
Concept explainers
Regression, activity-based costing, choosing cost drivers. Sleep Late, a large hotel chain, has been using activity-based costing to determine the cost of a night’s stay at their hotels. One of the activities, “Inspection,” occurs after a customer has checked out of a hotel room. Sleep Late inspects every 10th room and has been using “number of rooms inspected” as the cost driver for inspection costs. A significant component of inspection costs is the cost of the supplies used in each inspection.
Mary Adams, the chief inspector, is wondering whether inspection labor-hours might be a better cost driver for inspection costs. Mary gathers information for weekly inspection costs, rooms inspected, and inspection labor-hours as follows:
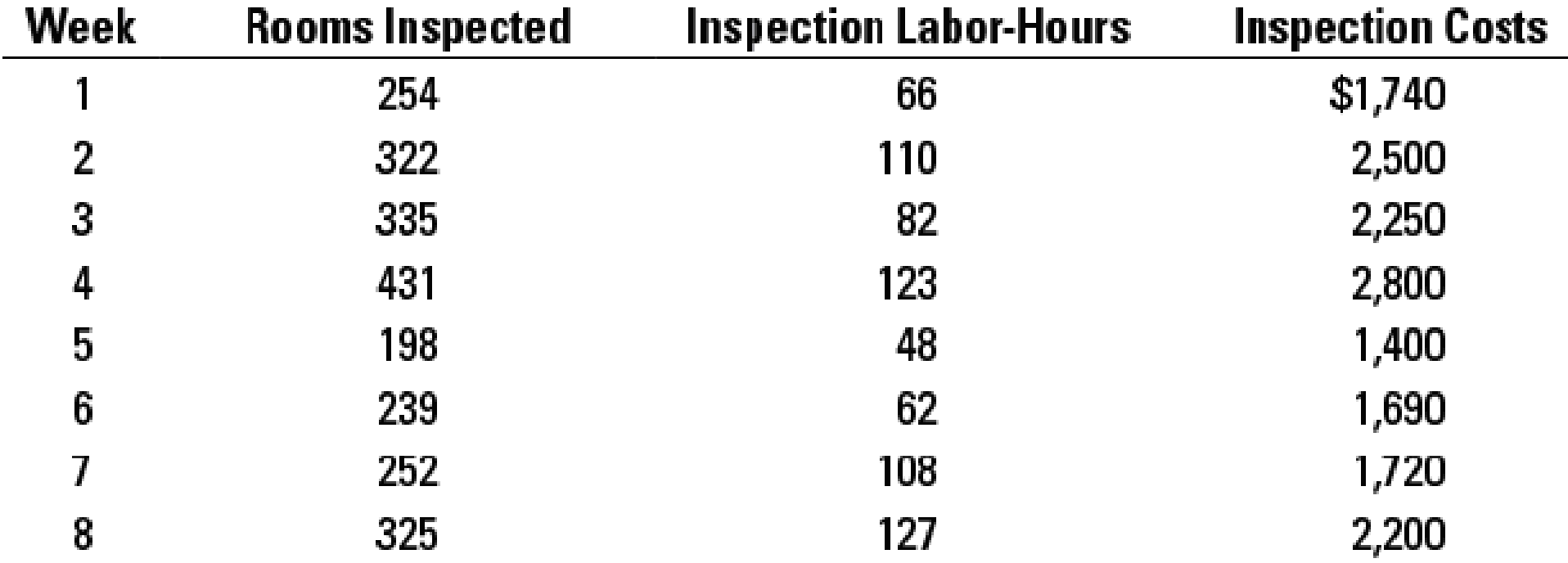
Mary runs regressions on each of the possible cost drivers and estimates these cost functions:
- 1. Explain why rooms inspected and inspection labor-hours are plausible cost drivers of inspection costs.
Required
- 2. Plot the data and regression line for rooms inspected and inspection costs. Plot the data and regression line for inspection labor-hours and inspection costs. Which cost driver of inspection costs would you choose? Explain.
- 3. Mary expects inspectors to inspect 300 rooms and work for 105 hours next week. Using the cost driver you chose in requirement 2, what amount of inspection costs should Mary budget? Explain any implications of Mary choosing the cost driver you did not choose in requirement 2 to budget inspection costs.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 10 Solutions
COST ACCOUNTING
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Financial Accounting (12th Edition) (What's New in Accounting)
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Business Essentials (12th Edition) (What's New in Intro to Business)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
- Wildhorse Windows manufactures and sells custom storm windows for three-season porches. Wildhorse also provides installation service for the windows. The installation process does not involve changes in the windows, so this service can be performed by other vendors. Wildhorse enters into the following contract on July 1, 2025, with a local homeowner. The customer purchases windows for a price of $2,650 and chooses Wildhorse to do the installation. Wildhorse charges the same price for the windows irrespective of whether it does the installation or not. The customer pays Wildhorse $1,988 (which equals the standalone selling price of the windows, which have a cost of $1,230) upon delivery and the remaining balance upon installation of the windows. The windows are delivered on September 1, 2025, Wildhorse completes installation on October 15, 2025, and the customer pays the balance due. (a) Wildhorse estimates the standalone selling price of the installation based on an estimated cost of…arrow_forwardPlease given answer general accountingarrow_forwardPlease help me this question general accountingarrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning





