
To calculate the surface area of prism using a net
Answer to Problem 3CR
The surface area of prism can be calculated using net
Explanation of Solution
Given information: A prism
Calculation:
The net of a solid figure is formed when a solid figure is unfolded along its edges and its faces are laid out in a pattern in two dimensions. Nets of rectangular prisms are made up of rectangles and squares. Using a net to find the surface area of a rectangular prism
Finding the areas of each of the rectangles and squares of the net of a rectangular prism and adding up those areas gives the surface area or total surface area of the prism.
For example, if the length of one side of the cube 4 units then the area of one its face is,
4 × 4 = 16 square units.
From the net, there are six equal faces and so the total surface area is,
6 × 16 = 96 square units.
Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism using Nets
A rectangular prism or cuboid is formed by folding a net as shown −
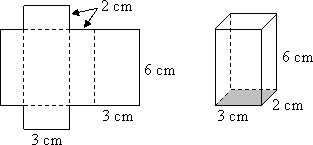
As can be seen from the net that there are two rectangles with dimensions 3 cm by 6 cm, two rectangles with dimensions 2 cm by 6 cm and two rectangles with dimensions 2 cm by 3 cm. The total surface area is then
2 × 3 × 6 + 2 × 2 × 6 + 2 × 2 × 3 = 72 cm2
Chapter 10 Solutions
Pre-Algebra
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
A Problem Solving Approach To Mathematics For Elementary School Teachers (13th Edition)
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
- 1. Given that h(t) = -5t + 3 t². A tangent line H to the function h(t) passes through the point (-7, B). a. Determine the value of ẞ. b. Derive an expression to represent the gradient of the tangent line H that is passing through the point (-7. B). c. Hence, derive the straight-line equation of the tangent line H 2. The function p(q) has factors of (q − 3) (2q + 5) (q) for the interval -3≤ q≤ 4. a. Derive an expression for the function p(q). b. Determine the stationary point(s) of the function p(q) c. Classify the stationary point(s) from part b. above. d. Identify the local maximum of the function p(q). e. Identify the global minimum for the function p(q). 3. Given that m(q) = -3e-24-169 +9 (-39-7)(-In (30-755 a. State all the possible rules that should be used to differentiate the function m(q). Next to the rule that has been stated, write the expression(s) of the function m(q) for which that rule will be applied. b. Determine the derivative of m(q)arrow_forwardSafari File Edit View History Bookmarks Window Help Ο Ω OV O mA 0 mW ర Fri Apr 4 1 222 tv A F9 F10 DII 4 F6 F7 F8 7 29 8 00 W E R T Y U S D பட 9 O G H J K E F11 + 11 F12 O P } [arrow_forwardSo confused. Step by step instructions pleasearrow_forward
- In simplest terms, Sketch the graph of the parabola. Then, determine its equation. opens downward, vertex is (- 4, 7), passes through point (0, - 39)arrow_forwardIn simplest way, For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. a) y = x 2 + 16 x + 39 b) y = 5 x2 - 50 x - 120arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step Write each quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = - 4( x + 6)2 + 36arrow_forward
- In simplest terms and step by step For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. 1) y = - 2 x2 - 28 x + 64 2) y = 6 x2 + 36 x - 42arrow_forwardWrite each relation in standard form a)y = 5(x + 10)2 + 7 b)y = 9(x - 8)2 - 4arrow_forwardIn simplest form and step by step Write the quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = 3(x - 1)2 - 147arrow_forward
- Step by step instructions The path of a soccer ball can be modelled by the relation h = - 0.1 d 2 + 0.5 d + 0.6, where h is the ball’s height and d is the horizontal distance from the kicker. a) Find the zeros of the relation.arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step how do you find the zeros of y = 6x2 + 24x - 192arrow_forwardStep by step Find the zeros of each quadratic relation. a) y = x2 - 16xarrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





