
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780133840544
Author: George F. Limbrunner, Craig D'Allaird, Leonard Spiegel
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 10.30SP
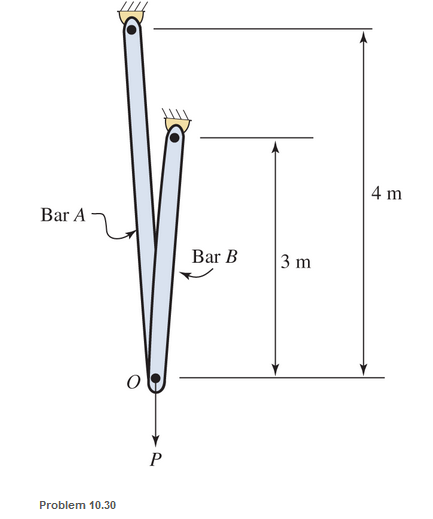
Two steel bars A and B support a load P, as shown. Bar A has an area of 580 mm2 and bar B has an area of 700 mm2. The yield stress is 275 MPa. Both bars elongate equally at point O. Neglect the slope of the bars.
a. Assume an allowable stress of 185 MPa and determine the allowable load using an elastic design approach.
b. Assume a factor of safety of 1.80 and determine the allowable load using an ultimate strength design approach.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Solve this problem and show all of the work
Solve this problem and show all of the work
Solve this problem and show all of the work
Chapter 10 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Ch. 10 - A 916 - in. - diameter steel rod is tested in...Ch. 10 - A concrete cylinder 150 mm in diameter was tested...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.3PCh. 10 - The data from the tension test of a steel specimen...Ch. 10 - An 18-in.-long titanium alloy rod is subjected to...Ch. 10 - ASTM A36 steel rods are used to support a balcony....Ch. 10 - A 450-mm-long AISI 1020 steel rod is subjected to...Ch. 10 - A tension member in a roof truss is composed of...Ch. 10 - A short, solid, compression member of circular...Ch. 10 - A main cable in a large bridge is designed for a...
Ch. 10 - Test results of a steel specimen indicated an...Ch. 10 - A concrete canoe in storage is supported by two...Ch. 10 - A load is applied to a rigid bar that is...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.14CPCh. 10 - Write a program that will allow a user to input...Ch. 10 - A 12 - in. - diaiíct.cr structural nickel steel...Ch. 10 - Compute the modulus of elasticity of a copper...Ch. 10 - A concrete cylinder 6 in. in diameter was tested...Ch. 10 - An aluminum bar 2 in. by 12 - in. in cross section...Ch. 10 - During a tensile test of a steel specimen, the...Ch. 10 - A 12.5-mm-diameter steel rod was subjected to a...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.22SPCh. 10 - A standard steel specimen having a diameter of...Ch. 10 - 10.24 A tension member in a structure is composed...Ch. 10 - A pair of wire cutters is designed to operate...Ch. 10 - Calculate the end bearing length required for a...Ch. 10 - Design a 3-m-long rod subjected to a tensile load...Ch. 10 - The collar bearing shown is subjected to a...Ch. 10 - A 10-ft-long steel member is subjected to a...Ch. 10 - Two steel bars A and B support a load P, as shown....Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.31SP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Part A The man pulls on the rope with a force of F = 30 N as shown in (Figure 1). Figure 1.5 m 3 m. 4m 10.5 m 1 of 1 Determine the position vector from O to A. Express the x, y, and z components of the position vector in meters to three significant figures separated by commas. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ vec (TOA). (TOA)y. (TOA)== Submit Request Answer Part B m Determine the position vector from O to B. Express the x, y, and z components of the position vector in meters to three significant figures separated by commas. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ↓↑ vec (TOB)x, (TOB)y, (TOB) = Submit Request Answer Part C Complete previous part(s) Provide Feedback ? marrow_forward4 Part A The tool is used to shut off gas valves that are difficult to access (Figure 1). Figure 0.25 m 30 0,4 m < 1 of 1 If the force F= {-60i+40j+15k} N is applied to the handle, determine the component of the moment created about the z axis of the valve. Express your answer with the appropriate units. Mz = Value Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback | ? Unitsarrow_forward3. A steam power plant has an average monthly net power delivery of 740 MW over the course of a year. This power delivery is accomplished by burning coal in the boiler. The coal has a heating value of 9150 Btu/lbm. The cost of the coal is $14.20/ton. The overall thermal efficiency of the plant is, nth Wnet Qboiler 0.26 = 26% Determine the annual cost of the coal required to deliver the given average monthly power.arrow_forward
- The cable exerts a force of P = 4 kN at the end of the 8-m-long crane boom. A P 8 m B -x- I'm En ▾ Part A If 0 = 30°, determine the placement x of the boom at B so that this force creates a maximum moment about point O. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. x = 9.81 m Submit Previous Answers ✓ Correct ▾ Part B What is this moment? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Assume the positive direction is counterclockwise. (Mo) max 43.7 = E ? N Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 28 attempts remaining Enter your answer with a different unit type. Review a list of acceptable units.arrow_forwardFind highest and lowest temperature.arrow_forwardExplained step by step.arrow_forward
- The bevel gear shown in is subjected to the force F which is caused from contact with another gear. Part A F (201+8j 15k) N 40 mm Determine the moment of this force about the y axis of the gear shaft. Express your answer with the appropriate units. My = Value Submit Request Answer ? Units 30 mmarrow_forwardConsider the beam in. Part A 1.5 ft 200 lb 200lb 2 ft 30° 1.25 ft 30° If F 90 lb, determine the resultant couple moment. = Express your answer in pound-feet to three significant figures. Assume the positive direction is counterclockwise. ΑΣΦ vec MR = Submit Request Answer ? lb.ftarrow_forward4. An operating parameter often used by power plant engineers is the heat rate. The heat rate is defined as, HR Qbioler Wnet where Qbioler is the heat transfer rate (Btu/h) to the water in the boiler due to the combustion of a fuel and Wnet is the net power (kW) delivered by the plant. In comparison, the thermal efficiency of the power plant is defined as, nth Wnet Qbioler where the numerator and denominator have the same units. Consider a power plant that is delivering 1000 MW of power while utilizing a heat transfer rate of 3570 MW at the boiler. Determine the heat rate and thermal efficiency of this power plant.arrow_forward
- The shaft shown in the sketch is subjected to tensile torsional and bending loads Determine the principal stresses at the location of stress concentration ✓ D=45MR F=3MM 1000-M 1000N チ d=30mm 500N 150 мм MM- 120 MA-arrow_forwardcalculate moment of inertia of this tapered beam structurearrow_forwardThe system shown below is in statics equilibrium. Cable OB lies in the xy plane and makes a 30° angle with the positive x-axis. Cable OA lies along the negative y-axis. If the weight of the load being supported is 100 lb, determine the magnitude of the forces in all four cables: OA, OB, OC, and OD.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Column buckling; Author: Amber Book;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AvvaCi_Nn94;License: Standard Youtube License