
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given reaction the under given conditions the valence electrons present in the given compound should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Valence electrons: The outermost electrons present in the compound other than the inner core electrons are denoted as valence electrons. The valence electrons are responsible for the bond formation.
There are about 19 valence electrons present in the given compound.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given compound
Similarly the chlorine atom contains 7 valence electrons in its outer most shell which totally comprises of
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given reaction the under given conditions the valence electrons present in the given compound
Concept introduction:
Lewis dot structure: It is the representation of chemical substance that how the valence are represented as dot and placed around the each atom present in the substance by considering the number of atoms with their valence electrons and number of bonds present in the given chemical substance.
(b)
Answer to Problem 116SCQ
The electron dot structure for the given compound is as follows,
Explanation of Solution
The electron dot structure for the given
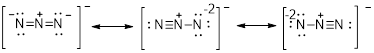
There are two oxygen atoms and one chlorine atom present in the given compound.
The oxygen atom contains 8 electrons that is represented as follows,
Similarly, the electrons present in the chlorine is represented as follows
Therefore, the chemical substance totally, has 20 valence electrons with it since addition of valence electrons present in the atom of the given compound says that. There are 2 O atoms each with 6 valence electrons one chlorine atom with 7 valence electrons and one negative charge which denotes present of one extra electrons which totally equals to 20.
The valence electrons are represented as dot around each atom present in the compound such that each atom tends to exhibit stable configuration that is 8electrons in its valence shell.
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given reaction the under given conditions the angle and the mass of
Concept introduction:
Hybridization refers to mixing of orbitals. The orbitals of different atoms overlap with each other and form a set of new orbitals called hybrid orbitals. The number of orbitals that are combined equal to the number of hybrid orbitals formed by combination.
An isolated atom remains in excited state and comes back to ground state. In this situation, it is difficult for orbitals to hybridize.
Hybridization is a hypothetical concept. It refers to mixing of atomic orbitals and the resultant orbitals formed are known as hybrid orbitals. After hybridization, the orbitals cannot be distinguished individually. Based on hybridization one can predict the geometry of the molecule though some deviations do exist.
(c)
Answer to Problem 116SCQ
The chlorine atom in the given compound is found to be
Explanation of Solution
The given compound contains chlorine with two oxygen atoms results to have two bonds with it.
The electronic configuration of Chlorine and oxygen is as follows,
Electronic configuration of chlorine is
The available orbitals that is s orbitals, one p orbital from chlorine and two p orbitals from oxygen atom gets hybridized and results to form new hybrid orbitals classified as
The central chlorine in compound
(d)
Interpretation:
For the given reaction the under given conditions the valence electrons present in the given compound
Concept introduction:
Bond angle: The angle formed between two bonds that is where two atoms gets bonded with the third central atom present.
(d)
Answer to Problem 116SCQ
The species
Explanation of Solution
The central chlorine in compound
Therefore,
(e)
Interpretation:
For the given reaction the under given conditions the mass of
Concept introduction:
Ideal gas equation:
Any gas is described by using four terms namely pressure, volume, temperature and the amount of gas. Thus combining three laws namely Boyle’s, Charles’s Law and Avogadro’s Hypothesis the following equation could be obtained. It is referred as ideal gas equation.
Under some conditions gases don not behave like ideal gas that is they deviate from their ideal gas properties. At lower temperature and at high pressures the gas tends to deviate and behave like real gases.
Boyle’s Law:
At given constant temperature conditions the mass of given ideal gas in inversely proportional to its volume.
Charles’s Law:
At given constant pressure conditions the volume of ideal gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature.
Avogadro’s Hypothesis:
Two equal volumes of gases with same temperature and pressure conditions tend to have same number of molecules with it.
The relationship between partial pressure and
(e)
Answer to Problem 116SCQ
The mass of given compound formed is equal to
Explanation of Solution
Given:
First the given mass of
There are about
Then, the amount of
Now, analyzing the given chemical equation it is evident that 2 moles of
Similarly, there are
Analyzing the above calculations we have only about
Examining the given chemical reaction show that 1 mole of
Therefore, available amount of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
CHEMISTRY+CHEM...HYBRID ED.(LL)>CUSTOM<
- What are the angles a and b in the actual molecule of which this is a Lewis structure? H- :0: C=N: b Note for advanced students: give the ideal angles, and don't worry about small differences from the ideal that might be caused by the fact that different electron groups may have slightly different sizes. a = 0° b=0 Xarrow_forwardA student proposes the transformation below in one step of an organic synthesis. There may be one or more products missing from the right-hand side, but there are no reagents missing from the left-hand side. There may also be catalysts, small inorganic reagents, and other important reaction conditions missing from the arrow. • Is the student's transformation possible? If not, check the box under the drawing area. • If the student's transformation is possible, then complete the reaction by adding any missing products to the right-hand side, and adding required catalysts, inorganic reagents, or other important reaction conditions above and below the arrow. • You do not need to balance the reaction, but be sure every important organic reactant or product is shown. + This transformation can't be done in one step. T iarrow_forwardDetermine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction: H+ O OH H+ + H₂O ☑ ☑ Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the missing organic molecule X. Molecule X shows up in multiple steps, but you only have to draw its structure once. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X § ©arrow_forward
- Table 1.1 Stock Standard Solutions Preparation. The amounts shown should be dissolved in 100 mL. Millipore water. Calculate the corresponding anion concentrations based on the actual weights of the reagents. Anion Amount of reagent (g) Anion Concentration (mg/L) 0.1649 Reagent Chloride NaCl Fluoride NaF 0.2210 Bromide NaBr 0.1288 Nitrate NaNO3 0.1371 Nitrite NaNO2 0.1500 Phosphate KH2PO4 0.1433 Sulfate K2SO4 0.1814arrow_forwardDraw the structure of the pound in the provided CO as a 300-1200 37(2), 11 ( 110, and 2.5 (20arrow_forwardPlease help me with # 4 and 5. Thanks in advance!arrow_forward
- A small artisanal cheesemaker is testing the acidity of their milk before it coagulates. During fermentation, bacteria produce lactic acid (K₁ = 1.4 x 104), a weak acid that helps to curdle the milk and develop flavor. The cheesemaker has measured that the developing mixture contains lactic acid at an initial concentration of 0.025 M. Your task is to calculate the pH of this mixture and determine whether it meets the required acidity for proper cheese development. To achieve the best flavor, texture and reduce/control microbial growth, the pH range needs to be between pH 4.6 and 5.0. Assumptions: Lactic acid is a monoprotic acid H H :0:0: H-C-C H :0: O-H Figure 1: Lewis Structure for Lactic Acid For simplicity, you can use the generic formula HA to represent the acid You can assume lactic acid dissociation is in water as milk is mostly water. Temperature is 25°C 1. Write the K, expression for the dissociation of lactic acid in the space provided. Do not forget to include state symbols.…arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. :0: :0 H. 0:0 :0: :6: S: :0: Select to Edit Arrows ::0 Select to Edit Arrows H :0: H :CI: Rotation Select to Edit Arrows H. < :0: :0: :0: S:arrow_forward3:48 PM Fri Apr 4 K Problem 4 of 10 Submit Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Mg. :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: :Br: Mg :0: :0: Select to Add Arrows Mg. Br: :0: 0:0- Br -190 H 0:0 Select to Add Arrows Select to Add Arrows neutralizing workup H CH3arrow_forward
- Iarrow_forwardDraw the Markovnikov product of the hydrobromination of this alkene. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for this problem. + Explanation Check 1 X E 4 1 1 1 1 1 HBr Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 80 LE #3 @ 2 $4 0 I அ2 % 85 F * K M ? BH 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center & 6 27 FG F10 8 9 R T Y U D F G H P J K L Z X C V B N M Q W A S H option command H command optiarrow_forwardBe sure to use wedge and dash bonds to show the stereochemistry of the products when it's important, for example to distinguish between two different major products. Predict the major products of the following reaction. Explanation Q F1 A Check F2 @ 2 # 3 + X 80 F3 W E S D $ 4 I O H. H₂ 2 R Pt % 05 LL ee F6 F5 T <6 G Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 27 & A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Center Acce Y U H DII 8 9 F10 4 J K L Z X C V B N M T H option command F11 P H commandarrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning


