
Determine the individual contribution each current source makes to the two nodal voltages V1 and V2 as represented in Fig. 10.67.
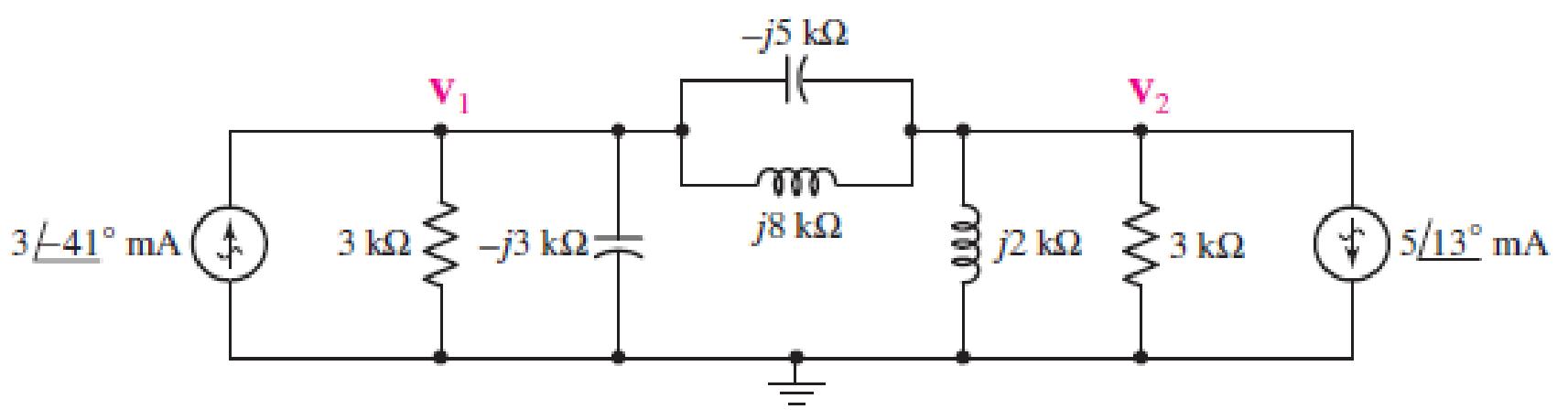
■ FIGURE 10.67
Find the expressions for nodal voltages
Answer to Problem 61E
The expressions for nodal voltages
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Refer to Figure in the respective question.
Case 1:
Redraw Figure, as shown in Figure 1 by making
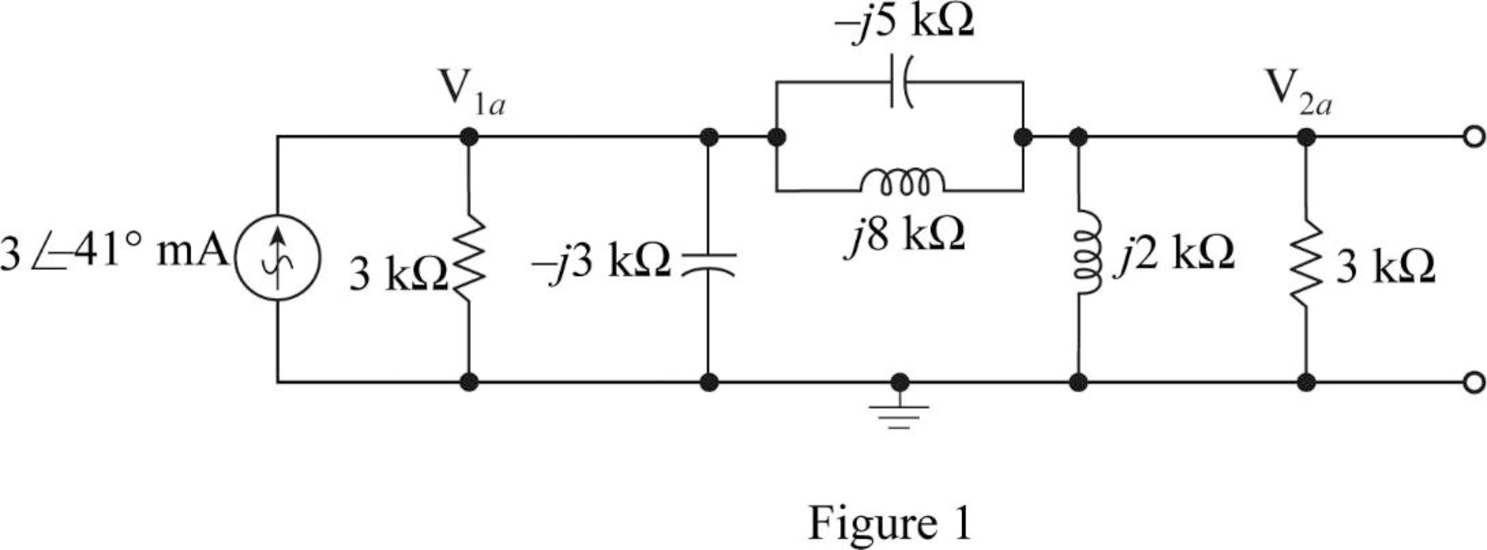
Apply KCL at node
Apply KCL at node
Write the equations (1) and (2) in matrix form.
Write the Matlab code to solve equation (3)
A = [(0.333+i*0.408) (-i*0.075); (-i*0.075) (0.333-i*0.425)];
B = [(2.264-i*1.968);(0)];
C = inv(A)*B
Matlab Output:
C =
-0.17551 - 5.58282i
0.49749 + 0.59541i
Polar equations of node voltages are as follows.
Case 2:
Redraw Figure, as shown in Figure 2 by making
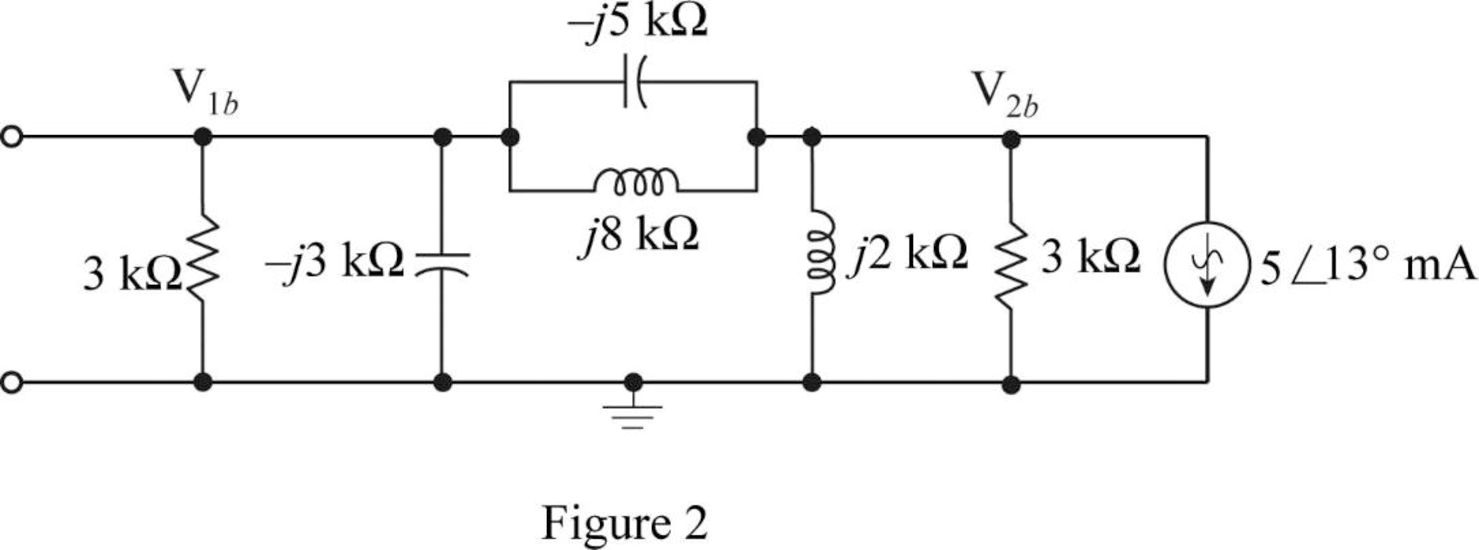
Apply KCL at node
Apply KCL at node
Write the equations (4) and (5) in matrix form.
Write the Matlab code to solve equation (6)
A = [(0.333+i*0.408) (-i*0.075); (-i*0.075) (0.333-i*0.425)];
B = [(0);(-4.87-i*1.124)];
C = inv(A)*B
Matlab Output:
C =
0.3153 - 1.2537i
-3.8514 - 8.2199i
Polar equations of node voltages are as follows.
Find nodal voltage
Substitute
Find nodal voltage
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the expressions for nodal voltages
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
- not use ai pleasearrow_forward17- In 8085 name the 16 bit registers. a) Program Counter b) Stack Pointer c) a and b d) Instruction Register 18- In response to RST 7.5 interrupt, the execution of control transfers to memory location. a) 0000H b) 003CH c) 002CH d) 0034H 19- Let contents of accumulator and B are 00000100 and 01000000 respectively. After execution of SUB B instruction, accumulator contents are a) 11000100 b) 01000000 c) 010001000 d) 00000100arrow_forward1.) A single instruction to clear the lower 4 bits of accumulator in 8085 alp is, a) XRI FOH b) XRI OFH c) ANI OFH d) ANI FO 2.) The status of Z, AC, CY flags after execution of following instructions are, MVI A, A9H MVI B, 57H ADD B HLT a) 0,1,1 b) 1,0,0 c) 1,1,1 d) 1,0,1 3.) Consider the loop: LXI H 000A MVI C OB LOOP: DCX H DCR C JNZ LOOP HLT This loop will be executed by: a) infinite times b) 11 time c) 10 times d) 1 timearrow_forward
- Fundamentals Of Energy Systems HW 6 Q6arrow_forwardFundamentals Of Energy Systems HW 6 Q4arrow_forward1. For the 2-dimensional lattice shown in the following figure, using the two sets of given primitive translation vectors to write the translation vectors that can translate lattice point A to point B. (10 pts) (1) (2) (1) T= (2) T T=arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





