
Concept explainers
Draw the constitutional isomer formed in each reaction.
a. ![]() d.
d.![]() g.
g.![]()
b.![]() e.
e.![]() h.
h.![]()
c.![]() f.
f. ![]()
(a)
Interpretation: The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: A reaction of hydrogen halide with alkene results in the formation of alkyl halide. This type of reaction is an electrophilic addition of hydrogen halide. Electrophilic addition reaction follows markovnikov�s rule.
According to markovnikov�s rule, the positive part of halogen acid attached to that carbon atom in
Answer to Problem 10.54P
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is shown below:
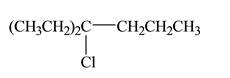
Explanation of Solution
A reaction of hydrogen halide with alkene results in the formation of alkyl halide. This type of reaction is an electrophilic addition of hydrogen halide.
The steps followed by electrophilic addition reaction are stated below:
• First protonation of the alkene take place to generate the carbocation.
• The halide ion will attack on the carbocation to give the final product
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is shown below.
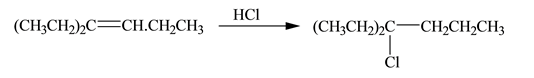
Figure 1
Therefore, the constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is
(b)
Interpretation: The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Hydration of alkenes is one the method used for the formation of alcohol.
The general steps followed by hydration reaction are stated below:
• First protonation of the alkene take place to generate the carbocation.
• Formation of protonated alcohol.
• Deprotonation.
Answer to Problem 10.54P
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
Hydration of alkenes is one the method used for the formation of alcohol.
The general steps followed by hydration reaction are stated below:
• First protonation of the alkene take place to generate the carbocation.
• Formation of protonated alcohol.
• Deprotonation.
In this type of reaction, hydroxyl group attacks on the more substituted carbon.
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is shown below.
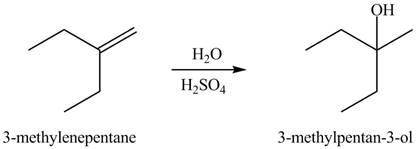
Figure 2
The first step in the given reaction is the abstraction of proton from sulfuric acid. This results in the formation of carbocation. In the next step, attack of water molecule takes place on the electrophilic carbon. The last step is the removal of
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is
(c)
Interpretation: The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Hydroboration reaction is a two step reaction, which involves conversion of alkene into alcohol. This type of reaction follows anti-markovnikov�s rule.
Anti markovnikov�s rule states that the positive part of acid attached to that carbon atom in
Answer to Problem 10.54P
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
Hydroboration reaction is a two step reaction, which involves conversion of alkene into alcohol. This type of reaction follows anti-markovnikov�s rule.
Anti markovnikov�s rule states that the positive part of acid attached to that carbon atom in
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is shown below.
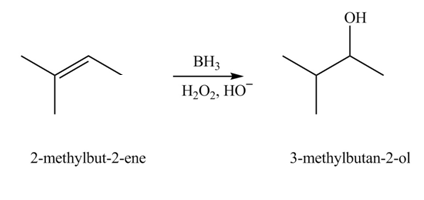
Figure 3
During hydroboration of
Therefore, the product formed is
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is
(d)
Interpretation: The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The addition of a halogen to an alkyne chain leads to the formation of corresponding alkene or alkane. The reaction which includes the addition of chlorine atoms to the alkyne chain is known as chlorination. Chlorination can be done by using the reagents like
Answer to Problem 10.54P
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
Chlorine gas is added to the double bond of the cyclohexene. Addition of chlorine is known as chlorination and this addition makes the compound saturated.
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is shown below.
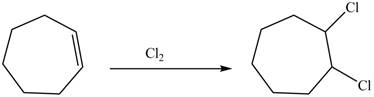
Figure 4
Therefore, the product formed is
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is
(e)
Interpretation: The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The reaction of alkene with halogen and water results in the formation of halohydrin product.
The general steps for the formation of halohydrin are stated below:
• The first step is the attack of halide ion to form a halonium ion.
• The second step is the attack of water from back side to opens the halonium ion.
• The last step is deprotonation to give the halohydrin product.
Answer to Problem 10.54P
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of alkene with halogen and water results in the formation of halohydrin product.
The general steps for the formation of halohydrin are stated below:
• The first step is the attack of halide ion to form a halonium ion.
• The second step is the attack of water from back side to opens the halonium ion.
• The last step is deprotonation to give the halohydrin product.
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is shown below.
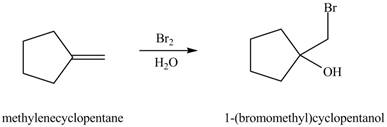
Figure 5
Therefore, the product formed is
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is
(f)
Interpretation: The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: Hydroboration reaction is a two step reaction, which involves conversion of alkene into alcohol. This type of reaction follows anti-markovnikov�s rule.
Anti markovnikov�s rule states that the positive part of acid attached to that carbon atom in
Answer to Problem 10.54P
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is cyclohexylmethanol.
Explanation of Solution
Hydroboration reaction is a two step reaction, which involves conversion of alkene into alcohol. This type of reaction follows anti-markovnikov�s rule.
Anti Markovnikov’s rule states that the positive part of acid attached to that carbon atom in
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is shown below.
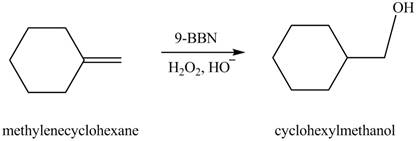
Figure 6
Therefore, the product formed is cyclohexylmethanol.
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is cyclohexylmethanol.
(g)
Interpretation: The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The free radical bromination of alkenes takes place at allylic position. NBS generates bromine radical in presence of heat or light. More than one product is formed when the allylic radical is resonance stabilized.
Answer to Problem 10.54P
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The general steps for the formation of halohydrin are stated below:
• The first step is the attack of halide ion to form a halonium ion.
• The second step is the attack of water from back side to opens the halonium ion.
• The last step is deprotonation to give the halohydrin product.
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is shown below.
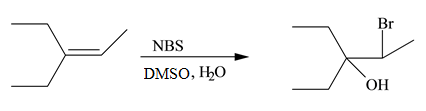
Figure 7
Therefore, the product formed is
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is
(h)
Interpretation: The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The general steps followed by the addition of Halogens to alkenes are stated below:
• The first step is the electrophilic attack of halide ion to form a halonium ion.
• The second step is the attack of halide ion from back side to opens the halonium ion.
Answer to Problem 10.54P
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The general steps involved in the addition of Halogens to alkenes are stated below:
• The first step is the electrophilic attack of halide ion to form a halonium ion.
• The second step is the attack of halide ion from back side to opens the halonium ion to give the final product.
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is shown below.
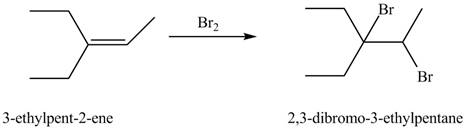
Figure 8
Therefore, the constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is
The constitutional isomer formed in the given reaction is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Draw the product of this reaction please. Ignore inorganic byproductsarrow_forwardOne of the pi molecular orbitals of 1,3-butadiene (CH2=CHCH=CH2) is shown below. Please identify the number of nodal planes perpendicular to the bonding axisarrow_forwardDraw the monomers required to synthesize this condensation polymer please.arrow_forward
- Provide the correct systematic name for the compound shown here. Please take into account the keyboard options belowarrow_forwardcurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s)arrow_forwardIdentify the 'cartoon' drawing of the acceptor orbital in the first mechanistic step of an electrophilic addition reaction of butadiene with HBr. Pleasearrow_forward
- H- H H H H H H Identify and select all structures below that represent a constitutional isomer(s) of the compound shown above. H- H H H A. H H H H-C CI H H D. H H H H H H C C -H H C C H H H H B. H CI H H- C C H H H H E. H CI H C.arrow_forwardWhy doesn't this carry on to form a ring by deprotonating the alpha carbon and the negatively-charged carbon attacking the C=O?arrow_forward6. A solution (0.0004 M) of Fe(S2CNEt2)3 (see the structural drawing below) in chloroform has absorption bands at: 350 nm (absorbance A = 2.34); 514 nm(absorbance A = 0.0532); Calculate the molar absorptivity values for these bands. Comment on their possible nature (charge transfer transitions or d-d S N- transitions?). (4 points)arrow_forward
- What is the mechanism for this?arrow_forwardFor questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6], [COC14]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ 4. Room temperature (20°C) measurement of molar magnetic susceptibility (Xm) for Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2×6H2O is 1.1888 x 102 cgs (Gaussian units). Calculate effective magnetic moment and provide a number of unpaired electrons for the iron ion. Use this number to rationalize the coordination geometry around iron center. (4 points)arrow_forward7. Describe the expected 31P and 19F (where applicable) NMR spectral patterns for the following compounds (indicate number of signals and their splitting patterns). a) tetraphenyldiphosphine Ph Ph P-P Ph Ph Ph Ph ' b) tetraphenyldiphosphine monoxide P-P-Ph Ph (2 points) (2 points c) tetrafluorophosphonium hexafluorophosphate [PF4]*[PF6]¯ (4 points)arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

