
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The most polar bond of methanol should be identified and polarity described with symbols
Concept Introduction:
Polarity of any molecule depends on electronegativity of atoms that forms covalent bonds. Depending upon the difference in electronegativity of atoms, polar or nonpolar molecule is determined. Polar molecule has electronegativity between 0.5 and 1.4 whereas in nonpolar molecule, it is less than 0.5.
Answer to Problem 43P
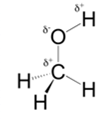
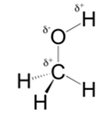
In methanol, most polar bond is O-H bond with electronegativity difference of 1.4 and oxygen atom becomes partial negative charge atom whereas hydrogen becomes partial positive charge atom.
Explanation of Solution
Polar covalent bonds contains more atoms with high electronegativity and acquire more partial negative charge represented as delta minus
In methanol, most polar bond is O-H with electronegativity difference of 1.4 and oxygen atom becomes partial negative charge atom whereas hydrogen becomes partial positive charge atom.
C-O bond have 1.0 electronegativity but it is less polar when compare to O-H bond.
(b)
Interpretation:
The most polar bond of methylamine should be identified and polarity described with symbols
Concept Introduction:
Polarity of any molecule depends on electronegativity of atoms that forms covalent bonds. Depending upon the difference in electronegativity of atoms, polar or nonpolar molecule is determined. Polar molecule has electronegativity between 0.5 and 1.4 whereas in nonpolar molecule, it is less than 0.5.
Answer to Problem 43P
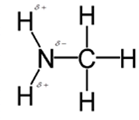
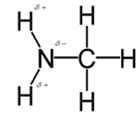
In methylamine, most polar bond is N-H bond with electronegativity difference of 0.9 and nitrogen atom becomes partial negative charge atom whereas hydrogen becomes partial positive charge atom.
Explanation of Solution
Polar covalent bonds contains more atoms with high electronegativity and acquire more partial negative charge represented as delta minus
In methylamine, most polar bond is N-H with electronegativity difference of 0.9 and nitrogen atom becomes partial negative charge atom whereas hydrogen becomes partial positive charge atom.
C-H bond is nonpolar because of electronegativity of 0.4 only.
(c)
Interpretation:
The most polar bond of 2-aminoethathiol should be identified and polarity described with symbols
Concept Introduction:
Polarity of any molecule depends on electronegativity of atoms that forms covalent bonds. Depending upon the difference in electronegativity of atoms, polar or nonpolar molecule is determined. Polar molecule has electronegativity between 0.5 and 1.4 whereas in nonpolar molecule, it is less than 0.5.
Answer to Problem 43P
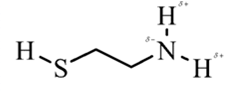
In 2-aminoethathiol, most polar bond is N-Hbond with electronegativity difference of 0.9 and nitrogen atom becomes partial negative charge atom whereas hydrogen becomes partial positive charge atom.
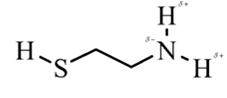
Explanation of Solution
Polar covalent bonds contains more atoms with high electronegativity and acquire more partial negative charge represented as delta minus
In 2-aminoethanethiol, most polar bond is N-H with electronegativity difference of 0.9 and nitrogen atom becomes partial negative charge atom whereas hydrogen becomes partial positive charge atom.
The bonds S-H, C-C and C-H have electronegativity difference are 0.4, 0, and 0.4 respectively.
(d)
Interpretation:
The most polar bond of acetone should be identified and polarity described with symbols
Concept Introduction:
Polarity of any molecule depends on electronegativity of atoms that forms covalent bonds. Depending upon the difference in electronegativity of atoms, polar or nonpolar molecule is determined. Polar molecule has electronegativity between 0.5 and 1.4 whereas in nonpolar molecule, it is less than 0.5.
Answer to Problem 43P
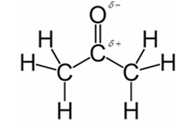
In acetone, most polar bond is C=O with electronegativity difference of 1.0 and oxygen atom becomes partial negative charge atom whereas carbon becomes partial positive charge atom.
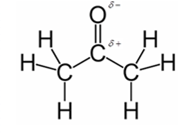
Explanation of Solution
Polar covalent bonds contains more atoms with high electronegativity and acquire more partial negative charge represented as delta minus
In acetone, most polar bond is C=O with electronegativity difference of 1.0 and oxygen atom becomes partial negative charge atom whereas carbon becomes partial positive charge atom.
Other bonds present in acetone are C-H and C-C with electronegativity of 0.4 and 0 respectively.
(e)
Interpretation:
The most polar bond of formaldehyde should be identified and polarity described with symbols
Concept Introduction:
Polarity of any molecule depends on electronegativity of atoms that forms covalent bonds. Depending upon the difference in electronegativity of atoms, polar or nonpolar molecule is determined. Polar molecule has electronegativity between 0.5 and 1.4 whereas in nonpolar molecule, it is less than 0.5.
