
Concept explainers
The management of Golding Company has determined that the cost to investigate a variance produced by its
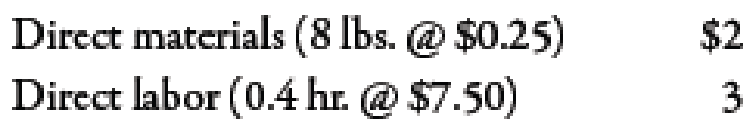
Actual production for the past 3 months follows, with the associated actual usage and costs for materials and labor. There were no beginning or ending raw materials inventories.
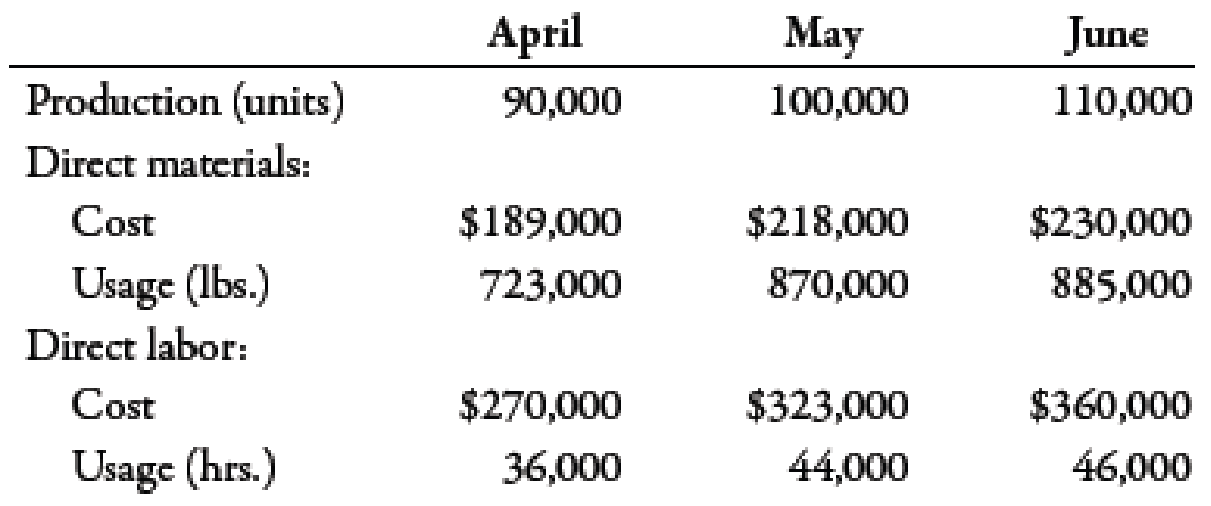
Required:
- 1. What upper and lower control limits would you use for materials variances? For labor variances?
- 2. Compute the materials and labor variances for April, May, and June. Identify those that would require investigation by comparing each variance to the amount of the limit computed in Requirement 1. Compute the actual percentage deviation from standard. Round all unit costs to four decimal places. Round variances to the nearest dollar. Round variance rates to three decimal places so that percentages will show to one decimal place.
- 3. CONCEPTUAL CONNECTION Let the horizontal axis be time and the vertical axis be variances measured as a percentage deviation from standard. Draw horizontal lines that identify upper and lower control limits. Plot the labor and material variances for April, May, and June. Prepare a separate graph for each type of variance. Explain how you would use these graphs (called control charts) to assist your
analysis of variances.
1.
Compute the upper and lower limit of materials and labor.
Explanation of Solution
Variance:
The amount obtained when actual cost is deducted from budgeted cost is known as variance. Variance is calculated to find whether the cost is over applied or under applied.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of upper limit of material for April:
Substitute 0.08 for direct material quantity and $180,750 for price standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of lower limit of material of price standard for April:
Substitute 0.08 for direct material quantity and $180,750 for price standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of upper limit of material of quantity standard for April:
Substitute 0.08 for direct material quantity and $180,000 for quantity standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of lower limit of material of quantity standard for April:
Substitute 0.08 for direct material quantity and $180,000 for quantity standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of upper limit of labor of price standard for April:
Substitute 0.08 for standard quantity and $270,000 for price standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of lower limit of labor of price standard for April:
Substitute 0.08 for standard quantity and $270,000 for price standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of upper limit of labor of efficiency standard for April:
Substitute 0.08 for standard quantity and $270,000 for efficiency standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of lower limit of labor of efficiency standard for April:
Substitute 0.08 for direct material quantity and $270,000 for quantity standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of upper limit of material for May:
Substitute 0.08 for direct material quantity and $217,500 for price standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of lower limit of material of price standard for May:
Substitute 0.08 for direct material quantity and $217,500 for price standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of upper limit of material of quantity standard for May:
Substitute 0.08 for direct material quantity and $200,000 for quantity standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of lower limit of material of quantity standard for May:
Substitute 0.08 for direct material quantity and $200,000 for quantity standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of upper limit of labor of price standard for May:
Substitute 0.08 for standard quantity and $330,000 for price standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of lower limit of labor of price standard for May:
Substitute 0.08 for standard quantity and $330,000 for price standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of upper limit of labor of efficiency standard for May:
Substitute 0.08 for standard quantity and $300,000 for efficiency standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of lower limit of labor of efficiency standard for May:
Substitute 0.08 for direct material quantity and $300,000 for quantity standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of upper limit of material for June:
Substitute 0.08 for direct material quantity and $221,250, for price standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of lower limit of material of price standard for June:
Substitute 0.08 for direct material quantity and $221,250 for price standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of upper limit of material of quantity standard for June:
Substitute 0.08 for direct material quantity and $220,000 for quantity standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of lower limit of material of quantity standard for June:
Substitute 0.08 for direct material quantity and $220,000 for quantity standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of upper limit of labor of price standard for June:
Substitute 0.08 for standard quantity and $345,000 for price standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of lower limit of labor of price standard for June:
Substitute 0.08 for standard quantity and $345,000 for price standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of upper limit of labor of efficiency standard for June:
Substitute 0.08 for standard quantity and $330,000 for efficiency standard in the above formula.
Use the following formula to calculate the value of lower limit of labor of efficiency standard for June:
Substitute 0.08 for direct material quantity and $330,000 for quantity standard in the above formula.
Working Note:
1. Calculation of price standard for material:
