.2. If the maximum compressive stress at the base of the wall is not to exceed 0.40 MPa, what is the maximum allowable depth(m) of the water?3. If the tensile stress at the base is zero, what is the maximum allowable depth (m) of the water?ANSWERS: (1) 1.13 MPa, (2) 2.0 m, (3) 1.20 marrow_forwardCORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I NEED FBD A short plate is attached to the center of the shaft as shown. The bottom of the shaft is fixed to the ground.Given: a = 75 mm, h = 125 mm, D = 38 mmP1 = 24 kN, P2 = 28 kN1. Calculate the maximum torsional stress in the shaft, in MPa.2. Calculate the maximum flexural stress in the shaft, in MPa.3. Calculate the maximum horizontal shear stress in the shaft, in MPa.ANSWERS: (1) 167.07 MPa; (2) 679.77 MPa; (3) 28.22 MPaarrow_forward
- CORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I REALLY NEED FBD. The roof truss shown carries roof loads, where P = 10 kN. The truss is consisting of circular arcs top andbottom chords with radii R + h and R, respectively.Given: h = 1.2 m, R = 10 m, s = 2 m.Allowable member stresses:Tension = 250 MPaCompression = 180 MPa1. If member KL has square section, determine the minimum dimension (mm).2. If member KL has circular section, determine the minimum diameter (mm).3. If member GH has circular section, determine the minimum diameter (mm).ANSWERS: (1) 31.73 mm; (2) 35.81 mm; (3) 18.49 mmarrow_forwardPROBLEM 3.23 3.23 Under normal operating condi- tions a motor exerts a torque of magnitude TF at F. The shafts are made of a steel for which the allowable shearing stress is 82 MPa and have diameters of dCDE=24 mm and dFGH = 20 mm. Knowing that rp = 165 mm and rg114 mm, deter- mine the largest torque TF which may be exerted at F. TF F rG- rp B CH TE Earrow_forward1. (16%) (a) If a ductile material fails under pure torsion, please explain the failure mode and describe the observed plane of failure. (b) Suppose a prismatic beam is subjected to equal and opposite couples as shown in Fig. 1. Please sketch the deformation and the stress distribution of the cross section. M M Fig. 1 (c) Describe the definition of the neutral axis. (d) Describe the definition of the modular ratio.arrow_forward
- using the theorem of three moments, find all the moments, I only need concise calculations with minimal explanations. The correct answers are provided at the bottomarrow_forwardMechanics of materialsarrow_forwardusing the theorem of three moments, find all the moments, I need concise calculations onlyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Column buckling; Author: Amber Book;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AvvaCi_Nn94;License: Standard Youtube License