
Concept explainers
Write Lewis symbols for the following atoms. (a) Kr; (b) Ge; (c) N; (d) Ga; (e) As; (f) Rb.
(a)
Interpretation:
Interpret Lewis symbol of Kr.
Concept introduction:
Lewis symbol is the representation of the atoms in elemental form found in the periodic table. The element is represented with the universal symbol along with the valence electron present in its valence shell.
The valence electron present in the atom is decided by total number of electrons present in outermost shell.
Answer to Problem 1E
Lewis symbol of Kr is:
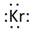
Explanation of Solution
In periodic table, Krypton is present in 18 group and in 4 period. The symbol of Krypton is Kr carrying 8 valence electrons in its valence shell.
Thus, the Lewis symbol of Kr is:
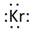
(b)
Interpretation:
Interpret the Lewis symbol of Ge.
Concept introduction:
Lewis symbol is the representation of the atoms in elemental form found in the periodic table. The element is represented with the universal symbol along with the valence electron present in its valence shell.
The valence electron present in the atom is decided by total number of electrons present in outermost shell.
Answer to Problem 1E
Lewis symbol of Ge is:

Explanation of Solution
In periodic table, Germanium is present in 14 group and in 4 period. The symbol of Germanium is Ge carrying 4 valence electrons in its valence shell.
Thus, the Lewis symbol of Ge is:

(c)
Interpretation:
Interpret the Lewis symbol of N.
Concept introduction:
Lewis symbol is the representation of the atoms in elemental form found in the periodic table. The element is represented with the universal symbol along with the valence electron present in its valence shell.
The valence electron present in the atom is decided by total number of electrons present in outermost shell.
Answer to Problem 1E
Lewis symbol of N is:
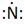
Explanation of Solution
In periodic table, Nitrogen is present in 15 group and in 2 period. The symbol of Nitrogen is N carrying 5 valence electrons in its valence shell.
Thus, the Lewis symbol of N is:
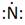
(d)
Interpretation:
Interpret the Lewis symbol of Ga.
Concept introduction:
Lewis symbol is the representation of the atoms in elemental form found in the periodic table. The element is represented with the universal symbol along with the valence electron present in its valence shell.
The valence electron present in the atom is decided by total number of electrons present in outermost shell.
Answer to Problem 1E
Lewis symbol of Ga is:
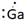
Explanation of Solution
In periodic table, Gallium is present in 13 group and in 4 period. The symbol of Gallium is Ga carrying 3 valence electrons in its valence shell.
Thus, Lewis symbol of Ga is:
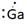
(e)
Interpretation:
Interpret the Lewis symbol of As.
Concept introduction:
Lewis symbol is the representation of the atoms in elemental form found in the periodic table. The element is represented with the universal symbol along with the valence electron present in its valence shell.
The valence electron present in the atom is decided by total number of electrons present in outermost shell.
Answer to Problem 1E
Lewis symbol of As is:
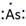
Explanation of Solution
In periodic table, Arsenic is present in 15 group and in 4 period. The symbol of Arsenic is As carrying 5 valence electrons in its valence shell.
Thus, the Lewis symbol of As is:
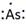
(f)
Interpretation:
Interpret the Lewis symbol of Rb.
Concept introduction:
Lewis symbol is the representation of the atoms in elemental form found in the periodic table. The element is represented with the universal symbol along with the valence electron present in its valence shell.
The valence electron present in the atom is decided by total number of electrons present in outermost shell.
Answer to Problem 1E
Lewis symbol of Rb is:
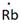
Explanation of Solution
In periodic table, Rubidium is present in 1 group and in 5th period. The symbol of rubidium is Rb carrying 1 valence electron in its valence shell.
Thus, the Lewis symbol of Rb is:
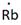
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK GENERAL CHEMISTRY
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
- The iron-iron carbide phase diagram. In the diagram, the letter L indicates that it is a liquid. Indicate what its components are. Temperature (°C) 1600 10 Composition (at% C) 15 25 1538°C -1493°C 8 1400 1200 1394°C y+L L 2500 1147°C y. Austenite 2.14 4.30 2000 1000 912°C y + Fe3C 800ㅏ 0.76 0.022 600 a, Ferrite a + Fe3C 400 0 (Fe) Composition (wt% C) 727°C 1500 Cementite (Fe3C) 1000 6 6.70 Temperature (°F)arrow_forwardPart V. Choose which isomer would give the 1H-NMR spectrum below. Justify your reasoning by assigning important signals to the Corresponding protons of the correct molecule. A D on of of of H H 88 2 90 7.8 7.6 7.4 80 5 6 [ppm] 7.2 6.8 6.6 6.4 ō [ppm]arrow_forwardShow work with explanation. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- Q7. a. Draw the line-bond structure of the major product for the following reaction, if a reaction occurs, assume monohalogenation. b. Calculate the product ratios using the following information (hint: use the number of hydrogens in each category present to calculate the ratios). Chlorination: 1° Reactivity=1 2° Reactivity=4 Heat + Cl2 3° Reactivity=5arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't use hand rating and don't use Ai solutionarrow_forwardQ10: Alkane halogenation a. Give the name and structures of the five isomeric hexanes. Page 4 of 5 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 Recitations b. For each isomer, give all the free radical monochlorination and monobromination products that are structurally isomeric.arrow_forward
- Q9. The insecticide DDT (in the box below) is useful in controlling mosquito populations and has low toxicity to humans, but is dangerous to birds and fish. Hoping to alleviate the dangers, little Johnny Whizbang, an aspiring chemist, proposes a new version of DDT ("Bromo-DDT") and shows his synthesis to his boss. Will Johnny Whizbang's synthesis work? Or will he be fired? Assume there is an excess of bromine and polybrominated products can be separated. Explain why. CH3 Br2, light CBR3 ok-ok Br Br Br Br CI "Bromo-DDT" CCl 3 DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) CIarrow_forwardDifferentiate the terms Monotectic, Eutectic, Eutectoid, Peritectic, Peritectoid.arrow_forwardQ5. Predict the organic product(s) for the following transformations. If no reaction will take place (or the reaction is not synthetically useful), write "N.R.". Determine what type of transition state is present for each reaction (think Hammond Postulate). I Br₂ CH3 F2, light CH3 Heat CH3 F₂ Heat Br2, light 12, light CH3 Cl2, lightarrow_forward
- a. For the following indicated bonds, rank them in order of decreasing AH° for homolytic cleavage. Based on your answer, which bond would be most likely to break homolytically? (a) (c) H3C CH3 .CH3 CH3 CH3 (b) Page 1 of 5 Chem 0310 Organic Chemistry 1 Recitations b. Draw all the possible radical products for 2-methylbutane, and determine which bond is most likely to be broken.arrow_forwardA 5-m³ rigid tank contains 5 kg of water at 100°C. Determine (a) the pressure, (b) the total enthalpy, and (c) the mass of each phase of water.arrow_forwardQ8. Draw the mechanism for this halogenation reaction. Show all steps including initiation, propagation, and recombination. Cl₂, hv CI Br Br2, hv, heatarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





