
Concept explainers
For Exercises 28 through 33, do a complete
a. Draw a
b. Compute the
c. State the hypotheses.
d. Test the hypotheses at α = 0.05. Use Table I.
e. Determine the regression line equation if r is significant.
f. Plot the regression line on the scatter plot, if appropriate.
g. Summarize the results.
32. Television Viewers A television executive selects 10 television shows and compares the average number of viewers the show had last year with the average number of viewers this year. The data (in millions) are shown. Describe the relationship.
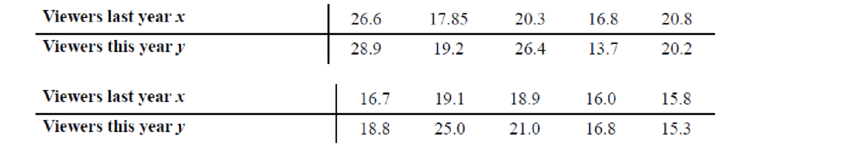
a.
To construct: The scatterplot for the variablesthe average number of viewers the show hadlast year and the average number of viewers this year.
Answer to Problem 32E
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The data shows the average number of viewers the show hadlast year (x) and the average number of viewers this year(y) values.
Calculation:
Step by step procedure to obtain scatterplot using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Scatterplot.
- Choose Simple and then click OK.
- Under Y variables, enter a column ofViewers last year.
- Under X variables, enter a column of Viewers this year.
- Click OK.
b.
To compute: The value of the correlation coefficient.
Answer to Problem 32E
The value of the correlation coefficientis 0.839.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Correlation coefficient r:
Software Procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the ‘correlation coefficient’ using the MINITAB software:
- Select Stat >Basic Statistics > Correlation.
- In Variables, select x and y from the box on the left.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:

From the MINITAB output, the value of the correlation is 0.839.
c.
To state: The hypothesis.
Answer to Problem 32E
The null hypothesis is
The alternative hypothesis is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no linear relation betweenthe average number of viewers the show hadlast year and the average number of viewers this year.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, there is a linear relationbetween the average number of viewers the show hadlast year and the average number of viewers this year.
d.
To test: The significance of the correlation coefficient at
Answer to Problem 32E
The conclusion is that, there is a sufficient evidence to support the claim that linear relation betweenthe average number of viewers the show had last year and the average number of viewers this year.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The level of significance is
Calculation:
The sample size is 10.
The formula to find the degrees of the freedom is
That is,
From the “TABLE –I: Critical Values for the PPMC”, the critical value for 4 degrees of freedom and
Rejection Rule:
If the absolute value of r is greater than the critical value then reject the null hypothesis.
Conclusion:
From part (b), the value of r is0.839 that is the absolute value of r is 0.839.
Here, the absolute value of r is greater than the critical value
That is,
By the rejection rule,reject the null hypothesis.
There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that “there is alinear relation betweenthe average number of viewers the show had last year and the average number of viewers this year”.
e.
To find: The regression equation for the given data.
Answer to Problem 32E
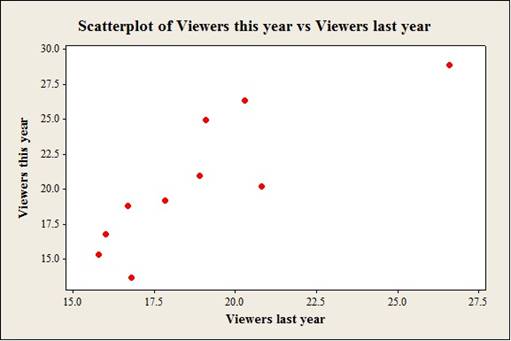
The regression equation for the given datais
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Regression:
Software procedure:
Step by step procedure to obtain the regression equation using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Regression > Regression.
- In Responses, enter the column ofViewers this year.
- In Predictors, enter the column ofViewers last year.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
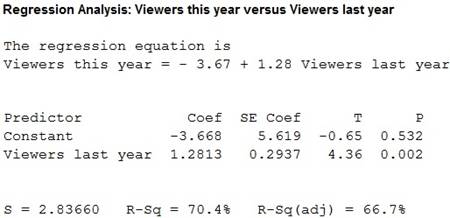
Thus, regression equation for the given datais
f.
To construct: The scatterplot for the variablesthe average number of viewers the show hadlast year and the average number of viewers this year.
Answer to Problem 32E
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
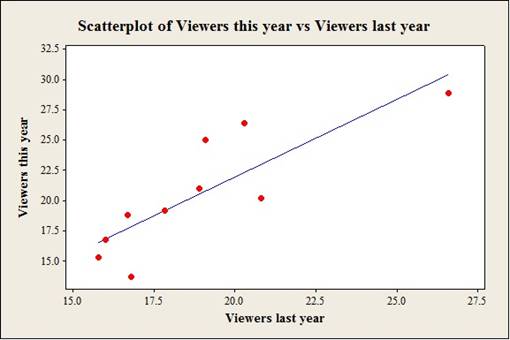
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Step by step procedure to obtain scatterplot using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Scatterplot.
- Choose with line and then click OK.
- Under Y variables, enter a column of Viewers last year.
- Under X variables, enter a column of Viewers this year.
- Click OK.
g.
To summarize: The results.
Answer to Problem 32E
Explanation of Solution
Justification:
Thus, there is a sufficient evidence to support the claim that linear relation betweenthe average number of viewers the show had last year and the average number of viewers this year.
h.
To explain: The type of relation.
Answer to Problem 32E
The type of relation is the positivelinear relation.
Explanation of Solution
Justification:
From part (a), it is observed that there is a positive linear relation between the variables.
Thus, it can be conclude that there is the type of the relation is “linear relation”.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
ELEMENTARY STATISTICS W/CONNECT >IP<
- how could the bar graph have been organized differently to make it easier to compare opinion changes within political partiesarrow_forwardDraw a picture of a normal distribution with mean 70 and standard deviation 5.arrow_forwardWhat do you guess are the standard deviations of the two distributions in the previous example problem?arrow_forward
- Please answer the questionsarrow_forward30. An individual who has automobile insurance from a certain company is randomly selected. Let Y be the num- ber of moving violations for which the individual was cited during the last 3 years. The pmf of Y isy | 1 2 4 8 16p(y) | .05 .10 .35 .40 .10 a.Compute E(Y).b. Suppose an individual with Y violations incurs a surcharge of $100Y^2. Calculate the expected amount of the surcharge.arrow_forward24. An insurance company offers its policyholders a num- ber of different premium payment options. For a ran- domly selected policyholder, let X = the number of months between successive payments. The cdf of X is as follows: F(x)=0.00 : x < 10.30 : 1≤x<30.40 : 3≤ x < 40.45 : 4≤ x <60.60 : 6≤ x < 121.00 : 12≤ x a. What is the pmf of X?b. Using just the cdf, compute P(3≤ X ≤6) and P(4≤ X).arrow_forward
- 59. At a certain gas station, 40% of the customers use regular gas (A1), 35% use plus gas (A2), and 25% use premium (A3). Of those customers using regular gas, only 30% fill their tanks (event B). Of those customers using plus, 60% fill their tanks, whereas of those using premium, 50% fill their tanks.a. What is the probability that the next customer will request plus gas and fill the tank (A2 B)?b. What is the probability that the next customer fills the tank?c. If the next customer fills the tank, what is the probability that regular gas is requested? Plus? Premium?arrow_forward38. Possible values of X, the number of components in a system submitted for repair that must be replaced, are 1, 2, 3, and 4 with corresponding probabilities .15, .35, .35, and .15, respectively. a. Calculate E(X) and then E(5 - X).b. Would the repair facility be better off charging a flat fee of $75 or else the amount $[150/(5 - X)]? [Note: It is not generally true that E(c/Y) = c/E(Y).]arrow_forward74. The proportions of blood phenotypes in the U.S. popula- tion are as follows:A B AB O .40 .11 .04 .45 Assuming that the phenotypes of two randomly selected individuals are independent of one another, what is the probability that both phenotypes are O? What is the probability that the phenotypes of two randomly selected individuals match?arrow_forward
- 53. A certain shop repairs both audio and video compo- nents. Let A denote the event that the next component brought in for repair is an audio component, and let B be the event that the next component is a compact disc player (so the event B is contained in A). Suppose that P(A) = .6 and P(B) = .05. What is P(BA)?arrow_forward26. A certain system can experience three different types of defects. Let A;(i = 1,2,3) denote the event that the sys- tem has a defect of type i. Suppose thatP(A1) = .12 P(A) = .07 P(A) = .05P(A, U A2) = .13P(A, U A3) = .14P(A2 U A3) = .10P(A, A2 A3) = .011Rshelfa. What is the probability that the system does not havea type 1 defect?b. What is the probability that the system has both type 1 and type 2 defects?c. What is the probability that the system has both type 1 and type 2 defects but not a type 3 defect? d. What is the probability that the system has at most two of these defects?arrow_forwardThe following are suggested designs for group sequential studies. Using PROCSEQDESIGN, provide the following for the design O’Brien Fleming and Pocock.• The critical boundary values for each analysis of the data• The expected sample sizes at each interim analysisAssume the standardized Z score method for calculating boundaries.Investigators are evaluating the success rate of a novel drug for treating a certain type ofbacterial wound infection. Since no existing treatment exists, they have planned a one-armstudy. They wish to test whether the success rate of the drug is better than 50%, whichthey have defined as the null success rate. Preliminary testing has estimated the successrate of the drug at 55%. The investigators are eager to get the drug into production andwould like to plan for 9 interim analyses (10 analyzes in total) of the data. Assume thesignificance level is 5% and power is 90%.Besides, draw a combined boundary plot (OBF, POC, and HP)arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL





