
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
6th Edition
ISBN: 8220102801448
Author: Alexander
Publisher: YUZU
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 31P
Use mesh analysis to determine current Io in the circuit of Fig. 10.79 below.
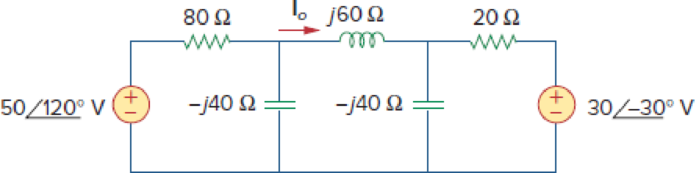
Figure 10.79
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Find Vb and Va using Mesh analysis
1. The communication channel bandwidth is 25 MHz centered at 1GHz and has a noise power spectral
density of 10^-9 W/Hz. The channel loss between the transmitter and receiver is 25dB. The application
requires a bit rate of 200Mbps and BER of less than 10^-4. Excluding Mary FSK, Determine the minimum
transmit power required.
2. An existing system uses noncoherent BASK. The application requires a BER of <10^-5. The current
transmit power is 25 Watts. If the system changes to a coherent BPSK modulation scheme, what is the
new transmit power required to deliver the same BER?
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
Ch. 10.2 - Using nodal analysis, find v1 and v2 is in the...Ch. 10.2 - Calculate V1 and V2 in the circuit shown in Fig....Ch. 10.3 - Find Io in Fig. 10.8 using mesh analysis. Figure...Ch. 10.3 - Figure 10.11 For Practice Prob. 10.4. Calculate...Ch. 10.4 - Find current Io in the circuit of Fig. 10.8 using...Ch. 10.4 - Calculate vo in the circuit of Fig. 10.15 using...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the Norton equivalent of the circuit in...Ch. 10.7 - Find vo and io in the op amp circuit of Fig....Ch. 10.7 - Obtain the closed-loop gain and phase shift for...Ch. 10.8 - Use PSpice to obtain vo and io in the circuit of...
Ch. 10.8 - Obtain Vx and Ix in the circuit depicted in Fig....Ch. 10.9 - Determine the equivalent capacitance of the op amp...Ch. 10.9 - In the Wien-bridge oscillator circuit in Fig....Ch. 10 - The voltage Vo across the capacitor in Fig. 10.43...Ch. 10 - The value of the current Io in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 10 - Using nodal analysis, the value of Vo in the...Ch. 10 - In the circuit of Fig. 10.46, current i(t) is: (a)...Ch. 10 - Refer to the circuit in Fig. 10.47 and observe...Ch. 10 - For the circuit in Fig. 10.48, the Thevenin...Ch. 10 - In the circuit of Fig. 10.48, the Thevenin voltage...Ch. 10 - Refer to the circuit in Fig. 10.49. The Norton...Ch. 10 - Figure 10.49 For Review Questions 10.8 and 10.9....Ch. 10 - PSpice can handle a circuit with two independent...Ch. 10 - Determine i in the circuit of Fig. 10.50. Figure...Ch. 10 - Using Fig. 10.51, design a problem to help other...Ch. 10 - Determine vo in the circuit of Fig. 10.52. Figure...Ch. 10 - Compute vo(t) in the circuit of Fig. 10.53. Figure...Ch. 10 - Find io in the circuit of Fig. 10.54.Ch. 10 - Determine Vx in Fig. 10.55. Figure 10.55 For Prob....Ch. 10 - Use nodal analysis to find V in the circuit of...Ch. 10 - Use nodal analysis to find current io in the...Ch. 10 - Use nodal analysis to find vo in the circuit of...Ch. 10 - Use nodal analysis to find vo in the circuit of...Ch. 10 - Using nodal analysis, find io(t) in the circuit in...Ch. 10 - Using Fig. 10.61, design a problem to help other...Ch. 10 - Determine Vx in the circuit of Fig. 10.62 using...Ch. 10 - Calculate the voltage at nodes 1 and 2 in the...Ch. 10 - Solve for the current I in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 10 - Use nodal analysis to find Vx in the circuit shown...Ch. 10 - By nodal analysis, obtain current Io in the...Ch. 10 - Use nodal analysis to obtain Vo in the