
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structural formulas of the initial and final oxidation products of the given compounds are to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
The chemical oxidant has the tendency to oxidize other substances. One of the strongest oxidizing agents is potassium permanganate which oxidizes various
(a)
Answer to Problem ISP
The structural formulas of the initial and final oxidation products of the given compounds are shown below.
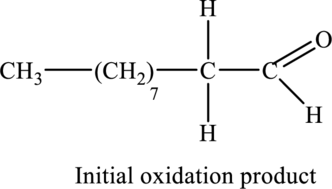
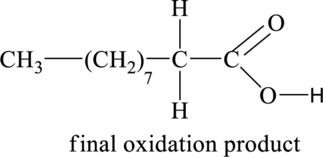
Explanation of Solution
The give compound,
According to the basic chemical properties, when alcohols are treated with aqueous potassium permanganate, they undergo oxidation and initially form aldehyde which on further oxidation gives carboxylic acid as potassium permanganate is strong oxidizing agent.
The oxidation of the given compound,
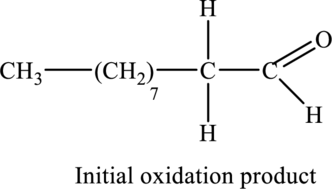
Figure 1
The above shown initial oxidation product undergoes further oxidation and results in the formation of final oxidation product. Thus, the structural formula of the final oxidation product is shown below.
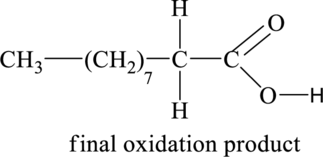
Figure 2
(b)
Interpretation:
The chemical equation for the reaction occurs in part (a) between the initial reactant and the final oxidation product has to be shown.
Concept Introduction:
Same as part (a).
(b)
Answer to Problem ISP
The chemical equation for the reaction occurs in part (a) between the initial reactant and the final oxidation product is shown below.
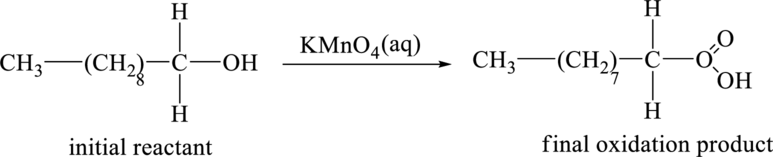
Explanation of Solution
The initial reactant in the part (a) is the give compound,
The initial reactant,
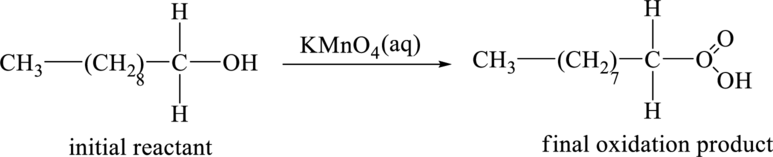
Figure 3
(c)
Interpretation:
The class of the product so obtained in the reaction of part (b) has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Same as part (a).
(c)
Answer to Problem ISP
The class of the product so obtained in the reaction of part (b) is carboxylic acid.
Explanation of Solution
The initial reactant,
The molecular formula of the product so obtained in part (b) contains
(d)
Interpretation:
The chemical equation for the reaction between the final product in part (b) and sodium hydroxide has to be determined. Also, the product of the reaction when it takes place in acidic condition has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Same as part (a).
(d)
Answer to Problem ISP
The chemical equation for the reaction between the final product in part (b) and sodium hydroxide is,
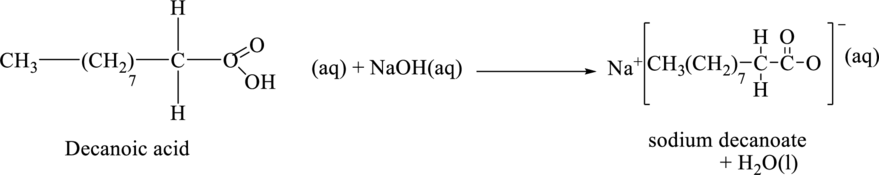
The product of the reaction when it takes place in acidic condition is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
The chemical formula of the final product of part (b) is
The chemical equation for the reaction between the final product of part (b) and sodium hydroxide is shown below.
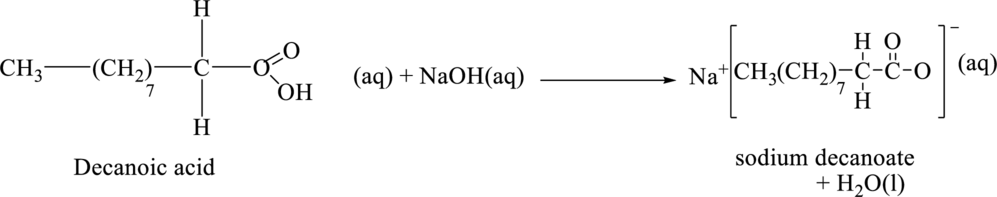
Figure 4
The dissociation of
(e)
Interpretation:
The structural formula for the product of the reaction when final oxidation product in part (a) reacts with dimethlyamine has to be determined. Also the class of the compound so formed has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Same as part (a).
(e)
Answer to Problem ISP
The structural formula for the product of the reaction when final oxidation product in part (a) reacts with dimethlyamine is,
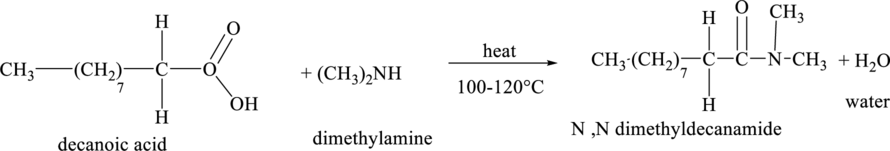
The molecular formula of the product so obtained in the above reaction contains
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula of the final oxidation product of part (a) is shown below.
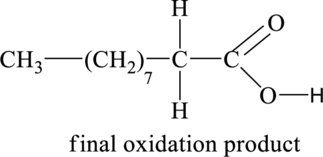
Figure 2
An amide bond is formed between a carboxylic acid and an amine. Peptide linkage is formed between two amino acids. The carboxylic acid group of one amino acid reacts with an amino group of another amino acid to form an amide bond by removing a water molecule.
The chemical reaction between the final oxidation productof part (a) with dimethlyamine is shown below.
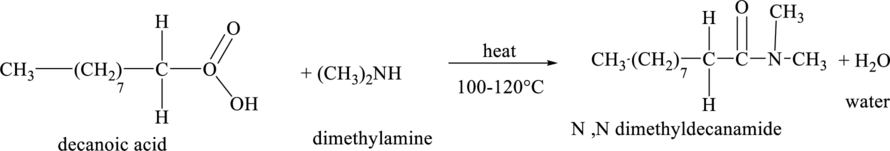
Figure 5
The molecular formula of the product so obtained in the above reaction contains
Thus, the structural formula of the product of the reaction of final oxidation product of part (a) with dimethlyamine is shown below.
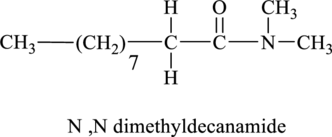
Figure 6
(f)
Interpretation:
The reason whether the formation of polymer between the two reactants in part (b) has to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
(f)
Answer to Problem ISP
The basic condition for condensation polymerization is that there should be two different functional groups present in the same monomer or in two different monomers. Since this basic condition or requirement is not fulfilled by the reactants of part (b). Thus, the formation of polymer cannot takes place.
Explanation of Solution
The formation of polymer between the two reactants cannot takes place as there is only one functional group present in their structural formula. The basic condition for condensation polymerization is that there should be two different functional groups present in the same monomer or in two different monomers. Since this basic condition or requirement is not fulfilled by the reactants of part (b).
Thus, the formation of polymer cannot takes place.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
- Show the mechanism steps to obtain the lowerenergy intermediate: *see imagearrow_forwardSoap is made by the previous reaction *see image. The main difference between one soap and another soap isthe length (number of carbons) of the carboxylic acid. However, if a soap irritates your skin, they mostlikely used too much lye.Detergents have the same chemical structure as soaps except for the functional group. Detergentshave sulfate (R-SO4H) and phosphate (R-PO4H2) functional groups. Draw the above carboxylic acidcarbon chain but as the two variants of detergents. *see imagearrow_forwardWhat are the reactions or reagents used? *see imagearrow_forward
- The two pKa values of oxalic acid are 1.25 and 3.81. Why are they not the same value? Show the protontransfer as part of your explanation. *see imagearrow_forwardасть Identify all the bonds that gauche interact with C-OMe in the most stable conformation of the above compound.arrow_forwardPredict the reactants used in the formation of the following compounds using Acid-Catalyzed dehydration reactionarrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this?arrow_forward.. Give the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions or sequences of reactions. Show ll relevant stereochemistry [3 ONLY]. A H Br 1. NaCN 2 NaOH, H₂O, heat 3. H3O+ B. CH₂COOH 19000 1. LiAlH4 THF, heat 2 H₂O* C. CH Br 1. NaCN, acetone 2 H3O+, heat D. Br 1. Mg. ether 3. H₂O+ 2 CO₂ E. CN 1. (CH) CHMgBr, ether 2 H₂O+arrow_forwardAssign this COSY spectrumarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