2. Calculation of quantity standard for material:
3. Calculation of price standard for labor:
4. Calculation of efficiency standard for labor:
Note: Other calculations are done in a same manner as mentioned above.
2.
Calculate the materials and labor variances for the month of April, May and June.
Explanation of Solution
| Month |
Variances ($) | Limit |
Deviation (%) |
| April | |||
| Material price variance | 8,242(U) | 14,460 | 4.6 |
| Material usage variance | 750(U) | 14,400 | 0.4 |
| Labor rate variance | 0 | 21,600 | 0.0 |
| Labor efficiency variance | 0 | 21,600 | 0.0 |
| May | |||
| Material price variance | 522(U) | 17,400 | 0.2 |
| Material usage variance | 17,500(U) | 16,000 | 8.8 |
| Labor rate variance | 7,000(F) | 26,400 | (2.1) |
| Labor efficiency variance | 30,000(U) | 24,000 | 10.0 |
| June | |||
| Material price variance | 8,762(U) | 17,700 | 4.0 |
| Material usage variance | 1,250(U) | 17,600 | 0.6 |
| Labor rate variance | 15,001(U) | 27,600 | 4.3 |
| Labor efficiency variance | 15,000(U) | 26,400 | 4.5 |
Table (1)
3.
Construct the graph for upper and lower limits for month of April, May and June.
Explanation of Solution
Graph of month of Material price variance:
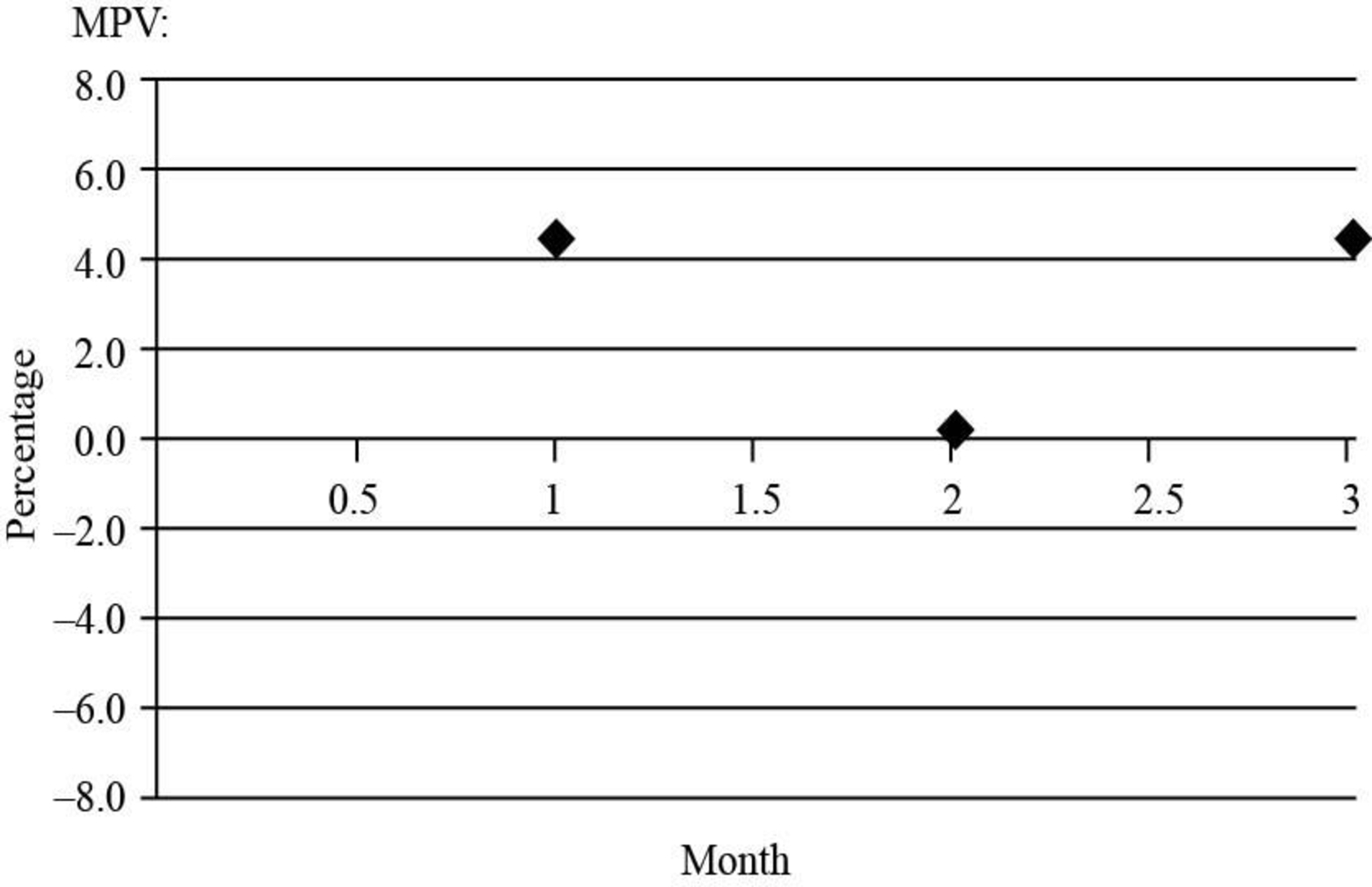
Fig (1)
Graph of month of material usage variance:
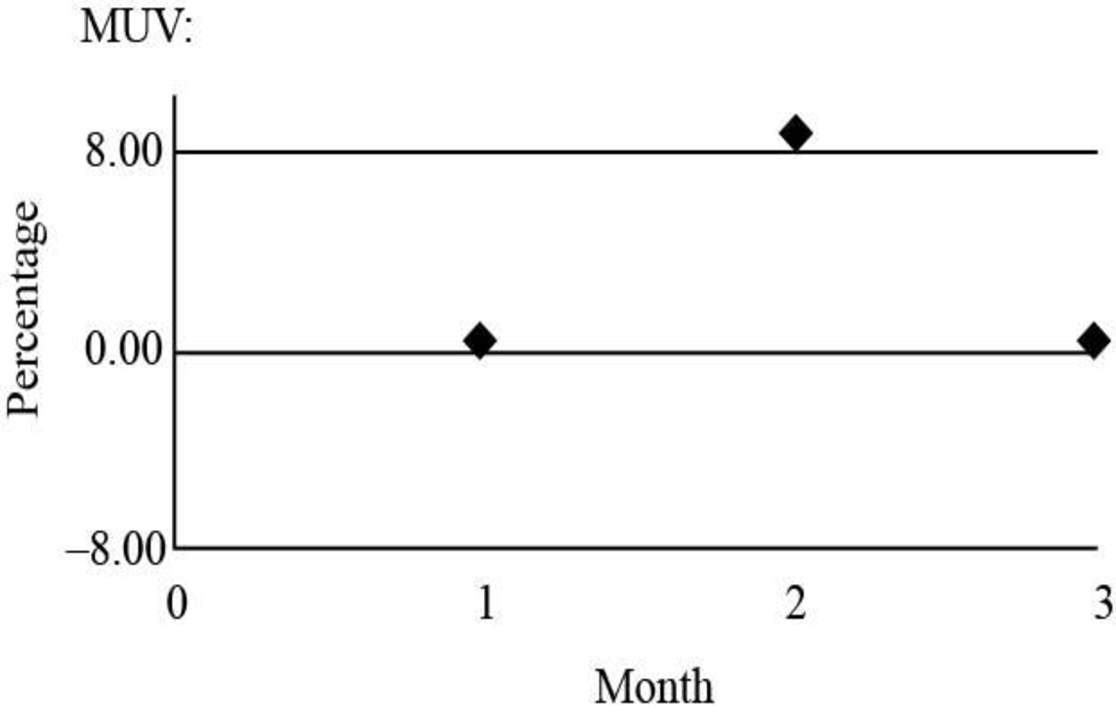
Fig (2)
Graph of month of labor rate variance:
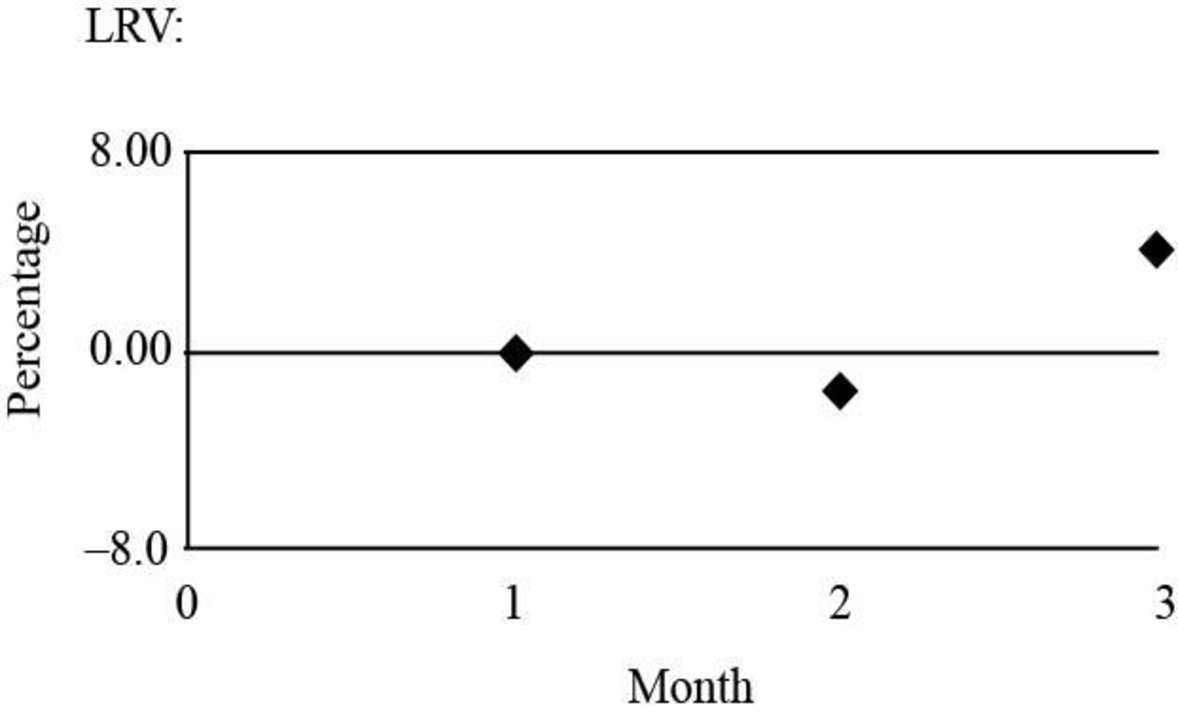
Fig (3)
Graph of month of labor efficiency variance
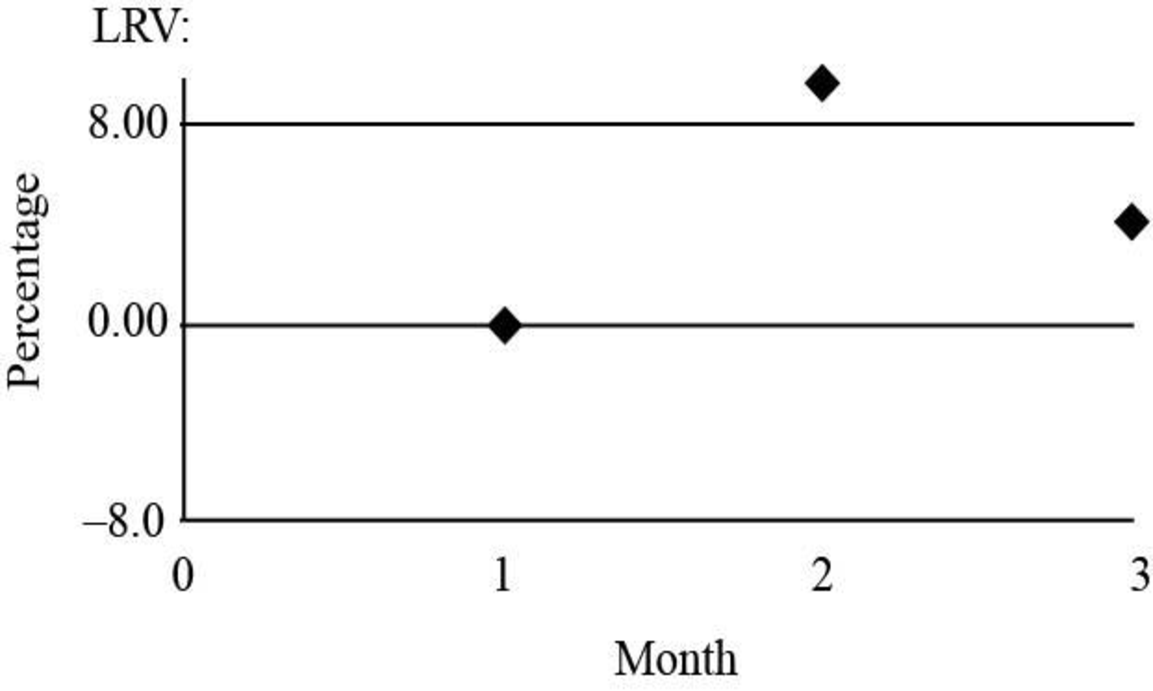
Fig (4)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Bundle: Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Business Decision-Making, 7th + CengageNOWv2, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- On the basis of the following data, what is the estimated cost of the inventory on May 31 using the retail method? Date Line Item Description Cost Retail May 1 Inventory $23,800 $39,670 May 1-31 Purchases 42,600 67,540 May 1-31 Sales 91,090 a. $24,690 b. $19,580 c. $29,564 d. $9,984arrow_forward00000000 The following lots of Commodity Z were available for sale during the year. Line Item Description Units and Cost Beginning inventory 12 units at $48 First purchase 15 units at $53 Second purchase 55 units at $56 Third purchase 13 units at $61 The firm uses the