
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The respective reactant (methyl substituted piperidine) and respective product (diene) should be given.
Concept introduction:
Generally
These quaternary ammonium salt under goes an elimination reaction easily.
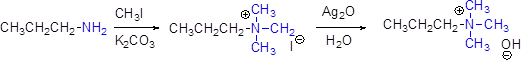
Hofmann elimination:
Quaternary ammonium ion undergoes elimination when using strong base like hydroxide ion this reaction is called as Hofmann elimination.
In the Hofmann elimination, abstraction of proton form β- carbon atom which is having more number of hydrogen to result the elimination product.

(b)
Interpretation:
The respective reactant (methyl substituted piperidine) and respective product (diene) should be given.
Concept introduction:
Hofmann elimination:
Quaternary ammonium ion undergoes elimination when using strong base like hydroxide ion this reaction is called as Hofmann elimination.
In the Hofmann elimination, abstraction of proton form β- carbon atom which is having more number of hydrogen to result the elimination product.

(c)
Interpretation:
The respective reactant (methyl substituted piperidine) and respective product (diene) should be given.
Concept introduction:
Hofmann elimination:
Quaternary ammonium ion undergoes elimination when using strong base like hydroxide ion this reaction is called as Hofmann elimination. Proton abstraction is takes place in β- carbon atom which is having more number of hydrogen.
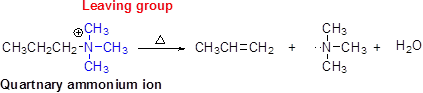
(d)
Interpretation:
The respective reactant (methyl substituted piperidine) and respective product (diene) should be given.
Concept introduction:
Generally amines can’t undergo elimination reaction, therefore amines can be converted in to quaternary ammonium halide by treating with ethyl iodide in basic solution of potassium carbonate, and this ammonium halide is treating with silver oxide to give ammonium hydroxide salt.
These quaternary ammonium salt under goes an elimination reaction easily.
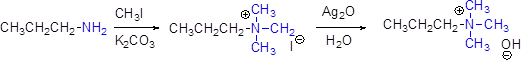
Hofmann elimination:
Quaternary ammonium ion undergoes elimination when using strong base like hydroxide ion this reaction is called as Hofmann elimination.
In the Hofmann elimination, abstraction of proton form β- carbon atom which is having more number of hydrogen to result the elimination product.

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Firefly luciferin exhibits three rings. Identify which of the rings are aromatic. Identify which lone pairs are involved in establishing aromaticity. The lone pairs are labeled A-D below.arrow_forwardWhat is the [OH⁻] of a 1.80 M solution of pyridine (C₅H₅N, Kb = 1.70 × 10⁻⁹)?arrow_forwardWhat is the percent ionization in a 0.260 M solution of formic acid (HCOOH) (Ka = 1.78 × 10⁻⁴)?arrow_forward
- Determine the pH of solution of HC3H5O2 By constructing an ICE table writing the equilibrium constant expression, and using this information to determine the pH. The Ka of HC3H5O2 is 1.3 x 10-5arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction LiNO3arrow_forwardAn unknown weak acid with a concentration of 0.410 M has a pH of 5.600. What is the Ka of the weak acid?arrow_forward
- (racemic) 19.84 Using your reaction roadmaps as a guide, show how to convert 2-oxepanone and ethanol into 1-cyclopentenecarbaldehyde. You must use 2-oxepanone as the source of all carbon atoms in the target molecule. Show all reagents and all molecules synthesized along the way. & + EtOH H 2-Oxepanone 1-Cyclopentenecarbaldehydearrow_forwardR₂ R₁ R₁ a R Rg Nu R₂ Rg R₁ R R₁₂ R3 R R Nu enolate forming R₁ R B-Alkylated carbonyl species or amines Cyclic B-Ketoester R₁₁ HOB R R₁B R R₁₂ B-Hydroxy carbonyl R diester R2 R3 R₁ RB OR R₂ 0 aB-Unsaturated carbonyl NaOR Aldol HOR reaction 1) LDA 2) R-X 3) H₂O/H₂O ketone, aldehyde 1) 2°-amine 2) acid chloride 3) H₂O'/H₂O 0 O R₁ R₁ R R₁ R₁₂ Alkylated a-carbon R₁ H.C R₁ H.C Alkylated methyl ketone acetoacetic ester B-Ketoester ester R₁ HO R₂ R B-Dicarbonyl HO Alkylated carboxylic acid malonic ester Write the reagents required to bring about each reaction next to the arrows shown. Next, record any regiochemistry or stereochemistry considerations relevant to the reaction. You should also record any key aspects of the mechanism, such as forma- tion of an important intermediate, as a helpful reminder. You may want to keep track of all reactions that make carbon-carbon bonds, because these help you build large molecules from smaller fragments. This especially applies to the reactions in…arrow_forwardProvide the reasonable steps to achieve the following synthesis.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