circuit of...Ch. 10 - Obtain Vo in Fig. 10.68 using nodal analysis.Ch. 10 - Refer to Fig. 10.69. If vs (t) = Vm sin t and vo...Ch. 10 - For each of the circuits in Fig. 10.70, find Vo/Vi...Ch. 10 - For the circuit in Fig. 10.71, determine Vo/Vs....Ch. 10 - Using nodal analysis obtain V in the circuit of...Ch. 10 - Design a problem to help other students better...Ch. 10 - Solve for io in Fig. 10.73 using mesh analysis....Ch. 10 - Use mesh analysis to find current io in the...Ch. 10 - Using mesh analysis, find I1 and I2 in the circuit...Ch. 10 - In the circuit of Fig. 10.76, determine the mesh...Ch. 10 - Using Fig. 10.77, design a problem help other...Ch. 10 - Use mesh analysis to find vo in the circuit of...Ch. 10 - Use mesh analysis to determine current Io in the...Ch. 10 - Determine Vo and Io in the circuit of Fig. 10.80...Ch. 10 - Compute I in Prob. 10.15 using mesh analysis....Ch. 10 - Use mesh analysis to find Io in Fig. 10.28 (for...Ch. 10 - Calculate Io in Fig. 10.30 (for Practice Prob....Ch. 10 - Compute Vo in the circuit of Fig. 10.81 using mesh...Ch. 10 - Use mesh analysis to find currents I1, I2, and I3...Ch. 10 - Using mesh analysis, obtain Io in the circuit...Ch. 10 - Find I1, I2, I3, and Ix in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 10 - Find io in the circuit shown in Fig. 10.85 using...Ch. 10 - Find vo for the circuit in Fig. 10.86, assuming...Ch. 10 - Using Fig. 10.87, design a problem to help other...Ch. 10 - Using the superposition principle, find ix in the...Ch. 10 - Use the superposition principle to obtain vx in...Ch. 10 - Use superposition to find i(t) in the circuit of...Ch. 10 - Solve for vo(t) in the circuit of Fig. 10.91 using...Ch. 10 - Determine io in the circuit of Fig. 10.92, using...Ch. 10 - Find io in the circuit of Fig. 10.93 using...Ch. 10 - Using source transformation, find i in the circuit...Ch. 10 - Using Fig. 10.95, design a problem to help other...Ch. 10 - Use source transformation to find Io in the...Ch. 10 - Use the concept of source transformation to find...Ch. 10 - Rework Prob. 10.7 using source transformation. Use...Ch. 10 - Find the Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 10 - For each of the circuits in Fig. 10.99, obtain...Ch. 10 - Using Fig. 10.100, design a problem to help other...Ch. 10 - For the circuit depicted in Fig. 10.101, find the...Ch. 10 - Calculate the output impedance of the circuit...Ch. 10 - Find the Thevenin equivalent of the circuit in...Ch. 10 - Using Thevenins theorem, find vo in the circuit of...Ch. 10 - Obtain the Norton equivalent of the circuit...Ch. 10 - For the circuit shown in Fig. 10.107, find the...Ch. 10 - Using Fig. 10.108, design a problem to help other...Ch. 10 - At terminals a-b, obtain Thevenin and Norton...Ch. 10 - Find the Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits...Ch. 10 - Find the Thevenin equivalent at terminals ab in...Ch. 10 - For the integrator shown in Fig. 10.112, obtain...Ch. 10 - Using Fig. 10.113, design a problem to help other...Ch. 10 - Find vo in the op amp circuit of Fig. 10.114....Ch. 10 - Compute io(t) in the op amp circuit in Fig. 10.115...Ch. 10 - If the input impedance is defined as Zin = Vs/Is,...Ch. 10 - Evaluate the voltage gain Av = Vo/Vs in the op amp...Ch. 10 - In the op amp circuit of Fig. 10.118, find the...Ch. 10 - Determine Vo and Io in the op amp circuit of Fig....Ch. 10 - Compute the closed-loop gain Vo/Vs for the op amp...Ch. 10 - Determine vo(t) in the op amp circuit in Fig....Ch. 10 - For the op amp circuit in Fig. 10.122, obtain Vo....Ch. 10 - Obtain vo(t) for the op amp circuit in Fig. 10.123...Ch. 10 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to determine Vo in the...Ch. 10 - Solve Prob. 10.19 using PSpice or MultiSim. Obtain...Ch. 10 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to find vo(t) in the...Ch. 10 - Obtain Vo in the circuit of Fig. 10.126 using...Ch. 10 - Using Fig. 10.127, design a problem to help other...Ch. 10 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to find V1, V2, and V3 in...Ch. 10 - Determine V1, V2, and V3 in the circuit of Fig....Ch. 10 - Use PSpice or MultiSim to find vo and io in the...Ch. 10 - The op amp circuit in Fig. 10.131 is called an...Ch. 10 - Figure 10.132 shows a Wien-bridge network. Show...Ch. 10 - Consider the oscillator in Fig. 10.133. (a)...Ch. 10 - The oscillator circuit in Fig. 10.134 uses an...Ch. 10 - Figure 10.135 shows a Colpitts oscillator. Show...Ch. 10 - Design a Colpitts oscillator that will operate at...Ch. 10 - Figure 10.136 shows a Hartley oscillator. Show...Ch. 10 - Refer to the oscillator in Fig. 10.137. (a) Show...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3. You are to design a 9-volt battery operated communication system that must last 3 years without replacing batteries. The communication channel bandwidth is 100 KHz centered at 5.8 GHz. The application requires a BER of <10^-5 and a data rate of 1 Mbps. The channel can be modeled as AWGN with a noise power spectral density of 10^-8 W/Hz. ((a) What modulation scheme would you use? B) what is the required capacity of the batteries? and (c) is the battery commercially available?arrow_forwardDesign a traffic light PIC microcontroller program with Green LED has 3 Sec Yellow LED has 0.5 Sec Red LED has 3 Sec RASAN4SSC20UT 8 RBOINT RB1 9 RB2 U1 PIC16F877A-I/PT 18 19 MCLRVPP RAOANO 20 RA1AN1 30 OSCICLKI 21 RAZAN2VREF-CVREF 31 OSC2CLKO RABAN3VREF+ 22 LED1 LED-3MM 〃 R1 330 RA4TOCKIC1OUT 23 7 VDD 28 VDD 6 VSS 29 VSS 24 LED2 LED-3MM R2 10 330 RB3PGM 11 + 14 RB4 38 RDOPSPO RB5 15 LED3 39 RD1PSP1 40 RD2PSP2 RB6PGC- RB7PGD 17 16 LED-3MM R3 330 41 RD3PSP3 2 RD4PSP4 RCOT1OSOTICKK 3 RDSPSPS RC1T10SICCP24 RD6PSP6 RC2CCP1 5 RD7PSP7 RC3SCKSCL RC4SDISDA 25 REORDANS RCSSDO 27 29 REIWRANG RC6TXCK- RE2CSAN7 RC7RXDT DAWWWW 32 35 36 37 42 43 44 1 12 NO 13 NC 33 NO 34 NCarrow_forward: +0 العنوان I need a detailed drawing with explanation しじ ined sove in peaper Anoting Q4// Draw and Evaluate √√√xy-²sin(y²)dydx PU+96er Lake Ge Q3// Find the volume of the region between the cylinder 2 = y² and the xy- plane that is bounded by the planes x = 1, x = 2, y = -2, and y = 2. T Marrow_forward
- What are the four conditions that must be met before a generator is connected to a 3 phase system?arrow_forwardPlease solve this question step by step and handwritten and do not use chat gpt or ai tools thank you very much!arrow_forwardPlease solve question c and d step by step and handwritten and do not use chat gpt or ai tools thank you very much!arrow_forward
- Please solve questions d,e,f step by step and handwritten and do not use chat gpt or ai tools thank you very much!arrow_forwardPlease solve this question step by step and handwritten and do not use chat gpt or ai tools thank you very much!arrow_forwardPlease solve question c,d,e step by step and handwritten and do not use chat gpt or ai tools thank you very much!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Current Divider Rule; Author: Neso Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hRU1mKWUehY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY