
(a)
Interpretation:
The 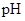 of water at given temperatures should be determined.
of water at given temperatures should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
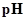 : The concentration of hydrogen ion is measured using
: The concentration of hydrogen ion is measured using 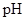 scale. The
scale. The 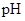 of a solution is a figure that expresses the acidity or the alkalinity of a given solution.
of a solution is a figure that expresses the acidity or the alkalinity of a given solution.
It is defined as the negative base-10 logarithm of the hydrogen or hydronium ion concentration.
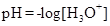
If the value of 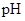 is less than
is less than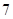 , then the solution is acidic whereas if the value of
, then the solution is acidic whereas if the value of 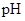 is greater than
is greater than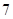 , then the solution is basic.
, then the solution is basic.
(b)
Interpretation:
The 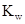 at given temperature should be determined.
at given temperature should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Ionic-product constant for water: It is the hydronium ion concentration times the 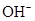 concentration present in the solution.
concentration present in the solution.
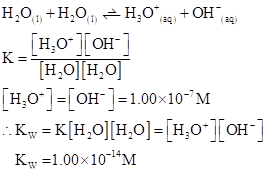
The 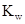 will apply to all aqueous solution.
will apply to all aqueous solution.
For acidic solution 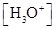 is large that is
is large that is 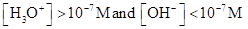
For basic solution 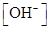 is large that is
is large that is 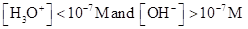
(c)
Interpretation:
The dissociation of water should be identified that whether it is an exothermic or endothermic reaction.
Concept Introduction:
Endothermic reaction: The reaction is considered as endothermic when heat energy is absorbed from surroundings during reaction.
Exothermic reaction: The reaction is considered as endothermic when heat energy is released to the surroundings during reaction.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
- Consider the four graphs shown. In each graph, the solid blue curve represents the unmodified allosteric enzyme and the dashed green curve represents the enzyme in the presence of the effector. Identify which graphs correctly illustrate the effect of a negative modifier (allosteric inhibitor) and a positive modifier (allosteric activator) on the velocity curve of an allosteric enzyme. Place the correct graph in the set of axes for each type of modifier. Negative modifier Reaction velocity - Positive modifier Substrate concentration - Reaction velocity →→→→ Substrate concentration Answer Bankarrow_forwardConsider the reaction: phosphoglucoisomerase Glucose 6-phosphate: glucose 1-phosphate After reactant and product were mixed and allowed to reach at 25 °C, the concentration of each compound at equilibrium was measured: [Glucose 1-phosphate] = 0.01 M [Glucose 6-phosphate] = 0.19 M Calculate Keq and AG°'. Код .0526 Incorrect Answer 7.30 AG°' kJ mol-1 Incorrect Answerarrow_forwardClassify each phrase as describing kinases, phosphatases, neither, or both. Kinases Phosphatases Neither Both Answer Bank transfer phosphoryl groups to acidic amino acids in eukaryotes may use ATP as a phosphoryl group donor remove phosphoryl groups from proteins catalyze reactions that are the reverse of dephosphorylation reactions regulate the activity of other proteins catalyze phosphorylation reactions PKA as an example turn off signaling pathways triggered by kinasesarrow_forward
- Consider the reaction. kp S P kg What effects are produced by an enzyme on the general reaction? AG for the reaction increases. The rate constant for the reverse reaction (kr) increases. The reaction equilibrium is shifted toward the products. The concentration of the reactants is increased. The activation energy for the reaction is lowered. The formation of the transition state is promoted.arrow_forwardThe graph displays the activities of wild-type and several mutated forms of subtilisin on a logarithmic scale. The mutations are identified as: • The first letter is the one-letter abbreviation for the amino acid being altered. • The number identifies the position of the residue in the primary structure. ⚫ The second letter is the one-letter abbreviation for the amino acid replacing the original one. • Uncat. refers to the estimated rate for the uncatalyzed reaction. Log₁(S-1) Wild type S221A H64A -5 D32A S221A H64A D32A -10 Uncat. How would the activity of a reaction catalyzed by a version of subtilisin with all three residues in the catalytic triad mutated compare to the activity of the uncatalyzed reaction? It would have more activity, because the reaction catalyzed by the triple mutant is approximately three-fold faster than the uncatalyzed reaction. It would have less activity, because the reaction catalyzed by the triple mutant is approximately 1000-fold slower than the…arrow_forwardB Substrate Product AL Product Substrate Reaction progress- Reaction progress- omplete the passage describing the two reactions. In reaction A, the stability of the substrate is (AG) of the reaction is positive, Incorrect Answer greater than the stability of the product. The free-energy change Incorrect Answer so the reaction is considered In reaction B, the stability of the substrate is (AG) of the reaction is less than Incorrect Answer endergonic and Incorrect Answer not spontaneous. Incorrect Answer the stability of the product. The free-energy change negative, so the reaction is considered Incorrect Answer exergonic and spontaneous. Incorrect Answer Incorrect Answerarrow_forward
- Match the descriptions and compounds with the terms competitive, uncompetitive, and noncompetitive inhibition. Competitive inhibition Uncompetitive inhibition Noncompetitive inhibition Answer Bank inhibitor binds to the enzyme-substrate complex only Vmax remains the same but Ky increases inhibitor and substrate can bind simultaneously lowers Vmax and KM doxycycline sulfanilamide KM remains unchanged, but Vis lower prevents substrate from binding to the active site Rounduparrow_forwardDraw a pentapeptide made of the following amino acids: glycine, tyrosine, lysine, glutamate, and leucine at pH 1, pH 7, and pH 12. Draw the correct stereochemistry for each pentapeptide. Calculate the charge of the three compounds you've drawn and the PI.arrow_forward7. a. Complete the following redox reaction with the missing products NADH H b. Provide an arrow-pushing mechanism for the oxidation reaction. Use the explicit structure of NADH or NAD' as needed. For simplicity, use only the nicotinamide portion of the moleculearrow_forward
- Discuss the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells with regards to their genetic materials. Including in your discussion the structure and organisation of genetic material, as well as any implications these differences may have on cellular functions and evolution. Rubric Understanding of genetic material differences (provides a comprehensive and accurate explanation of the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells in terms of their genetic material, including the structure, organisation and function of genetic material in each cell type. Demonstrates a thorough understanding of the topic) Analysis of implications (analyze the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells in terms of their genetic material with depth and insight, discussing the implications of these differences on cellular functions and evolution. Provides specific examples and explanations.)arrow_forwardWhen was the dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker isradipine first patented and by whom? Please provide information on the origin and history of isradipine and who owns it/manufactures it.arrow_forward9) Below, there is a representation of an SDS-PAGE gel. Assuming the samples in the MW standard have masses of: 66 kDa, 45 kDa, 36 kDa, 29 kDa, 24 kDa, 20.1 kDa, and 14.2 kDa, a) Figure 4: indicate where each of the measurements were taken and label as in II.6. figure 2 above. b) As in II.7. Table 1 above create Table 2 using the data below. Determine the r.f. values for the MW standards, plot the relative mobility versus the log of the mass for the standards, and use the best fit straight line to determine the molecular weights of the proteins in the whey, peak 1, and peak 2 lanes. (5 pts—this will be scaled up appropriately if your gel did not develop properly) dye MW Whey Peak 1 Peak 2arrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning





