
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product of given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
In the nucleophilic substitution reaction, the
In
The rate determination step is formation of carbocation.
The stability order of carbocation is,
Tertiary > Secondary > Primary
Therefore, tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation. Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergoes
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product of given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
In the nucleophilic substitution reaction, the rate of reaction depends on reactant as well as nucleophile, which are involved in reaction is called bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
In
Reactant and nucleophile are present at the rate determination step.
The order of species involving in
Tertiary < Secondary < Primary
(c)
Interpretation:
The major product of given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Chromic Acid:
Chromic Acid (
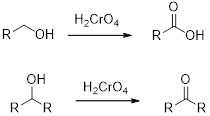
(d)
Interpretation:
The major product of given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid.
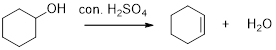
The stability of carbocation is given below,
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary and primary.
(e)
Interpretation:
The major product of given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
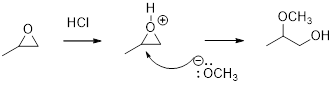
In the presence of acid catalyst, this reaction takes place through partial SN1 and partial SN2 pathway.
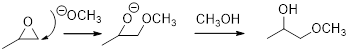
Epoxides are reactive, methoxide ion attacks the Epoxides in a less sterically hindered position which forms the alkoxide ion, and then it gets proton from alcohol which form the product.
(f)
Interpretation:
The major product of given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:

In the presence of acid catalyst, this reaction takes place through partial SN1 and partial SN2 pathway. Epoxides are reactive, Epoxides get protonated followed by alcohol attacks to the stable carbocation and form the product.
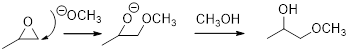
Epoxides are reactive, methoxide ion attacks the Epoxides in a less sterically hindered position which forms the alkoxide ion, and then it gets proton from alcohol which form the product.
(g)
Interpretation:
The major product should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Tosylation reaction:
The alcohol is treated with any tosyl chloride (methane sulfonyl chloride) which yields tosylated product this reaction is called as alkyl tosylate and which is shown below,
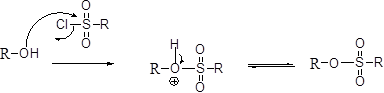
The alcohols is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic acid, the bromine atom attacks back side of the carbon atoms which is bearing alcohol group which yield the corresponding inversion product.
(h)
Interpretation:
The major product of given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Oxidation of alcohol:
Alcohols reaction with hypochlorous (oxidizing agent) in the presence of acetic acid which yields the corresponding
Primary alcohols gives aldehyde, secondary alcohols gives ketone.
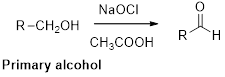
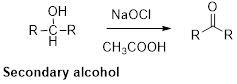
(i)
Interpretation:
The major product should be identified.
Concept introduction:
Generally
For elimination reaction quartnary ammonium halide can be converted in to quartnary ammonium hydroxide by using aqueous silver oxide.
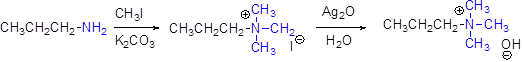
Hofmann elimination:
Quartnary ammonium ion undergoes elimination when using strong base like hydroxide ion this reaction is called as hofmann elimination. Proton abstraction is takes place in β- carbon atom which is having more number of hydrogen.

(j)
Interpretation:
The major product should be identified.
Concept introduction:
The alcohols is reaction with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic which yield the corresponding carbocation intermediate, this carbocation intermediate undergoes substitution reaction which yields the corresponding substitution product.
Tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation.
Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergoes
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions Manual, Books a la Carte Edition (8th Edition)
- Can the target compound at right be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the unsubstituted benzene at left? starting material target If so, draw a synthesis below. If no synthesis using reagents ALEKS recognizes is possible, check the box under the drawing area. Be sure you follow the standard ALEKS rules for submitting syntheses. + More... Note for advanced students: you may assume that you are using a large excess of benzene as your starting material. C T Add/Remove step X ноarrow_forwardWhich one of the following atoms should have the largest electron affinity? a) b) c) d) 으으 e) 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s¹ 1s² 2s² 2p5 1s² 2s² 2p 3s² 3p² 1s² 2s 2p 3s² 3p6 4s2 3ds 1s² 2s² 2p6arrow_forwardAll of the following are allowed energy levels except _. a) 3f b) 1s c) 3d d) 5p e) 6sarrow_forward
- A student wants to make the following product in good yield from a single transformation step, starting from benzene. Add any organic reagents the student is missing on the left-hand side of the arrow, and any addition reagents that are necessary above or below the arrow. If this product can't be made in good yield with a single transformation step, check the box below the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume that an excess of benzene is used as part of the reaction conditions. : ☐ + I X This product can't be made in a single transformation step.arrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction:arrow_forwardCalculate the density of 21.12 g of an object that displaces 0.0250 L of water.arrow_forward
- Draw the expected reactant R28. Cu(II) CO₂Mearrow_forwardPpplllleeeaaasssseeee helllppp wiithhh thisss Organic chemistryyyyyy I talked like this because AI is very annoyingarrow_forwardName the family to which each organic compound belongs. The first answer has been filled in for you. compound CH₂ || CH3-C-NH2 0 ။ CH3-C-CH₂ CH=O–CH=CH, CH₂ HO CH2-CH2-CH-CH3 family amine Darrow_forward
- 1b. Br LOHarrow_forwardI would like my graphs checked please. Do they look right? Do I have iodine and persulfate on the right axis ?arrow_forwardReaction Fill-ins Part 2! Predict the product(s) OR starting material of the following reactions. Remember, Hydride shifts are possible if/when a more stable carbocation can exist (depending on reaction mechanism)! Put your answers in the indicated boxes d. d. ง HCIarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