Answer to Problem 43P
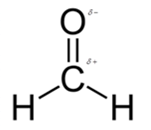
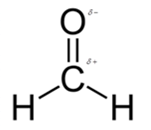
In formaldehyde, most polar bond is C=O with electronegativity difference of 1.0 and oxygen atom becomes partial negative charge atom whereas carbon becomes partial positive charge.
Explanation of Solution
Polar covalent bonds contains more atoms with high electronegativity and acquire more partial negative charge represented as delta minus
In formaldehyde, most polar bond is C=O with electronegativity difference of 1.0 and oxygen atom becomes partial negative charge atom whereas carbon becomes partial positive charge atom.
The bond C-H has electronegativity difference of 0.4 and it is a nonpolar bond.
(f)
Interpretation:
The most polar bond of acetic acid should be identified and polarity described with symbols
Concept Introduction:
Polarity of any molecule depends on electronegativity of atoms that forms covalent bonds. Depending upon the difference in electronegativity of atoms, polar or nonpolar molecule is determined. Polar molecule has electronegativity between 0.5 and 1.4 whereas in nonpolar molecule, it is less than 0.5.
Answer to Problem 43P
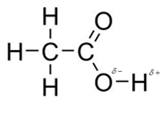
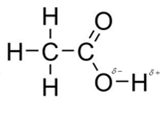
In acetic acid, most polar bond is O-H with electronegativity difference of 1.4 and oxygen atom becomes partial negative charge atom whereas hydrogen becomes partial positive charge atom.
Explanation of Solution
Polar covalent bonds contains more atoms with high electronegativity and acquire more partial negative charge represented as delta minus
In acetic acid, most polar bond is O-H with electronegativity difference of 1.4 and oxygen atom becomes partial negative charge atom whereas hydrogen becomes partial positive charge atom.
The other bonds are C-C, C=O and C-H with electronegativity of 0, 1.0 and 0.4 but bond O-H has more electronegativity as compared to other bonds.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- What are examples of analytical methods that can be used to analyse salt in tomato sauce?arrow_forwardA common alkene starting material is shown below. Predict the major product for each reaction. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the relative stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicable. Ignore any inorganic byproducts H Šali OH H OH Select to Edit Select to Draw 1. BH3-THF 1. Hg(OAc)2, H2O =U= 2. H2O2, NaOH 2. NaBH4, NaOH + Please select a drawing or reagent from the question areaarrow_forwardWhat is the MOHR titration & AOAC method? What is it and how does it work? How can it be used to quantify salt in a sample?arrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this reaction. Cl₂ hv ? Draw only the major product or products in the drawing area below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. If there will be no products because there will be no significant reaction, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Note for advanced students: you can ignore any products of repeated addition. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 80 10 m 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility DII A F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 EO F11arrow_forwardGiven a system with an anodic overpotential, the variation of η as a function of current density- at low fields is linear.- at higher fields, it follows Tafel's law.Calculate the range of current densities for which the overpotential has the same value when calculated for both cases (the maximum relative difference will be 5%, compared to the behavior for higher fields).arrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) AGº = -34. KJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 8.06 atm of nitrogen (N2) and 2.58 atm of ammonia (NH3) at 106. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2 tend to rise or fall? ☐ x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding H2? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding H₂? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. yes no ☐ atm Х ด ? olo 18 Ararrow_forward
- Four liters of an aqueous solution containing 6.98 mg of acetic acid were prepared. At 25°C, the measured conductivity was 5.89x10-3 mS cm-1. Calculate the degree of dissociation of the acid and its ionization constant.Molecular weights: O (15.999), C (12.011), H (1.008).Limiting molar ionic conductivities (λ+0 and λ-0) of Ac-(aq) and H+(aq): 40.9 and 349.8 S cm-2 mol-1.arrow_forwardDetermine the change in Gibbs energy, entropy, and enthalpy at 25°C for the battery from which the data in the table were obtained.T (°C) 15 20 25 30 35Eo (mV) 227.13 224.38 221.87 219.37 216.59Data: n = 1, F = 96485 C mol–1arrow_forwardIndicate the correct options.1. The units of the transport number are Siemens per mole.2. The Siemens and the ohm are not equivalent.3. The Van't Hoff factor is dimensionless.4. Molar conductivity does not depend on the electrolyte concentration.arrow_forward
- Ideally nonpolarizable electrodes can1. participate as reducers in reactions.2. be formed only with hydrogen.3. participate as oxidizers in reactions.4. form open and closed electrochemical systems.arrow_forwardIndicate the options for an electrified interface:1. Temperature has no influence on it.2. Not all theories that describe it include a well-defined electrical double layer.3. Under favorable conditions, its differential capacitance can be determined with the help of experimental measurements.4. A component with high electronic conductivity is involved in its formation.arrow_forwardTo describe the structure of the interface, there are theories or models that can be distinguished by:1. calculation of the charge density.2. distribution of ions in the solution.3. experimentally measured potential difference.4. external Helmoltz plane.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

