
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780073398242
Author: Ferdinand P. Beer, E. Russell Johnston Jr., David Mazurek, Phillip J. Cornwell, Brian Self
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10.1, Problem 10.47P
Denoting the coefficient of static friction between collar C and the vertical rod by μS, derive an expression for the magnitude of the largest couple M for which equilibrium is maintained in the position shown. Explain what happens if μS ≥ tan θ.
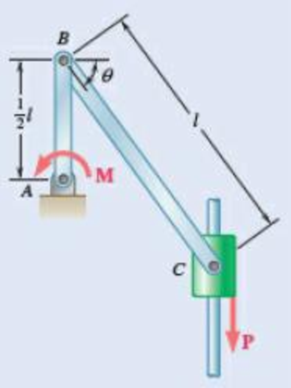
Fig. P10.47and P10.48
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
In the image is a right rectangular pyramid of total mass m. Note the location of point Q. Determine the inertia dyadic for the pyramid P, relative to point Q for e hat unit vectors.
auto controls
I am having a hard time solving for the vector v in the equation in the image. Can you help me?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Ch. 10.1 - Determine the vertical force P that must be...Ch. 10.1 - Determine the horizontal force P that must be...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.3PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.4PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.5PCh. 10.1 - A spring of constant 15 kN/m connects points C and...Ch. 10.1 - The two-bar linkage shown is supported by a pin...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.8PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.9PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.10P
Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.11PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.12PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.13PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.14PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.15PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.16PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.17PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.18PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.19PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.20PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.21PCh. 10.1 - A couple M with a magnitude of 100 Nm isapplied as...Ch. 10.1 - Rod AB is attached to a block at A that can...Ch. 10.1 - Solve Prob. 10.23, assuming that the 800-N force...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.25PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.26PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.27PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.28PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.29PCh. 10.1 - Two rods AC and CE are connected by a pin at Cand...Ch. 10.1 - Solve Prob. 10.30 assuming that force P is movedto...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.32PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.33PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.34PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.35PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.36PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.37PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.38PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.39PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.40PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.41PCh. 10.1 - The position of boom ABC is controlled by...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.43PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.44PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.45PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.46PCh. 10.1 - Denoting the coefficient of static friction...Ch. 10.1 - Prob. 10.48PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.49PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.50PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.51PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.52PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.53PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.54PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.55PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.56PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.57PCh. 10.1 - Prob. 10.58PCh. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob. 10.29....Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.60PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.61PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.62PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.63PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.64PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.65PCh. 10.2 - Using the method of Sec. 10.2C, solve Prob. 10.38....Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.67PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.68PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.69PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.70PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.71PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.72PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.73PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.74PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.75PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.76PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.77PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.78PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.79PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.80PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.81PCh. 10.2 - A spring AB of constant k is attached to two...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.83PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.84PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.85PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.86PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.87PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.88PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.89PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.90PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.91PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.92PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.93PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.94PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.95PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.96PCh. 10.2 - Bars AB and BC, each with a length l and of...Ch. 10.2 - Prob. 10.98PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.99PCh. 10.2 - Prob. 10.100PCh. 10 - Determine the vertical force P that must be...Ch. 10 - Determine the couple M that must be applied...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.103RPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.104RPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.105RPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.106RPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.107RPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.108RPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.109RPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.110RPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.111RPCh. 10 - Prob. 10.112RP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 4 ft 300 Ib 1000 Ib.ft 350 Ib C 2 ft 3. 45° 250 Ib B. 3ft B 25ft 200 Ib 150 Ib Replace the force system acting on the frame shown in the figure by a resultant force (magnitude and direction), and specify where its line of action intersects member (AB), measured from point (A).arrow_forwardCan you research the standard percentage of Steam Quality in:(1.) Boiler - leaving boilerBoiler -> Out(2.) Condenser - coming in condenser In -> CondenserProvide reference Also define: steam quality, its purpose and importancearrow_forwardNumbers 1 and 2 and 5 are are optional problems. However, I only need the values (with units) of 3, 4 and 6. Thank you :)arrow_forward
- Three cables are pulling on a ring located at the origin, as shown in the diagram below. FA is 200 N in magnitude with a transverse angle of 30° and an azimuth angle of 140°. FB is 240 N in magnitude with coordinate direction angles α = 135° and β = 45°. Determine the magnitude and direction of FC so that the resultant of all 3 force vectors lies on the z-axis and has a magnitude of 300 N. Specify the direction of FC using its coordinate direction angles.arrow_forwardturbomachieneryarrow_forwardauto controlsarrow_forward
- auto controlsarrow_forward1 Pleasearrow_forwardA spring cylinder system measures the pressure. Determine which spring can measure pressure between 0-1 MPa with a large excursion. The plate has a diameter of 20 mm. Also determine the displacement of each 0.1 MPa step.Spring power F=c x fF=Springpower(N)c=Spring constant (N/mm)f=Suspension (mm) How do I come up with right answer?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Introduction To Engg Mechanics - Newton's Laws of motion - Kinetics - Kinematics; Author: EzEd Channel;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ksmsp9OzAsI;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY