
Concept explainers
Answers to all problems are at the end of this book. Detailed solutions are available in the Student Solutions Manual, Study Guide, and Problems Book.
The Structure and Ionization Properties of
Interpretation: The principal ionic species of
Concept introduction: A nucleotide refers to a basic DNA building block and structural unit. It contains a five-sided sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The nucleotides join together to form a chain of DNA. The nucleotides of DNA and RNA are linked covalently by bridges of the phosphate group. A phosphodiester linkage joins the
Answer to Problem 1P
The principal ionic species of
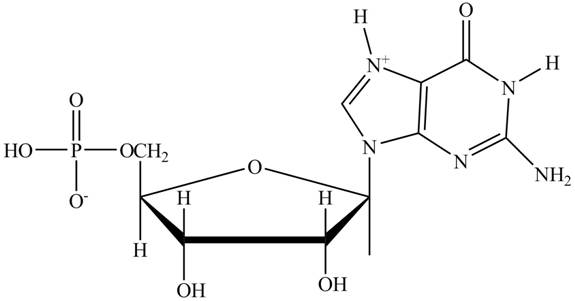
Explanation of Solution
In the polar backbone of DNA and RNA, the phosphate groups are completely ionizable and negatively charged at
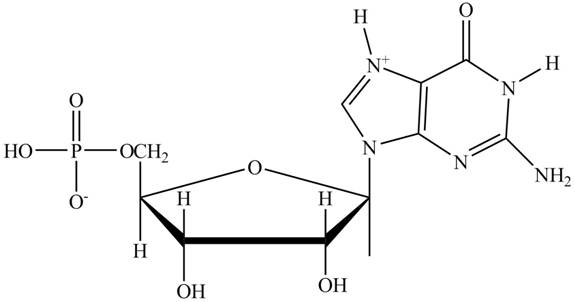
Figure 1
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Biochemistry
- Do schwann cells produce or act as myelin in the peripheral nervous system? I know that they encase and wrap around axons, but where does the myelin come into play?arrow_forwardThe enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) catalyzes the conversion of pyruvate to lactatein skeletal muscle cells using NAD/NADH during anaerobic “balanced” fermentation.Answer the following questions about this reaction. (a) Write out the two reductive half reactions and indicate the E ̊' for each half reaction. Write out the full balanced reaction for the pyruvate to lactate rxn and indicate the ∆E ̊' for the reaction. (b) What is the free energy change under standard state conditions for thisreaction? Which direction is spontaneous?(c) Assume that in skeletal muscle cells the ratio of [NAD+] to [NADH] is 100, and that the[pyruvate] = 0.40 mM and [lactate] = 4.0 mM. What is the free energy change (∆G')for the conversion of pyruvate to lactate? Indicate the direction in which the reactionis spontaneous under these cellular conditions.arrow_forwardWhy did the authors worry about the temperature-dependent solubility of the carriers in thebilayer? How did the authors determine whether the effect of freezing the lipid bilayer wasto decrease the solubility of the carriers (nonactin and valinomycin) or whether the effectwas to impair their ability to diffuse through the membrane (decrease their mobility)?arrow_forward
- Kranse et. al. measured the temperature dependence of conductance using membranescontaining the phospholipids glyceryl dipalmitate and glyceryl distearate. Describe themodifications in membrane content that you would employ to: (a) shift the temperature of the phase transition (b) make the ion conductance curve for valinomycin andnonactin more like that of gramicidinarrow_forwardObtain the sequence for the 5-HT receptor HTR1A and generate a hydropathy plot usingthe ExPASY tool ProtScale, the appropriate window, and the Kyte-Doolittle weightingalgorithm. How many transmembrane domains are present in this receptor? Attach yourhydropathy plot to your assignment.arrow_forwardCompare and contrast the structural features of the ion carrier valinomycin with those of achannel former like gramicidin. How does structural information help explain the mechanismby which these molecules conduct ions across membranes?arrow_forward
- A typical integral membrane protein has a stretch (or stretches) of ~20 hydrophobic aminoacids that form an α-helix that spans the bilayer (as is found in membrane proteins such asglycophorin A and bacteriorhodopsin). Compare and contrast the molecular and structural features of gramicidin with a membrane-spanning α-helix. Explain how gramicidin can forman ion channel when a typical membrane-spanning α-helix cannot (eg, glycophorin A).arrow_forwardThe titration curve of alanine shows the ionization of two functional groups with pK values of 2.34 and 9.69, corresponding to the ionization of the carboxyl and the protonated amino groups, respectively. The titration of di-, tri-, and larger oligopeptides of alanine also shows the ionization of only two functional groups, although the experimental pK values are different. The table summarizes the trend in pK values. Amino acid or peptide Ala Ala-Ala pKj pk₂ 2.34 9.69 3.12 8.30 Ala-Ala-Ala 3.39 8.03 Ala-(Ala)-Ala, n ≥ 4 3.42 7.94 Modify the molecules to show the oligopeptide Ala-Ala-Ala. You can modify the molecules by moving, adding, deleting, or changing atoms, bonds, or charges. C Select c Draw Templates More H с N 0 S Cl H H | | || H CH3 H CH, H CH₂ Complete the statements about the the pK, values of the Ala-Ala-Ala oligopeptide. The pK₁ value of 3.39 is associated with the -COO group of Ala-Ala-Ala. The pK2 value of 8.03 is associated with the -NH group of Ala-Ala-Ala. Erase Q2 Q…arrow_forwardFacts from the bacterium mals and to dept kan apa in a peptide with antidic properties. This peptide complex with the call membrance of other hacterial species, leading in bacterial death The structure of the peptide has been determined from (a) Cmplete acid hydes of the peptide, followed by amino acid analys, yielded quiar anunt of Lan, Om, Pfx, Prxa, and Wall Cmtiti, an amino acid od prosentin pockets but present in some peptides. Com has the tracture H *H,N-CH-CH-CH, -C- COO (b) The weight of the peptide in approximately 1,200 Th (c) The peptide failed to undergo hydrolysis when treated with the Hydrolysis of the carbonyl-terminal residue of a polypeptide une "NH, the year. This call there Pro or the police does not contain a froz (d) Treatment of the peptide with 1-haw-2,4-dicherer (11N1), followed by complete hydrolysis and ched only from and the derivative NO, Н ON NHCHI CH, CH, C coo +NH, (Hint: The 2,4-diphenyl derivative involves the amino group of a side chain rather than the…arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
