
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration of lithium has to be given.
The given orbital diagram is,
Concept Introduction:
Aufbau’s principle:
Aufbau’s principle states that electrons are filled into atomic orbitals in the increasing order of orbital energy level. According to the Aufbau principle the available atomic orbitals with the lowest energy levels are occupied before those with higher energy levels.
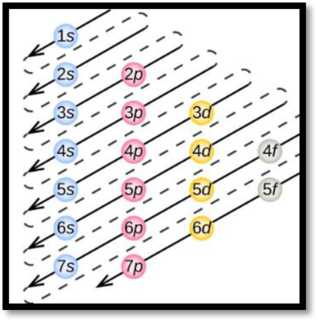
Figure 1
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given orbital diagram is,
Lithium is a chemical element with chemical symbol
(b)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration of phosphorous has to be given.
The given orbital diagram is,
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The given orbital diagram is,
The electronic configuration of Phosphorous is
(c)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration of zinc has to be given.
The given orbital diagram is,
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The given orbital diagram is,
The electronic configuration of Zinc is
(d)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration of sodium has to be given.
The given orbital diagram is,
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The given orbital diagram is,
Sodium is a chemical element with chemical symbol
(e)
Interpretation:
The electronic configuration of potassium has to be given.
The given orbital diagram is,
Concept Introduction:
Refer to part (a).
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The given orbital diagram is,
Potassium is a chemical element with chemical symbol
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK FOUNDATIONS OF COLLEGE CHEMISTRY
- Steps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forwardSteps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forwardSteps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forward
- Steps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forwardSteps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forwardSteps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forward
- Label the α and ẞ carbons in each alkyl halide. Draw all possible elimination products formed when each alkyl halide is treated with K-OC(CH3), b. ان Brarrow_forwardSuppose a reaction has the following mechanism:A + B → C + D C + C → F F + B → A + A + GIt is known that C is a reaction intermediate. Of the following options, indicate which are true:1. The overall reaction could be 3B → 2D + G.2. A could be a catalyst.3. C is the only intermediate that can exist.arrow_forwardSteps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forward
- Steps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forwardSteps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forwardSteps and explanations. Also provide, if possible, ways to adress this kind of problems in general.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
