
Concept explainers
Devise a synthesis of each product from the given starting material. More than one step is required.
a. 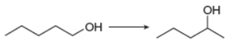 d.
d. 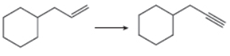
b. 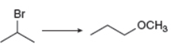 e.
e. 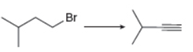
c. 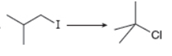 f.
f. 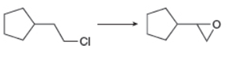
(a)
Interpretation: The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The removal of two substituents from a molecule either in one step or in two steps is called an elimination reaction.
For preparation of alkenes, acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols is one of the best methods. Less substituted alkene is the minor product when a mixture of constitutional isomers is possible. The reaction occurs via E1 mechanism or by an E2 mechanism. For primary alcohols, the reaction involves E2 mechanism, whereas for secondary and tertiary alcohols, the reaction occurs via E1 mechanism.
Hydration of alkenes is one the method used for the formation of alcohol.
The general steps involved in the hydration reaction are stated below:
• First protonation of the alkene take place to generate the carbocation.
• Formation of protonated alcohol.
• Deprotonation.
Answer to Problem 10.64P
The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is shown below.
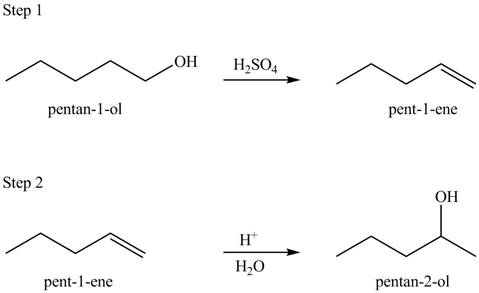
Explanation of Solution
For preparation of alkenes, acid-catalyzed dehydration of alcohols is one of the best methods. Less substituted alkene is the minor product when a mixture of constitutional isomers is possible. The reaction occurs via E1 mechanism or by an E2 mechanism. For primary alcohols, the reaction involves E2 mechanism, whereas for secondary and tertiary alcohols, the reaction occurs via E1 mechanism.
The general steps involved in the hydration reaction are stated below:
• First protonation of the alkene take place to generate the carbocation.
• Formation of protonated alcohol.
• Deprotonation.
The given conversion is,
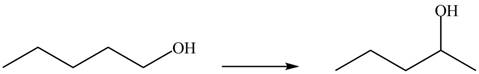
Figure 1
The above diagram shows the conversion of primary alcohol into secondary alcohol. The process involves two steps. The first step is the dehydration of alcohol that results in the formation of alkene. In the next step, hydration of alkene takes place to give secondary alcohol.
The reaction that shows the formation of secondary alcohol is shown below.
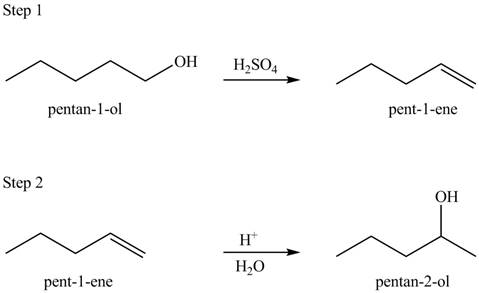
Figure 2
The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is rightfully stated.
(b)
Interpretation: The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The removal of two substituents from a molecule either in one step or in two steps is called an elimination reaction.
In elimination reaction, abstraction of proton occurs to form an alkene. Elimination reactions are of two types that is
Hydroboration reaction is a two step reaction, which involves conversion of alkene into alcohol. This type of reaction follows anti-markovnikov’s rule.
Answer to Problem 10.64P
The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is shown below.
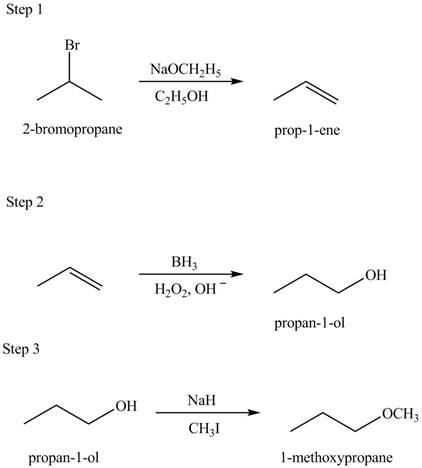
Explanation of Solution
Hydroboration reaction is a two step reaction, which involves conversion of alkene into alcohol. This type of reaction follows anti-markovinokov’s rule.
Anti markovinokov’s rule states that the positive part of acid attached to that carbon atom in
The given conversion is,
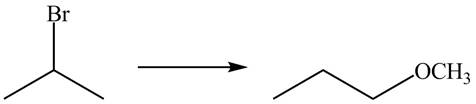
Figure 3
The above diagram shows the conversion of
The reaction that shows the formation of
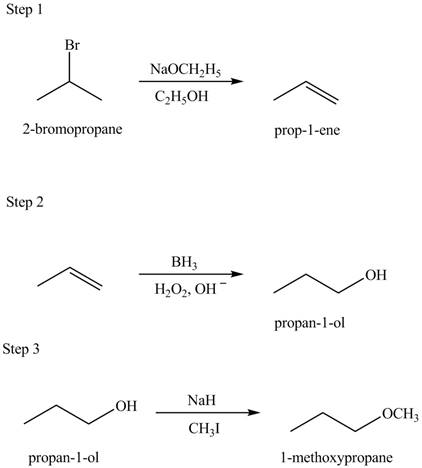

Figure 4
The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is rightfully stated.
(c)
Interpretation: The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The removal of two substituents from a molecule either in one step or in two steps is called an elimination reaction. Dehydrohalogenation is the elimination of halogen that results in the formation of alkene.
The reaction of hydrogen halide with alkene results in the formation of alkyl halide. This type of reaction is an electrophilic addition of hydrogen halide.
Electrophilic addition reactions are those in which breaking of pi bond take place to form new sigma bond. In this type of reaction, carbocation is formed during the formation of new bond.
Answer to Problem 10.64P
The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is shown below.
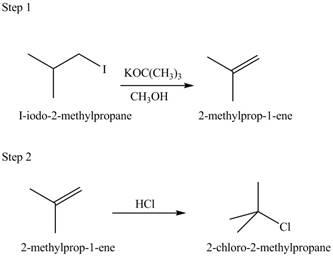
Explanation of Solution
The removal of two substituents from a molecule either in one step or in two steps is called an elimination reaction. Dehydrohalogenation is the elimination of halogen that results in the formation of alkene.
The reaction of hydrogen halide with alkene results in the formation of alkyl halide. This type of reaction is an electrophilic addition of hydrogen halide.
Electrophilic addition reactions are those in which breaking of pi bond take place to form new sigma bond. In this type of reaction, carbocation is formed during the formation of new bond.
The given conversion is,
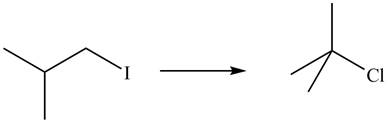
Figure 5
The above diagram shows the conversion of
The reaction that shows the formation of
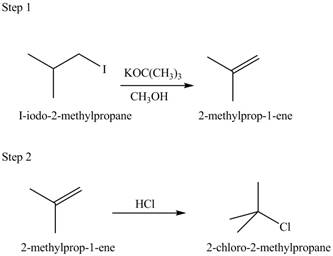
Figure 6
The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is rightfully stated.
(d)
Interpretation: The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The general steps followed by the given reaction are as follows:
• Bromination of alkene.
• Reaction of dihalide product with soda amide to form alkyne product.
Answer to Problem 10.64P
The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is shown below.
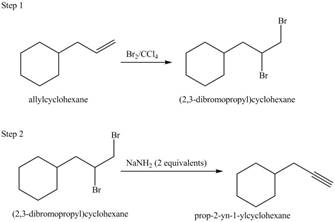
Explanation of Solution
The given conversion is,
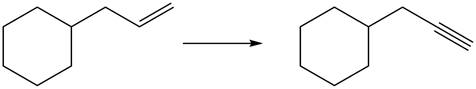
Figure 7
The above diagram shows the conversion of allylcycohexane into
The reaction that shows the formation of alkyne is shown below.
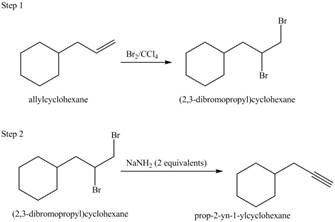
Figure 8
The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is rightfully stated.
(e)
Interpretation: The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The removal of two substituents from a molecule either in one step or in two steps is called an elimination reaction. Dehydrohalogenation is the elimination of halogen that results in the formation of alkene.
Bromination of alkene results in the formation of bromo products.
The reaction of dihalide reactant with soda amide results in the formation of alkyne product.
Answer to Problem 10.64P
The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is shown below.
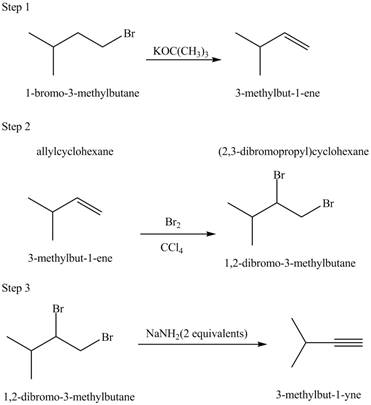
Explanation of Solution
The given conversion is,
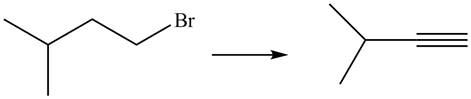
Figure 9
The above diagram shows the conversion of
The reaction that shows the formation of alkyne is shown below.

Figure 10
The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is rightfully stated.
(f)
Interpretation: The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The removal of two substituents from a molecule either in one step or in two steps is called an elimination reaction. Dehydrohalogenation is the elimination of halogen that results in the formation of alkene.
Answer to Problem 10.64P
The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is shown below.
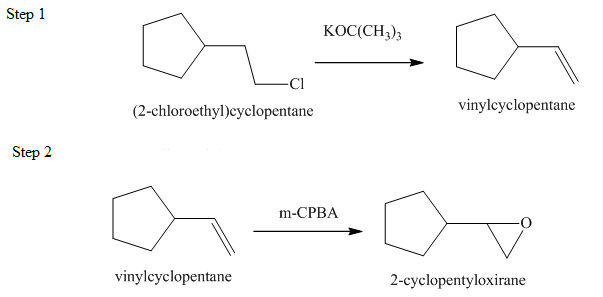
Explanation of Solution
The given conversion is,
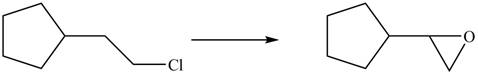
Figure 11
The above diagram shows the conversion of
The reaction that shows the formation of alkyne is shown below.

Figure 12
The synthesis of each product from the given starting material having more than one step is rightfully stated.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Biochemistry: Concepts and Connections (2nd Edition)
Organic Chemistry
- At a metal-solution interface, an electron is exchanged, and the symmetry factor beta < 0.5 is found in the Butler-Volmer equation. What does this indicate?arrow_forwardTopic: Photochemistry and Photophysics of Supramoleculesarrow_forwardTopic: Photochemistry and Photophysics of Supramoleculesarrow_forward
- How to name hydrocarbonsarrow_forwardPlease do these questions within the SCH4U course please with full steps since I am still unsure how to format my answers! Thank you so much.arrow_forwardWhen two solutions, one of 0.1 M KCl (I) and the other of 0.1 M MCl (II), are brought into contact by a membrane. The cation M cannot cross the membrane. At equilibrium, x moles of K+ will have passed from solution (I) to (II). To maintain the neutrality of the two solutions, x moles of Cl- will also have to pass from I to II. Explain this equality: (0.1 - x)/x = (0.1 + x)/(0.1 - x)arrow_forward
- Calculate the variation in the potential of the Pt/MnO4-, Mn2+ pair with pH, indicating the value of the standard potential. Data: E0 = 1.12.arrow_forwardGiven the cell: Pt l H2(g) l dis X:KCl (sat) l Hg2Cl2(s) l Hg l Pt. Calculate the emf of the cell as a function of pH.arrow_forwardThe decimolar calomel electrode has a potential of 0.3335 V at 25°C compared to the standard hydrogen electrode. If the standard reduction potential of Hg22+ is 0.7973 V and the solubility product of Hg2Cl2 is 1.2x 10-18, find the activity of the chlorine ion at this electrode.Data: R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1, F = 96485 C mol-1, T = 298.15 K.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





