
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
The fatty acid can react with glycerol to form triglyceride with the formation of ester linkages. The reaction between acid and alcohol gives an ester as a major product. The ester group is derived by a
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: A triglyceride _______
The triglyceride is formed by the reaction of glycerol and fatty acids. It is characterized by the presence of ester linkages. Box C contains a triglyceride.
Thus, A triglyceride Box C.
(b)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into carboxyl group or into an
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Final oxidation product of a primary alcohol Box G.
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into carboxyl group or into an aldehyde or to ketone. Product obtained may depend on the oxidising agent used. Therefore, in presence of mild oxidising agent, one gets aldehyde or ketone. In the presence of strong oxidizing agent, carboxylic acid is obtained.
Thus, final oxidation product of a primary alcohol Box G.
(c)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Condensation polymerization monomer _____.
Box G contains a compound in which two carboxylic groups are present. These two carboxylic groups can undergo condensation polymerization which is characterized by the loss of water molecule.
Thus, Condensation polymerization monomer Box G.
(d)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
Polymers are the high molecular mass compounds. The small monomers units joined together to form large molecule, this reaction is known as polymerization reaction. Addition polymerization is the polymerization in which monomer units are linked together with no side product formation. Addition polymerization is given by the molecules which contains carbon-carbon double bond.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Segment of an
Addition polymers are formed by the addition reaction of two monomer units. There is no by product formed in addition polymerization reaction. The given polymer is formed by the addition polymerization reaction of dichloroethene molecule.
Thus, Segment of an addition polymer molecule Box F.
(e)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into an aldehyde or into ketone. To get an aldehyde or ketone, oxidation of acohol must takes place in the presence of mild oxidising agent such as copper at 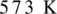 . Product obtained may be aldehyde or ketone. It depends on the nature of alcohol which may be primary, or secondary alcohol.
. Product obtained may be aldehyde or ketone. It depends on the nature of alcohol which may be primary, or secondary alcohol.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Initial oxidation product of a primary alcohol _____.
The initial oxidation of a primary alcohol results in the formation of an aldehyde. Compound in Box D is an aldehyde.
Thus, initial oxidation product of a primary alcohol Box D.
(f)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
An amide bond is formed between a carboxylic acid and an
(f)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Contains an amide bond _____.
An amide bond is formed between a carboxylic acid and an amine. The carboxylic acid group of one amino acid reacts with an amino group of another amino acid to form an amide bond by removing a water molecule. Compound in Box B contains an amide bond.
Thus, Contains an amide bond Box B.
(g)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
Addition polymerization is the polymerization in which monomer units are linked together with no side product formation. Addition polymerization is given by the molecules which contains carbon-carbon double bond.
(g)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Addition polymerization monomer _____.
Addition polymerization is given by the molecules which contains carbon-carbon double bond. Compounds in Boxes A and H contain a double bond.
Thus, Addition polymerization monomers are Box A and Box H.
(h)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
The reaction between acid and alcohol gives an ester as a major product. The ester is derived by a carboxylic acid group in which the acidic hydrogen is replaced by an alkyl group.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Contains an ester linkage _____.
The triglyceride is formed by the reaction of glycerol and fatty acids. It is characterized by the presence of ester linkages. Box C contains a triglyceride.
Thus, contains an ester linkage Box C.
(i)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into an aldehyde or into ketone. To get an aldehyde or ketone, oxidation of acohol must takes place in the presence of mild oxidizing agent such as copper at 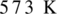 . Product obtained may be aldehyde or ketone. It depends on the nature of alcohol which may be primary, or secondary alcohol.
. Product obtained may be aldehyde or ketone. It depends on the nature of alcohol which may be primary, or secondary alcohol.
(i)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: Final oxidation product of a secondary alcohol _____.
Oxidation of alcohol is the process in which the hydroxyl group of alcohol gets transformed either into an aldehyde or into ketone. Secondary alcohols undergo oxidation to form ketons. Compound in Box I is a ketone.
Thus, final oxidation product of a secondary alcohol is Box I.
(j)
Interpretation:
The given blanks have to be filled with suitable words.
Concept Introduction:
There are three types of alcohols: primary, secondary and tertiary. The type of alcohols depends upon the carbon atom to which the hydroxyl group is attached.
(j)
Explanation of Solution
The given blank is: A tertiary alcohol _____.
The compound given in Box E is a tertiary alcohol. The hydroxyl group is attached with a carbon atom that is attached with three other carbon atoms.
Thus, a tertiary alcohol Box E.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
- Can I get helpp drawing my arrowsarrow_forwardWhich of the m/z values corresponds to the base peak in the mass spectrum shown? 100 80 A. 45 B. 44 C. 29 D. 15 Intensity 20 0 10 20 30 40 B- m/z -8 50 E. 30 Which of the m/z values correspond to the molecular ion for the compound shown? A. 18 B. 82 OH C. 100 D. 102 E. 103arrow_forwardCan someone help me with drawing my arrows.arrow_forward
- I'm having trouble with converting lewis diagrams into VSEPR diagrams. I currently have this example of C2BrCl3 which I want to turn into a lewis structure, but I'm not sure what steps I need to do in order to do so. I have the table written down, however, there's two central atoms so what would I do? There seems to be 4 electron domains on the carbon atom and no lone pairs so it would seem like this shape would be tetrahedral. Here's what I have now. Thanks!arrow_forwardWe discussed the solid phase resin using in peptide synthesis. Provide a mechanism, for its formation. DRAW THE MECHANISM.arrow_forwardPlease help. Every time I've asked an expert in the past, it's been wrong :(arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