periodic inventory system, and there are 25 units of the commodity on hand at the end of the year. What is the ending inventory balance of Commodity Z using LIFO? a. $1,465 b. $1,265 c. $5,244 d. $1,200arrow_forwardBeginning inventory 8 units at $51 First purchase 17 units at $55 Second purchase 26 units at $58 Third purchase 15 units at $63 The firm uses the periodic inventory system, and there are 23 units of the commodity on hand at the end of the year. What is the ending inventory balance of Commodity Z using FIFO? a. $1,173 b. $1,409 c. $3,773 d. $3,796arrow_forward
- 00000arrow_forwardThe inventory data for an item for November are: Nov. 1 Inventory 4 Sold 19 units at $23 8 units 10 Purchased 32 units at $21 25 units 17 Sold 30 Purchased 21 units at $23 Using a perpetual system, what is the cost of goods sold for November if the company uses LIFO? a. $731 b. $861 c. $962 Od. $709arrow_forwardI got the 3rd incorrect. can you help me go step by step. Date Line Item Description Units and Cost Amount Mar. 1 Inventory 21 units @ $31 $651 June 16 Purchase 29 units @ $33 957 Nov. 28 Purchase 39 units @ $39 1,521 Total 89 units $3,129 There are 13 units of the product in the physical inventory at November 30. The periodic inventory system is used. Determine the inventory cost using the weighted average cost methods. $arrow_forward
- 3arrow_forwardBoxwood Company sells blankets for $31 each. The following information was taken from the inventory records during May. The company had no beginning inventory on May 1. Boxwood uses a perpetual inventory system. Date Blankets Units Cost May 3 Purchase 8 $15 10 Sale 5 17 Purchase 10 $18 20 Sale 7 23 Sale 2 30 Purchase 12 $19 Determine the cost of goods sold for the sale of May 20 using the FIFO inventory costing method. a. $201 b. $114 c. $117 O d. $171arrow_forwardIn the month of March, Horizon Textiles Ltd. had 7,500 units in beginning work in process that were 65% complete. During March, 29,500 units were transferred into production from another department. At the end of March, there were 3,800 units in ending work in process that were 40% complete. Compute the equivalent units of production for materials and conversion costs using the weighted-average method.arrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,




