
Concept explainers
Biker Bob rides his bicycle inside the rotating space station at the speeds and directions given. The tangential speed of the floor of the station is 10 m/s clockwise.
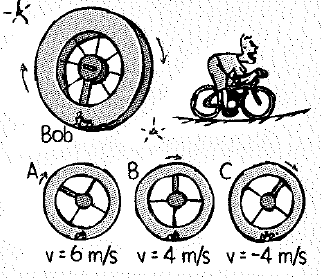
a. Rank his speeds from highest to lowest relative to the stars.
b. Rank the normal forces on Bob from largest to smallest.
(a)
The rank of the speed of the biker from highest to lowest relative to the stars.
Answer to Problem 16A
The rank of the speed of the biker from highest to lowest relative to the stars is
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The tangential speed of the floor of the station is
Formula used:
The expression for the speed for the objects moving in same direction as follows:
Here,
Calculation:
The speed of the biker for case A as follows:
The speed of the biker for case B as follows:
The speed of the biker for case C as follows:
By comparing the values, the speed of the biker is
Hence, the rank of the speed of the biker from highest to lowest relative to the stars is
Conclusion:
Thus, the rank of the speed of the biker from highest to lowest relative to the stars is
(b)
The rank of the normal forces on Bob from largest to smallest.
Answer to Problem 16A
The rank of the normal forces on Bob from largest to smallest is
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
The tangential speed of the floor of the station is
Formula used:
The expression for the normal force on the bicycle as follows:
Here,
Calculation:
Refer part (a).
The speed of the biker for case A
The speed of the biker for case B
The speed of the biker for case C
The normal force for case A as follows:
The normal force for case B as follows:
The normal force for case C as follows:
By comparing the values, the normal force is
Conclusion:
Thus, the rank of the normal forces on Bob from largest to smallest is
Chapter 10 Solutions
Conceptual Physics C2009 Guided Reading & Study Workbook Se
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forward3arrow_forward13. After a gust of wind, an orb weaver spider with a mass of 35 g, hanging on a strand of web of length L = .420 m, undergoes simple harmonic motion (SHO) with an amplitude A and period T. If the spider climbs 12.0 cm up the web without perturbing the oscillation otherwise, what is the period of oscillation, in Hz to three significant figures?arrow_forward
- 15. An object of mass m = 8.10 kg is attached to an ideal spring and allowed to hang in the earth's gravitational field. The spring stretches 23.10 cm before it reaches its equilibrium position. The mass then undergoes simple harmonic motion with an amplitude of 10.5 cm. Calculate the velocity of the mass in m/s at a time t= 1.00s to three significant figures.arrow_forwardplease solve and answer the question correctly. Thank you!!arrow_forward18arrow_forward
- 1. Some 1800 years ago Roman soldiers effectively used slings as deadly weapons. The length of these slings averaged about 81 cm and the lead shot that they used weighed about 30 grams. If in the wind up to a release, the shot rotated around the Roman slinger with a period of .14 seconds. Find the maximum acceleration of the shot before being released in m/s^2 and report it to two significant figures.arrow_forward16arrow_forward11. A small charged plastic ball is vertically above another charged small ball in a frictionless test tube as shown in the figure. The balls are in equilibrium at a distance d= 2.0 cm apart. If the charge on one ball is tripled, find the new equilibrium distance between the balls in cm and report it to the proper number of significant figures.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





