
Assuming the passive sign convention and an operating frequency of 314 rad/s, calculate the phasor voltage V which appears across each of the following when driven by the phasor current 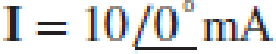 : (a) a 2 Ω resistor; (b) a 1 F capacitor; (c) a 1 H inductor; (d) a 2 Ω resistor in series with a 1 F capacitor; (e) a 2 Ω resistor in series with a 1 H inductor. (f) Calculate the instantaneous value of each voltage determined in parts (a) to (e) at t = 0.
: (a) a 2 Ω resistor; (b) a 1 F capacitor; (c) a 1 H inductor; (d) a 2 Ω resistor in series with a 1 F capacitor; (e) a 2 Ω resistor in series with a 1 H inductor. (f) Calculate the instantaneous value of each voltage determined in parts (a) to (e) at t = 0.
(a)
Find the phasor voltage across
Answer to Problem 33E
The phasor voltage across
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Formula used:
Consider the expression of phasor voltage across resistor.
Here,
Calculation:
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the phasor voltage across
(b)
Find the phasor voltage across
Answer to Problem 33E
The phasor voltage across
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
Consider the expression of phasor voltage across capacitor.
Here,
Calculation:
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the phasor voltage across
(c)
Find the phasor voltage that developed across
Answer to Problem 33E
The phasor voltage that developed across
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
Consider the expression of phasor voltage across inductor.
Here,
Calculation:
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the phasor voltage that developed across
(d)
Find the phasor voltage across series connected
Answer to Problem 33E
The phasor voltage across a series connected
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Find total voltage across a series connected
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the phasor voltage across a series connected
(e)
Find the phasor voltage across series connected
Answer to Problem 33E
The phasor voltage across a series connected
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Find total voltage across a series connected
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the phasor voltage across a series connected
(f)
Find the instantaneous value of each voltage obtained in parts (a) to (e) at
Answer to Problem 33E
The instantaneous value of each voltage obtained in parts (a) to (e) at
Explanation of Solution
Formula used:
Consider the general expression for voltage response.
The complex form of voltage response is,
Calculation:
Part (a):
The phasor voltage across
The instantaneous voltage across
Part (b):
The phasor voltage across
The instantaneous voltage across
Part (c):
The phasor voltage across
The instantaneous voltage across
Part (d):
The phasor voltage across a series connected
The instantaneous voltage across series connected
Part (e):
The phasor voltage across a series connected
The instantaneous voltage across series connected
Conclusion:
Thus, the instantaneous value of each voltage obtained in parts (a) to (e) at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Engineering Circuit Analysis Format: Loose-leaf
- Not use ai pleasearrow_forwardHelp on this equation system?arrow_forwardTransmitting and receiving antennas operating at 1 GHz with gains of 20 and 15 dB, respectively, are separated by a distance of 1 km. Find the power delivered to the load when the input power is 150 W. Assume the PLF = 1.arrow_forward
- Calculate the voltage gain and I/O impedance of circuits shown in Fig. 1. Assume (60 points- each section 20 points) J Vina кат Vb J Vina кат VCC VCC VCC Vino - Vout - Vout Rs w Q2 Q2 (c) (b) Q2 = (a) - Voutarrow_forwardNot use ai please letarrow_forwardUse PSpice to create the circuit and show the circuit along with simulation results. Also please explicitly answer the question (i.e. have the answer make sense and not in parts where there is no final answer.)arrow_forward
- Problem 5 Plot the impulse response of the system shown below. Hint: This is done graphically with 4 convolutions. x[n] D y[n]< D D D D D D D D D D Darrow_forwardUse PSpice to create the circuit. Also please explicitly answer whether the load line intersects the -0.7 line at the computed point.arrow_forwardIn class, we wrote on the blackboard a byte addressable memory where each element was 2 nibbles: For example: Main memory A Address Offset Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 Ox10 0x00 0x02 0x2B Ox4F 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x11 0x12 0x20 0x10 0x10 0x00 OxFF Ox3E DxDD 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 7 0x1C 0x00 8 9 A 0x00 0x00 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x01 B с D E 0x00 0x05 0x04 0x03 0x02 0x00 Ox3D 0x00 0x1C Ox2F 0x00 Ox1F OxFF 0x03 0x02 F What is the contents of address 0x1C in main memory A for a 32 bit machine using Big Endian format? What is the contents of address 0x1C in main memory A for a 16 bit machine using Little Endian format? What is the contents of the indirect address at 0x04 in main memory A for a Big Endian 32 bit machine ((0x4))? What is the contents of 4(0x10) in main memory A for a 16 bit Little Endian machine? What is the contents of the address 16(0xC) for a 64 bit Little Endian machine?arrow_forward
 Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning

