
Concept explainers
Interpretation: The structure of six
Concept introduction: Alkenes are the compounds in which
Answer to Problem 10.1P
The structure of six alkenes having molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular formula of the compound is
The first possible structure of alkene with molecular formula
![]()
Figure 1
The first possible structure of alkene contains five carbon and ten hydrogen atoms. The double bond is present between first and second carbon atom.
The second possible structure of alkene with molecular formula
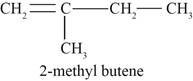
Figure 2
The second possible structure of alkene contains five carbon and ten hydrogen atoms. The double bond is present between first and second carbon atom. One methyl substituent is attached to the second carbon atom.
The third possible structure of alkene with molecular formula
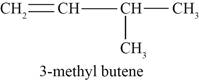
Figure 3
The third possible structure of alkene contains five carbon and ten hydrogen atoms. The double bond is present between first and second carbon atom. One methyl substituent is attached to the third carbon atom.
The fourth possible structure of alkene with molecular formula
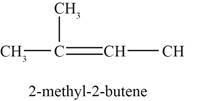
Figure 4
The fourth possible structure of alkene contains five carbon and ten hydrogen atoms. The double bond is present between second and third carbon atom. One methyl substituent is attached to the second carbon atom.
The fifth possible structure of alkene with molecular formula
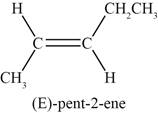
Figure 5
The fifth possible structure of alkene contains five carbon and ten hydrogen atoms. The double bond is present between second and third carbon atom. Substituents attached to the second and third carbon atom are on different side.
The sixth possible structure of alkene with molecular formula
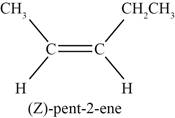
Figure 6
The sixth possible structure of alkene contains five carbon and ten hydrogen atoms. The double bond is present between second and third carbon atom. Substituents attached to the second and third carbon atom are on same side.
A pair of diastereomers exists when two substituents attached to each of the double bonded carbon atoms are different. The fifth and sixth structure indicates that the substituents bonded to the
Therefore, a pair of disatereomers is shown below.
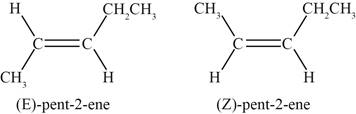
Figure 7
The structure of six alkenes having molecular formula
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- The reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forwardWhich of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forward
- Which of the following is true for a particular reaction if ∆G° is -40.0 kJ/mol at 290 K and –20.0 kJ/mol at 390 K?arrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? O O OH OH 1. BH 2. H₂O₂, NaOH OH OHarrow_forwardDraw the products formed when each ester is hydrolyzed with water and sulfuric acid.arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning

