
Effect of Paternal Grandmother's Food Supply on Infant Mortality Widely available historical data on periods of famine show that before the industrial revolution, a failed harvest in one autumn often led to severe food shortages the following winter. Retrospective studies have correlated infant mortality with the abundance or food during a grandparent's child hood. FIGURE 10.11 shows results from one or these studies.
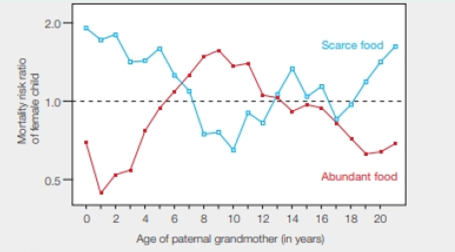
FIGURE 10.11 Relative risk of early death of female child, correlated with the age at which her paternal grandmother experienced a winter with a food supply, that was scarce (blue) or abundant (red) during childhood. The dotted line represents no difference in risk of mortality. A value above the line means increased risk; one below the line indicates reduced risk.
Children have a period of show growth around age 9. What trend in this data can you see around that age?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
- What did the Cre-lox system used in the Kikuchi et al. 2010 heart regeneration experiment allow researchers to investigate? What was the purpose of the cmlc2 promoter? What is CreER and why was it used in this experiment? If constitutively active Cre was driven by the cmlc2 promoter, rather than an inducible CreER system, what color would you expect new cardiomyocytes in the regenerated area to be no matter what? Why?arrow_forwardWhat kind of organ size regulation is occurring when you graft multiple organs into a mouse and the graft weight stays the same?arrow_forwardWhat is the concept "calories consumed must equal calories burned" in regrads to nutrition?arrow_forward
- You intend to insert patched dominant negative DNA into the left half of the neural tube of a chick. 1) Which side of the neural tube would you put the positive electrode to ensure that the DNA ends up on the left side? 2) What would be the internal (within the embryo) control for this experiment? 3) How can you be sure that the electroporation method itself is not impacting the embryo? 4) What would you do to ensure that the electroporation is working? How can you tell?arrow_forwardDescribe a method to document the diffusion path and gradient of Sonic Hedgehog through the chicken embryo. If modifying the protein, what is one thing you have to consider in regards to maintaining the protein’s function?arrow_forwardThe following table is from Kumar et. al. Highly Selective Dopamine D3 Receptor (DR) Antagonists and Partial Agonists Based on Eticlopride and the D3R Crystal Structure: New Leads for Opioid Dependence Treatment. J. Med Chem 2016.arrow_forward
- The following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. You are a chef in a fancy new science-themed restaurant. You have a recipe that calls for 1 teaspoon of resinferatoxin, but you feel uncomfortable serving foods with "toxins" in them. How much capsaicin could you substitute instead?arrow_forwardWhat protein is necessary for packaging acetylcholine into synaptic vesicles?arrow_forward1. Match each vocabulary term to its best descriptor A. affinity B. efficacy C. inert D. mimic E. how drugs move through body F. how drugs bind Kd Bmax Agonist Antagonist Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamicsarrow_forward
- 50 mg dose of a drug is given orally to a patient. The bioavailability of the drug is 0.2. What is the volume of distribution of the drug if the plasma concentration is 1 mg/L? Be sure to provide units.arrow_forwardDetermine Kd and Bmax from the following Scatchard plot. Make sure to include units.arrow_forwardChoose a catecholamine neurotransmitter and describe/draw the components of the synapse important for its signaling including synthesis, packaging into vesicles, receptors, transporters/degradative enzymes. Describe 2 drugs that can act on this system.arrow_forward
 Understanding Nutrition (MindTap Course List)Health & NutritionISBN:9781337392693Author:Eleanor Noss Whitney, Sharon Rady RolfesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Nutrition (MindTap Course List)Health & NutritionISBN:9781337392693Author:Eleanor Noss Whitney, Sharon Rady RolfesPublisher:Cengage Learning Nutrition Through The Life CycleHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337919333Author:Brown, Judith E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Nutrition Through The Life CycleHealth & NutritionISBN:9781337919333Author:Brown, Judith E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





